Archi language
Archi /ɑːˈtʃiː/[1] is a Northeast Caucasian language spoken by the Archis in the village of Archib, southern Dagestan, Russia, and the six surrounding smaller villages.
| Archi | |
|---|---|
| аршаттен чIат | |
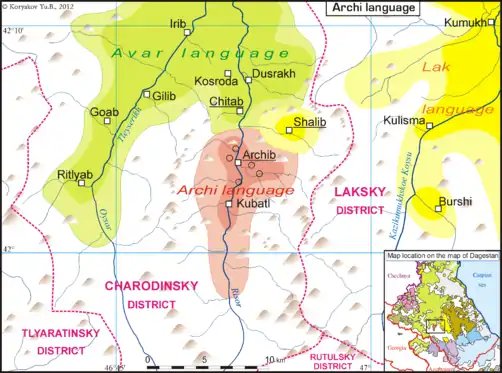 Map of where Archi is spoken (red area) | |
| Native to | Russia |
| Region | Archib, Dagestan |
Native speakers | 970 (2010 census)[2] |
| Cyrillic script (developed in 2006 based on the Avar alphabet) | |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 | aqc |
| Glottolog | arch1244 |
| ELP | Archi |
It is unusual for its many phonemes and for its contrast between several voiceless velar lateral fricatives, /𝼄, 𝼄ʷ, 𝼄ː, 𝼄ːʷ/, voiceless and ejective velar lateral affricates, /k͡𝼄, k͡𝼄ʷ, k͡𝼄ʼ, k͡𝼄ʷʼ/, and a voiced velar lateral fricative, /ʟ̝/. It is an ergative–absolutive language with four noun classes[4] and has a remarkable morphological system with irregularities on all levels.[5] Mathematically, there are 1,502,839 possible forms that can be derived from a single verb root.[6]
Classification
The classification of the Archi language has not been definitively established. Peter von Uslar felt it should be considered a variant of Avar, but Roderich von Erckert saw it as closer to Lak. The language has also been considered as a separate entity that could be placed somewhere between Avar and Lak. The Italian linguist Alfredo Trombetti placed Archi within an Avar–Ando–Dido group, but today the most widely recognized opinion follows that of the Soviet scholar Bokarev, who regards Archi as one of the Lezgian–Samur group of the Dagestan languages. Schulze places it in the Lezgian branch with all other Lezgian languages belonging to the Samur group.[3]
Phonology
Archi has, like its Northeast Caucasian relatives, a very complicated phonological system, with Archi being an extreme example. It has 26 vowel phonemes and, depending on analysis, between 74 and 82 consonant phonemes.
Vowels
Archi has a symmetric six-vowel system (/i e ə a o u/).[4]
| Front | Central | Back | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Close | i | u | |
| Mid | e | ə | o |
| Open | a |
All vowels except for /ə/ can occur in five varieties: short, pharyngealized, high tone, long (with high tone), and pharyngealized with high tone (e.g. /a/, /aˤ/, /á/, /áː/, and /áˤ/). Of all these, only /ə/ and /íˤ/ do not occur word-initially.[7] Examples of non-initial /íˤ/ are /díˤt͡ʃa/ ('to be fat')[8] and /iˤntíˤmmaj/ ('brain').[9]
Consonants
Of all known languages, Archi has the world's largest phonemic non-click consonant inventory, with only the recently extinct Ubykh of the Northwest Caucasian languages having a few more. The table below shows all consonants that can be found in the Archi Language Tutorial[4] and the Archi Dictionary.[7]
| Labial | Dental | (Post)- alveolar |
(Pre-)velar | Uvular | Epiglottal | Glottal | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| lenis | |||||||||||||||
| pl. | lab. | pl. | lab. | pl. | lab. | pl. | lab. | phar. | phar.+lab. | ||||||
| Nasal | m | n | |||||||||||||
| Plosive | voiced | b | d | dʷ2 | ɡ | ɡʷ | |||||||||
| voiceless | p | t | tʷ | k | kʷ | q | qʷ | qˤ | qˤʷ | ʡ | ʔ1 | ||||
| fortis | pː1 | tː1 | kː1 | kːʷ2 | qːʼ1 | qːˤʼ | |||||||||
| ejective | pʼ | tʼ | kʼ | kʷʼ | qʼ | qʷʼ | qˤʼ | qˤʷʼ | |||||||
| Affricate | voiceless | lenis | t͡s | t͡sʷ2 | t͡ʃ | t͡ʃʷ | k͡𝼄 | k͡𝼄ʷ | |||||||
| fortis | t͡sː3 | ||||||||||||||
| ejective | lenis | t͡sʼ | t͡sʷʼ | t͡ʃʼ | t͡ʃʷʼ | k͡𝼄ʼ | k͡𝼄ʷʼ | ||||||||
| fortis | t͡sːʼ1 | t͡ʃːʼ2 | |||||||||||||
| Fricative | voiceless | lenis | s | sʷ2 | ʃ | ʃʷ | 𝼄 | 𝼄ʷ | χ | χʷ | χˤ | χˤʷ | ʜ | h | |
| fortis | sː | sːʷ2 | ʃː | ʃːʷ | 𝼄ː | 𝼄ːʷ | χː | χːʷ | χːˤ | χːˤʷ | |||||
| voiced | z | zʷ | ʒ | ʒʷ | ʟ̝1 | ʁ | ʁʷ2 | ʁˤ | ʁˤʷ | ||||||
| Trill | r | ||||||||||||||
| Approximant | l | j | w | ||||||||||||
- These have no word-initial dictionary entries (even though /pː/, /tː/, and /kː/ are relatively common).
- These appear in the Tutorial but have no dictionary entries.
- This does not appear in the Tutorial but does have a word-internal dictionary entry (in /mot͡sːór/, 'alpine pasture used in summer').[10]
Some of these sounds are very rare. For example, /ʁˤʷ/ has only one dictionary entry word-internally (in /íʁˤʷdut/, 'heavy')[11] and two entries word-initially. Likewise, /ʟ̝/ has only two dictionary entries: /náʟ̝dut/ ('blue; unripe')[12] and /k͡𝼄ʼéʟ̝dut/ ('crooked, curved').[13]
The fortis consonants are not simply two instances of the same consonant, though they do appear largely complementary, with the double instances /mm/, /ll/, and /nn/ being the most common and /zz/ less so. That said, /pp/ can still be found in /𝼄íppu/ ('three').[14] This is also noted by Kodzasov (1977),[15] who describes the fortis consonants as follows:
"Strong phonemes are characterized by the intensiveness (tension) of the articulation. The intensity of the pronunciation leads to a natural lengthening of the duration of the sound, and that is why strong [consonants] differ from weak ones by greater length. [However,] the adjoining of two single weak sounds does not produce a strong one […] Thus, the gemination of a sound does not by itself create its tension."
The voiceless velar lateral fricative /𝼄/, the voiced velar lateral fricative /ʟ̝/, and the corresponding voiceless and ejective affricates /k͡𝼄/, /k͡𝼄ʼ/ are extremely unusual speech sounds among the languages of the world, because velar fricatives are usually central rather than lateral. The velar laterals are further forward than velars in most languages and could better be called prevelar, like the Tutorial does.[4]
Orthography
Until recently Archi did not have a written form, except in studies by specialists who used the Latin script. In 2006, the Surrey Morphology Group developed a Cyrillic alphabet for Archi based on the Avar alphabet, which is used in the Archi–Russian–English Dictionary alongside an IPA transcription.[6]
| Base letter | Derived letters and their pronunciation in IPA | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IPA | +в | IPA | +ӏ | IPA | +ӏв / long | IPA | ||
| а | А а | /a/ | Аӏ аӏ | /aˤ/ | ||||
| А́ а́ | /á/ | А́ӏ а́ӏ | /áˤ/ | А́а а́а | /áː/ | |||
| б | Б б | /b/ | ||||||
| в | В в | /w/ | various others, see below | |||||
| г | Г г | /ɡ/ | Гв гв | /ɡʷ/ | Гӏ гӏ | /ʡ/ | ||
| Гъ гъ | /ʁ/ | Гъв гъв | /ʁʷ/ | Гъӏ гъӏ | /ʁˤ/ | Гъӏв гъӏв | /ʁˤʷ/ | |
| Гь гь | /h/ | |||||||
| д | Д д | /d/ | Дв дв | /dʷ/ | ||||
| е | Е е | /e/ | Еӏ еӏ | /eˤ/ | ||||
| Е́ е́ | /é/ | Е́ӏ е́ӏ | /éˤ/ | Е́е е́е | /éː/ | |||
| ж | Ж ж | /ʒ/ | Жв жв | /ʒʷ/ | ||||
| з | З з | /z/ | Зв зв | /zʷ/ | ||||
| и | И и | /i/ | Иӏ иӏ | /iˤ/ | ||||
| И́ и́ | /í/ | и́ӏ | /íˤ/ | И́и и́и | /íː/ | |||
| й | Й й | /j/ | ||||||
| к | К к | /k/ | Кв кв | /kʷ/ | Кӏ кӏ | /kʼ/ | Кӏв кӏв | /kʷʼ/ |
| кк | /kː/ | ккв | /kːʷ/ | |||||
| Къ къ | /qʼ/ | Къв къв | /qʷʼ/ | Къӏ къӏ | /qˤʼ/ | Къӏв къӏв | /qˤʷʼ/ | |
| ккъ | /qːʼ/ | Ккъӏ ккъӏ | /qːˤʼ/ | |||||
| Кь кь | /k͡𝼄ʼ/, /ʟ̝/ | Кьв кьв | /k͡𝼄ʷʼ/ | |||||
| л | Л л | /l/ | Лӏв лӏв | /k͡𝼄ʷ/ | Лӏ лӏ | /k͡𝼄/ | ||
| Лъ лъ | /𝼄/ | Лъв лъв | /𝼄ʷ/ | |||||
| Ллъ ллъ | /𝼄ː/ | Ллъв ллъв | /𝼄ːʷ/ | |||||
| м | М м | /m/ | ||||||
| н | Н н | /n/ | ||||||
| о | О о | /o/ | Оӏ оӏ | /oˤ/ | ||||
| О́ о́ | /ó/ | О́ӏ о́ӏ | /óˤ/ | О́о о́о | /óː/ | |||
| п | П п | /p/ | Пӏ пӏ | /pʼ/ | ||||
| пп | /pː/ | |||||||
| р | Р р | /r/ | ||||||
| с | С с | /s/ | Св св | /sʷ/ | ||||
| Сс сс | /sː/ | Ссв ссв | /sːʷ/ | |||||
| т | Т т | /t/ | Тв тв | /tʷ/ | Тӏ тӏ | /tʼ/ | ||
| тт | /tː/ | |||||||
| у | У у | /u/ | Уӏ уӏ | /uˤ/ | ||||
| У́ у́ | /ú/ | У́ӏ у́ӏ | /úˤ/ | У́у у́у | /úː/ | |||
| х | Х х | /χ/ | Хв хв | /χʷ/ | Хӏ хӏ | /ʜ/ | Ххв ххв | /χːʷ/ |
| Хх хх | /χː/ | |||||||
| Хъ хъ | /q/ | Хъв хъв | /qʷ/ | Хъӏ хъӏ | /qˤ/ | Хъӏв хъӏв | /qˤʷ/ | |
| Хьӏ хьӏ | /χˤ/ | Хьӏв хьӏв | /χˤʷ/ | |||||
| Ххьӏ ххьӏ | /χːˤ/ | Ххьӏв ххьӏв | /χːˤʷ/ | |||||
| ц | Ц ц | /t͡s/ | Цв цв | /t͡sʷ/ | Цӏ цӏ | /t͡sʼ/ | Цӏв цӏв | /t͡sʷʼ/ |
| Цц цц | /t͡sː/ | Ццӏ ццӏ | /t͡sːʼ/ | |||||
| ч | Ч ч | /t͡ʃ/ | Чв чв | /t͡ʃʷ/ | Чӏ чӏ | /t͡ʃʼ/ | Чӏв чӏв | /t͡ʃʷʼ/ |
| Ччӏ ччӏ | /t͡ʃːʼ/ | |||||||
| ш | Ш ш | /ʃ/ | Шв шв | /ʃʷ/ | ||||
| щ | Щ щ | /ʃː/ | Щв щв | /ʃːʷ/ | ||||
| ы | ы | /ə/ | ||||||
| ъ | ъ | /ʔ/ | various others, see above | |||||
Grammar
Nouns
Archi nouns inflect for number (singular or plural) and for one of 10 regular cases and 5 locative cases that can all take one of 6 directional suffixes.[4] There are four noun classes, which are only evident from verbal agreement.[4]
Case
| Case | Marker | Sg. 'ram' | Pl. 'rams' |
|---|---|---|---|
| Absolutive | -∅ | baˁkʼ | baˁkʼ-ur |
| Ergative | -∅ | beˁkʼ-iri | baˁkʼ-ur-čaj |
| Genitive | -n | beˁkʼ-iri-n | baˁkʼ-ur-če-n |
| Dative | -s, -sː | beˁkʼ-iri-s | baˁkʼ-ur-če-s |
| Comitative | -𝼄ːu | beˁkʼ-iri-𝼄ːu | baˁkʼ-ur-če-𝼄ːu |
| Similative | -qˁdi | beˁkʼ-iri-qˁdi | baˁkʼ-ur-če-qˁdi |
| Causal | -šːi | beˁkʼ-iri-šːi | baˁkʼ-ur-če-šːi |
| Comparative | -χur | beˁkʼ-iri-χur | baˁkʼ-ur-če-χur |
| Partitive | -qˁiš | beˁkʼ-iri-qˁiš | baˁkʼ-ur-če-qˁiš |
| Substitutive | -k͡𝼄ʼəna | beˁkʼ-iri-k͡𝼄ʼəna | baˁkʼ-ur-če-k͡𝼄ʼəna |
Depending on the specifics of the analysis, the ergative and the absolutive cases are not always marked by a specific suffix. Rather, they are marked by the use of the basic (for the absolutive) and oblique (for the ergative) stems in the absence of other markers. There is also a locative-case series in which 6 directional-case suffixes are combined with 5 spatial cases to produce a total of 30 case-localization combinations. However, they do not constitute 30 distinct case forms because they are easily derivable from a pair of morphemes.
| Spatial case | Marker | Directional case | Marker |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inessive ("in") | -aj / -a | Essive ("As") | -∅ |
| Intrative ("between") | - qˁ(a-) | Elative ("Out of") | -š |
| Superessive ("above") | -tːi- / -t | Lative ("To"/"Into") | -k |
| Subessive ("below") | -k͡𝼄ʼ(a-) | Allative ("Onto") | -ši |
| Pertingent ("against") | -ra- | Terminative (Specifies a limit) | -kena |
| Translative (Indicates change) | -χutː | ||
Noun classes
The four noun classes of Archi are only evident from verbal inflection. This table summarizes the noun classes and their associated verbal morphology:
| Class | Description | Singular | Plural | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prefix | Infix | Prefix | ||
| I | Male human | w- | ⟨w⟩ | b- |
| II | Female human | d- | ⟨r⟩ | |
| III | All insects, some animates, some inanimates |
b- | ⟨b⟩ | ∅- |
| IV | Abstracts, some animates, some inanimates |
∅ | ∅ | |
Example phrases
The following phrases were phonetically transcribed from Archi:[16]
| Archi transcription | English |
|---|---|
| x́it barḳur | The ladle breaks. |
| x́it ax̄u | The spoon (literally: little ladle) became dirty. |
| k̂ut̄ali berx̄ur | The bag stays. |
| k̂ut̄ali eku | The little bag fell. |
| č̣ut abḳu | The jug broke. |
| č̣ut aḳu | The little jug broke. |
| ḳunḳum barx̄ur | The kettle becomes dirty. |
| ḳunḳum oq̄́u | The little kettle sank (literally: drowned). |
| motol orq̄́ur | The young goat drowns. |
| uri arč̣ur | The young horse hides itself. |
| biš ač̣u | The young cow hid itself. |
| ḳêrt erkur | The young donkey falls. |
| dogi ebku | The donkey fell. |
| q̇on abč̣u | The goat hid itself. |
| nôiš ebx̄u | The horse stayed. |
Diminutive
The inclusions of "little" and "young" in the phrases translate a diminutive, which in Archi language commonly refers either to a smaller or younger version of the subject. The non-diminutive nouns in the above examples belong to noun class III, while their diminutives belong to noun class IV. This difference in noun class is reflected on the verb in all of these examples, by the contrast between class III agreement in b from class IV in ∅ (with no b). The -b- in the past tense appears in front of the -x̄u / -č̣u / -ku inflection, while in the present tense the b- is the first letter of the verb. For the nouns referring to inanimate objects, the class shift is the only sign of the diminutive: the noun itself does not change in form. E.g. x́it means both "ladle" (III) and "spoon" (IV), k̂ut̄ali both "bag" (III) and "little bag" (IV). Nouns pertaining to younger animals have different words, e.g. dogi "donkey" (III) but ḳêrt "young donkey" (IV), nôiš "horse" (III) but uri "young horse" (IV).
References
- Laurie Bauer, 2007, The Linguistics Student’s Handbook, Edinburgh
- Archi at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- Schulze's classification schemata of the Caucasian languages
- The Archi language tutorial, presenting an overview of the grammar of Archi Archived 2011-09-04 at the Wayback Machine
- "Archi language home page of the Surrey Morphology Group". Archived from the original on 1 March 2015. Retrieved 14 March 2015.
- Kibrik, A. E. (2001). "Archi (Caucasian—Daghestanian)", The Handbook of Morphology, Blackwell, pg. 468
- "Archi Dictionary". Retrieved 14 March 2015.
- "Archi - 1083 - диIча". Retrieved 14 March 2015.
- "Archi - 1420 - иIнтиIммай". Retrieved 14 March 2015.
- "Archi - 2101 - моццор". Retrieved 14 March 2015.
- "Archi - 1387 - игъIвдут". Retrieved 14 March 2015.
- "Archi - 2213 - наIкьдут". Retrieved 14 March 2015.
- "Archi - 1838 - кьекьдут". Retrieved 14 March 2015.
- "Archi - 3833 - лъибтIу". Retrieved 14 March 2015.
- translated in Ladefoged & Maddieson (1996:97–98)
- Lubotsky, Alexander (2010). Van Sanskriet tot Spijkerschrift: Breinbrekers uit alle talen [From Sanskrit to Cuneiform: Brain teasers from all languages] (in Dutch). Amsterdam University Press. pp. 17, 68–69. ISBN 978-9089641793. Retrieved 30 April 2016.
Bibliography
- Kodzasov, Sandro (1977). "Fonetika Archinskogo Jazyka, part 2". In Kibrik, A. E.; Samedov, I. P.; Olovjannikova, D. S.; Kodzasov, S. V. (eds.). Opyt Strukturnogo Opisanija Archinskogo Jazyka. Vol. 1. Moscow: Izdatel’stvo Moskovskogo Universiteta.
- Ladefoged, Peter; Maddieson, Ian (1996). The Sounds of the World's Languages. Oxford: Blackwell. ISBN 978-0-631-19815-4.
- Chumakina, Marina; Dunstan Brown; Greville G. Corbett; Harely Quilliam (2007). A dictionary of Archi: Archi-Russian-English (Online edition). University of Surrey. doi:10.15126/SMG.16/2.
- Bond, Oliver, Greville G. Corbett, Marina Chumakina & Dunstan Brown (eds.). 2016. Archi: Complexities of agreement in cross-theoretical perspective. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Further reading
- Chumakina, Marina (2014). Семантическое согласование в арчинском языке [Semantic agreement in Archi]. In Plungyan V.A. et al (eds), Язык. Константы. Переменные. Памяти Александра Евгеньевича Кибрика [Language. Constants. Variables. In memoriam of A.E. Kibrik], 454-470. St Petersburg: Aleteya (in Russian).
- Chumakina, Marina (2015). Archi. In Peter O. Müller, Ingeborg Ohnheiser, Susan Olsen & Franz Rainer (eds), Word formation: An international handbook of the languages of Europe (Handbooks of Linguistics and Communication Science, HSK40). Berlin: de Gruyter Mouton.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - Dirr, A. M. (1908). "Arčinskij jazyk". Sbornik materialov dlja opisanija mestnostej i plemen Kavkaza (in Russian). Tbilisi.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - Kaxadze, O. I. (1979). The Archi language and its relation to other Daghestan languages (in Georgian). Tbilisi: Mecniereba.
- Kibrik, Aleksandr E. (1972). "O formal'nom vydelenii soglasovatel'nyx klassov v arčinskom jazyke". Voprosy jazykoznanija (in Russian). 1: 124–31.
- Kibrik, Aleksandr E. (1977). Taksonomičeskaja grammatika (in Russian). vol. 2 of Opyt strukturnogo opisanija arčinskogo jazyka. Moscow: Izdatel'stvo moskovskogo universiteta.
- Kibrik, Aleksandr E. (1977). Dinamičeskaja grammatika (in Russian). vol. 3 of Opyt strukturnogo opisanija arčinskogo jazyka. Moscow: Izdatel'stvo moskovskogo universiteta.
- Kibrik, Aleksandr E. (1993). "Archi". In R. Smeets (ed.). Indigenous languages of the Caucasus. vol. 3. New York: Caravan Books. pp. 297–365.
- Kibrik, Aleksandr E. (1998). "Archi". In Andrew Spencer; Arnold M. Zwicky (eds.). The Handbook of Morphology. Blackwell Publishers. pp. 455–476.
- Kibrik, Aleksandr E.; Kodzasov, S. V.; Olovjannikova, I. P. & Samedov, D. S. (1977). Arčinskij jazyk. Teksiy i slovari (in Russian). Moscow: Izdatel'stvo moskovskogo universiteta.
- Kibrik, Aleksandr E.; Kodzasov, S. V.; Olovjannikova, I. P. & Samedov, D. S. (1977). Opyt strukturnogo opisanija arčinskogo jazyka. Tom 1. Leksika. Fonetika (in Russian). Moscow: Izdatel'stvo moskovskogo universiteta.
- Mikailov, K. Š. (1967). Arčinskij jazyk (in Russian). Maxachkala.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - Xajdakov, S. M. (1967). "Arčinskij jazyk". Jazyki narodov SSSR (in Russian). vol. 4. Moscow: Nauka.
External links
- Appendix:Cyrillic script
- Archi–Russian–English dictionary
- Archi language tutorial
- Archi Vocabulary List (from the World Loanword Database)
- Archi basic lexicon at the Global Lexicostatistical Database
- A sample of the Archi language, 'the Bear Story':
- https://www.smg.surrey.ac.uk/languages/archi/ Archi language overview
