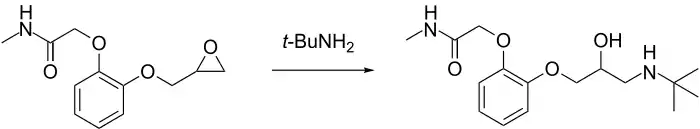
Cetamolol
Cetamolol is a beta adrenergic antagonist, more specifically a β1-adrenergic blocker.[1]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2-[2-[3-(tert-Butylamino)-2-hydroxypropoxy]phenoxy]-N-methylacetamide | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C16H26N2O4 | |
| Molar mass | 310.394 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
References
- Klausner, MA; Irwin, C; Mullane, JF; Shand, DG; Leese, PT; Arnold, JD; Wollberg, W; Wagner, NB; Wagner, GS (1988). "Effect of cetamolol on epinephrine-induced hypokalemia". Journal of Clinical Pharmacology. 28 (8): 751–6. doi:10.1002/j.1552-4604.1988.tb03210.x. PMID 2905711. S2CID 30767741.
- GB 1458392, "Optically-active 1-aryloxy-2,3-epoxypropane derviatives", published 1976-12-15, assigned to Imperial Chemical Industries Ltd.
- BE 767781, "Alkanolamines", published 1971-11-29, assigned to Imperial Chemical Industries Ltd.
- D. J. Lecount, C. J. Squire, U.S. Patent 4,059,622 (1977 to ICI).
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.