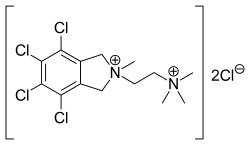
Chlorisondamine
Chlorisondamine is a nicotinic acetylcholine receptor antagonist that produces both neuronal and ganglionic blockade.
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C14H20Cl6N2 |
| Molar mass | 429.03 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Chlorisondamine has been shown to form noncovalent complexes with various biomolecules including sphingomyelin and other associated glycolipids.[1][2][3]
References
- Woods AS, Moyer SC, Wang HY, Wise RA (2003). "Interaction of chlorisondamine with the neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptor". Journal of Proteome Research. 2 (2): 207–12. doi:10.1021/pr025578h. PMID 12716135.
- Jackson SN, Wang HY, Woods AS, Ugarov M, Egan T, Schultz JA (February 2005). "Direct tissue analysis of phospholipids in rat brain using MALDI-TOFMS and MALDI-ion mobility-TOFMS". Journal of the American Society for Mass Spectrometry. 16 (2): 133–8. doi:10.1016/j.jasms.2004.10.002. PMID 15694763. S2CID 5894935.
- Woods AS, Ugarov M, Egan T, Koomen J, Gillig KJ, Fuhrer K, Gonin M, Schultz JA (April 2004). "Lipid/peptide/nucleotide separation with MALDI-ion mobility-TOF MS". Analytical Chemistry. 76 (8): 2187–95. doi:10.1021/ac035376k. PMID 15080727.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.