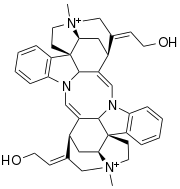
Toxiferine
Toxiferine (C-toxiferine I) is a curare toxin. It is a bisindole alkaloid derived from Strychnos toxifera and a nicotinic acetylcholine receptor antagonist. This alkaloid is the main toxic component of Calabash curare, and one of the most toxic plant alkaloids known. The lethal dose (LD50) for mice has been determined as 10 - 60 µg/kg by intravenous administration.[1] It is a muscle relaxant that causes paralysis of skeletal muscle, which takes approximately 2 hours to recovery for a moderate dose, and 8 hours of total paralysis with a 20-fold paralytic dose. The paralysis can be antagonized by neostigmine[2]
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C40H46N4O2 |
| Molar mass | 614.834 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
References
- Entry on C-Toxiferine I. at: Römpp Online. Georg Thieme Verlag, retrieved 8 June 2020.
- Saxton JE, Gorman AA, Hesse M, Schmid H, Waser PG, Hopff WH (1971). "Bisindole alkaloids". In Saxton JE (ed.). The Alkaloids: v. 1: A Review of Chemical Literature. Specialist Periodical Reports. Cambridge, Eng: Royal Society of Chemistry. p. 330. ISBN 0-85186-257-8.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.