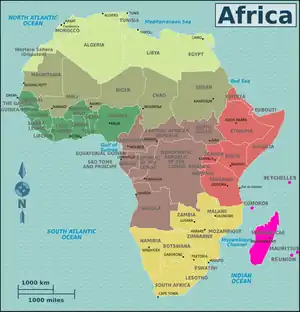
Portal:Africa


.svg.png.webp)
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both aspects. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 20% of Earth's land area and 6% of its total surface area. With 1.4 billion people0 as of 2021, it accounts for about 18% of the world's human population. Africa's population is the youngest amongst all the continents; the median age in 2012 was 19.7, when the worldwide median age was 30.4. Despite a wide range of natural resources, Africa is the least wealthy continent per capita and second-least wealthy by total wealth, ahead of Oceania. Scholars have attributed this to different factors including geography, climate, tribalism, colonialism, the Cold War, neocolonialism, lack of democracy, and corruption. Despite this low concentration of wealth, recent economic expansion and the large and young population make Africa an important economic market in the broader global context.
Africa straddles the equator and the prime meridian. It is the only continent to stretch from the northern temperate to the southern temperate zones. The majority of the continent and its countries are in the Northern Hemisphere, with a substantial portion and a number of countries in the Southern Hemisphere. Most of the continent lies in the tropics, except for a large part of Western Sahara, Algeria, Libya and Egypt, the northern tip of Mauritania, and the entire territories of Morocco, Ceuta, Melilla, and Tunisia which in turn are located above the tropic of Cancer, in the northern temperate zone. In the other extreme of the continent, southern Namibia, southern Botswana, great parts of South Africa, the entire territories of Lesotho and Eswatini and the southern tips of Mozambique and Madagascar are located below the tropic of Capricorn, in the southern temperate zone.
Africa is highly biodiverse; it is the continent with the largest number of megafauna species, as it was least affected by the extinction of the Pleistocene megafauna. However, Africa also is heavily affected by a wide range of environmental issues, including desertification, deforestation, water scarcity and pollution. These entrenched environmental concerns are expected to worsen as climate change impacts Africa. The UN Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change has identified Africa as the continent most vulnerable to climate change.
The history of Africa is long, complex, and has often been under-appreciated by the global historical community. Africa, particularly Eastern Africa, is widely accepted as the place of origin of humans and the Hominidae clade (great apes). The earliest hominids and their ancestors have been dated to around 7 million years ago, including Sahelanthropus tchadensis, Australopithecus africanus, A. afarensis, Homo erectus, H. habilis and H. ergaster—the earliest Homo sapiens (modern human) remains, found in Ethiopia, South Africa, and Morocco, date to circa 233,000, 259,000, and 300,000 years ago, respectively, and Homo sapiens is believed to have originated in Africa around 350,000–260,000 years ago. Africa is also considered by anthropologists to be the most genetically diverse continent as a result of being the longest inhabited. (Full article...)
Selected article –
The dodo (Raphus cucullatus) is an extinct flightless bird that was endemic to the island of Mauritius, which is east of Madagascar in the Indian Ocean. The dodo's closest genetic relative was the also-extinct Rodrigues solitaire. The two formed the subfamily Raphinae, a clade of extinct flightless birds that were a part of the family which includes pigeons and doves. The closest living relative of the dodo is the Nicobar pigeon. A white dodo was once thought to have existed on the nearby island of Réunion, but it is now believed that this assumption was merely confusion based on the also-extinct Réunion ibis and paintings of white dodos.
Subfossil remains show the dodo was about 1 metre (3 ft 3 in) tall and may have weighed 10.6–17.5 kg (23–39 lb) in the wild. The dodo's appearance in life is evidenced only by drawings, paintings, and written accounts from the 17th century. Since these portraits vary considerably, and since only some of the illustrations are known to have been drawn from live specimens, the dodos' exact appearance in life remains unresolved, and little is known about its behaviour. It has been depicted with brownish-grey plumage, yellow feet, a tuft of tail feathers, a grey, naked head, and a black, yellow, and green beak. It used gizzard stones to help digest its food, which is thought to have included fruits, and its main habitat is believed to have been the woods in the drier coastal areas of Mauritius. One account states its clutch consisted of a single egg. It is presumed that the dodo became flightless because of the ready availability of abundant food sources and a relative absence of predators on Mauritius. Though the dodo has historically been portrayed as being fat and clumsy, it is now thought to have been well-adapted for its ecosystem. (Full article...)Featured pictures –
Did you know (auto-generated) -
- ... that Professor Shabir Madhi, who led trials of the Oxford–AstraZeneca COVID-19 vaccine in South Africa, did not originally want to study medicine?
- ... that during the First World War, Senegalese Tirailleurs would be withdrawn from the Western Front to overwinter in camps in the south of France or northern Africa?
- ... that nursing educator Helen Turner Watson was one of the first African-American women to become a commissioned officer in the United States Navy?
- ... that after anti-apartheid activist David Rabkin was sentenced to prison in South Africa, he gave the courtroom the clenched-fist black power salute?
- ... that only posthumously was Patrick Francis Healy described as the first black American to become a Jesuit, earn a Ph.D., and become the president of a predominantly white university?
- ... that during his mayoralty of South Bend, Indiana, Pete Buttigieg faced controversy when he fired the city's first African-American police chief for wiretapping?
Categories
Selected biography –
.jpg.webp)
Jaramogi Ajuma Oginga Odinga (October 1911 – 20 January 1994) was a Kenyan politician who became a prominent figure in Kenya's struggle for independence. He served as Kenya's first vice-president, and thereafter as opposition leader. Odinga's son Raila Odinga is a former prime minister, and another son, Oburu Odinga, is a former assistant minister in the Ministry of Finance.
Jaramogi is credited for the phrase "Not Yet Uhuru" which is the title of his autobiography published in 1967. "Uhuru" means freedom in Swahili and he was referencing his belief that even after independence from British colonialism, the brutal oppression of opposition in political affairs in Kenya, meant that the country had still not attained real freedom. Jaramogi's son Raila was also in detention for a period of eight years. (Full article...)Selected country –
 Flag of the Republic of South Africa |
.svg.png.webp) Coat of arms of South Africa (heraldic) |
||
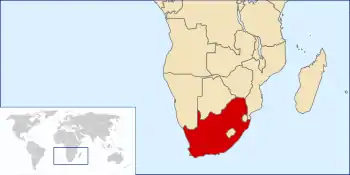 | |||
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa, is a country located at the southern tip of the African continent. It borders Namibia, Botswana, Zimbabwe, Mozambique, Swaziland, and Lesotho. South Africa is often called the "Rainbow Nation", a term coined by Archbishop Desmond Tutu and later adopted by then President Nelson Mandela.
South Africa is an ethnically diverse nation with the largest white, Indian, and racially-mixed communities in Africa. Black South Africans, who speak nine officially-recognized languages and many more dialects, account for slightly less than 80% of the population. Racial strife between the white minority and the black majority has played a large part in the country's history and politics, culminating in apartheid, which was instituted in 1948 by the National Party (although segregation existed prior to then). The laws that defined apartheid began to be repealed or abolished by the National Party in 1990 after a long and sometimes violent struggle. (Read more...)
Selected city –

Port Said (Egyptian Arabic: بورسعيد [poɾ-, boɾ.sæˈʕiːd], locally: [boɾ.sæˈʕeːd]) is a city that lies in northeast Egypt extending about 30 km (19 mi) along the coast of the Mediterranean Sea, west of the Suez Canal. With an approximate population of 603,787 (2010), it is the fifth-largest city in Egypt. The city was established in 1859 during the building of the Suez Canal.
There are numerous old houses with grand balconies on all floors, giving the city a distinctive look. Port Said's twin city is Port Fuad, which lies on the eastern bank of the Suez Canal. The two cities coexist, to the extent that there is hardly any town centre in Port Fuad. The cities are connected by free ferries running all through the day, and together they form a metropolitan area with over a million residents that extends both on the African and the Asian sides of the Suez Canal. The only other metropolitan area in the world that also spans two continents is Istanbul. (Full article...)In the news
- 19 March 2022 – Politics of Australia
- Preliminary election results show Peter Malinauskas and his Labor Party winning a majority. (ABC News Australia)
- 15 March 2022 –
- Burkinabè architect Diébédo Francis Kéré wins the 2022 Pritzker Architecture Prize, becoming the first African and black person to do so. (The Guardian)
- 15 March 2022 – COVID-19 pandemic
- COVID-19 pandemic in Namibia
- Namibia drops its requirement of face mask and mandatory PCR COVID-19 test for vaccinated visitors as the number of cases falls. (Reuters)
- 14 March 2022 –
- Cameroon bans shisha smoking, becoming the sixth African country to do so. (Africanews)
- 13 March 2022 – Insurgency in Northern Chad; aftermath of the 2021 Northern Chad offensive
- The Transitional Military Council of Chad meets with 44 different armed rebel and opposition groups, including the Front for Change and Concord in Chad, Movement for Democracy and Justice in Chad, and the Union of Forces for Democracy and Development in Doha, Qatar for peace talks. The President of Chad, Mahamat Déby, hopes that the talks will be the first step towards agreeing on a new constitution and holding free elections. (ABC News) (France24)
Updated: 7:33, 20 March 2022
General images -
Africa topics
More did you know –
- ...that members of the Senegalese rap group Daara J were hired by campaigners in the Senegalese election of 2000 to edit their speeches?
- ...that Senegalese hip hop group Positive Black Soul's name abbreviation, PBS, is a play on that of the Parti Démocratique Sénégalais, PDS?
- ...that Mamadou Diabaté, a Malian kora player, was nominated for a Grammy Award in 2005, but lost to his cousin Toumani Diabaté?
- ...that, in November 2007, The Sowetan published an article which erroneously claimed that South African political activist Dan Mokonyane had died?
Related portals
Major Religions in Africa
North Africa
West Africa
Central Africa
East Africa
Southern Africa
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
 Commons
Commons
Free media repository -
 Wikibooks
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
 Wikidata
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
 Wikinews
Wikinews
Free-content news -
 Wikiquote
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
 Wikisource
Wikisource
Free-content library -
 Wikispecies
Wikispecies
Directory of species -
 Wikiversity
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
 Wikivoyage
Wikivoyage
Free travel guide -
 Wiktionary
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus
More portals
-
 List of all portalsList of all portals
List of all portalsList of all portals -
 The arts portal
The arts portal -
 Biography portal
Biography portal -
 Current events portal
Current events portal -
 Geography portal
Geography portal -
 History portal
History portal -
 Mathematics portal
Mathematics portal -
 Science portal
Science portal -
 Society portal
Society portal -
 Technology portal
Technology portal -
 Random portalRandom portal
Random portalRandom portal -
 WikiProject PortalsWikiProject Portals
WikiProject PortalsWikiProject Portals



.jpg.webp)

.jpg.webp)



.jpg.webp)




.jpg.webp)


_adult_male.jpg.webp)















.jpg.webp)








.jpg.webp)




