Solar eclipse of May 22, 2096
A total solar eclipse will occur on Tuesday, May 22, 2096. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. This will be the first eclipse of saros series 139 to exceed series 136 in length of totality. The length of totality for saros 139 is increasing, while that of Saros 136 is decreasing.
| Solar eclipse of May 22, 2096 | |
|---|---|
 Map | |
| Type of eclipse | |
| Nature | Total |
| Gamma | 0.1196 |
| Magnitude | 1.0737 |
| Maximum eclipse | |
| Duration | 367 sec (6 m 7 s) |
| Coordinates | 27.3°N 153.4°E |
| Max. width of band | 241 km (150 mi) |
| Times (UTC) | |
| Greatest eclipse | 1:37:14 |
| References | |
| Saros | 139 (34 of 71) |
| Catalog # (SE5000) | 9724 |
The eclipse will begin when the Moon's shadow first reaches Earth in Indonesia, the Philippines and the Western Pacific Ocean, which are west of the International Date Line, in the morning hours of Tuesday, May 22, 2096 and will be seen east of the line in the afternoon hours of Monday, May 21, 2096. It will end as a partial eclipse over the United States West Coast.
Overall, at 6 minutes and 7 seconds, this will be the third longest total solar eclipse of the 21st century. The only two longer eclipses in the century are July 22, 2009 and August 2, 2027. The longest duration of this eclipse on land is not as long however, and it will be seen in Surigao del Sur, the Philippines, for 4 minutes and 38 seconds.
Related eclipses
Solar eclipses 2094–2098
This eclipse is a member of a semester series. An eclipse in a semester series of solar eclipses repeats approximately every 177 days and 4 hours (a semester) at alternating nodes of the Moon's orbit.[1]
| 119 | June 13, 2094 Partial |
124 | December 7, 2094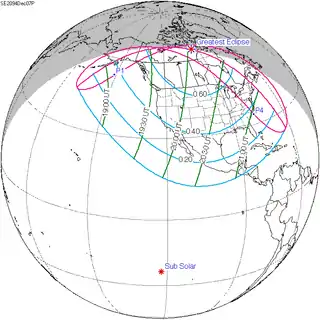 Partial |
| 129 | June 2, 2095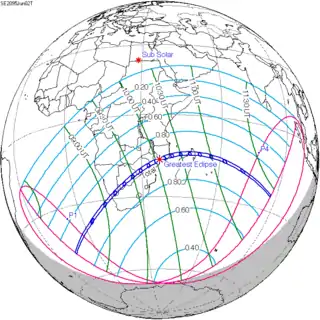 Total |
134 | November 27, 2095 Annular |
| 139 | May 22, 2096 Total |
144 | November 15, 2096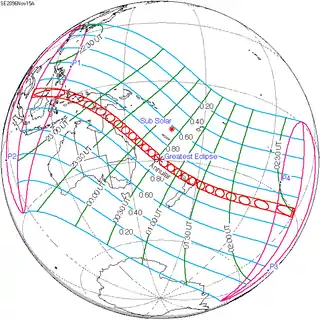 Annular |
| 149 | May 11, 2097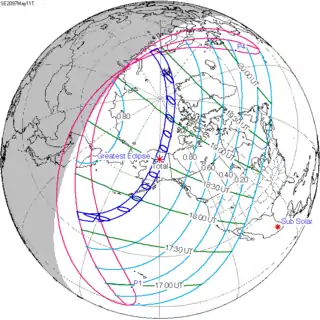 Total |
154 | November 4, 2097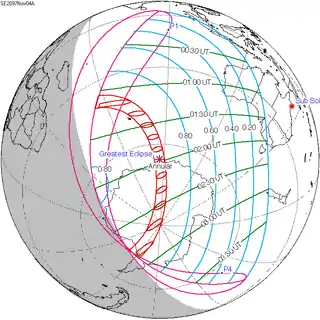 Annular |
| 164 | October 24, 2098 Partial |
Saros 139
It is a part of saros series 139, repeating every 18 years, 11 days, 8 hours, containing 71 events. The series started with partial solar eclipse on May 17, 1501. It contains hybrid eclipses on August 11, 1627 through to December 9, 1825 and total eclipses from December 21, 1843 through to March 26, 2601. The series ends at member 71 as a partial eclipse on July 3, 2763. Its eclipses are entabulated in three columns; each one in the same column, every third eclipse, is one exeligmos apart so cast shadows over approximately the same parts of the Earth.
The solar eclipse of June 13, 2132 will be the longest total solar eclipse since July 11, 1991 at 6 minutes, 55.02 seconds.
The longest duration of totality will be produced by member 39 at 7 minutes, 29.22 seconds on July 16, 2186.[2] After that date each duration will decrease, until the series end. This date is the longest solar eclipse computed between 4000 BC and 6000 AD.[3] Saros series eclipses are during the Moon’s ascending node (a term related to our equator and polar-naming conventions).
| Series members 24–45 occur between 1901 and 2300 | ||
|---|---|---|
| 24 | 25 | 26 |
 February 3, 1916 |
 February 14, 1934 |
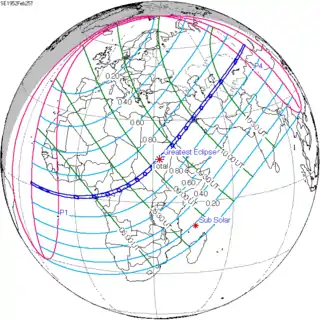 February 25, 1952 |
| 27 | 28 | 29 |
 March 7, 1970 |
 March 18, 1988 |
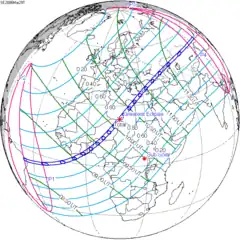 March 29, 2006 |
| 30 | 31 | 32 |
 April 8, 2024 |
 April 20, 2042 |
 April 30, 2060 |
| 33 | 34 | 35 |
 May 11, 2078 |
 May 22, 2096 |
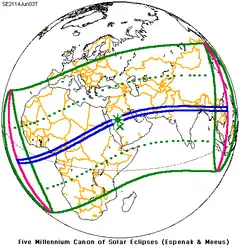 June 3, 2114 |
| 36 | 37 | 38 |
 June 13, 2132 |
 June 25, 2150 |
 July 5, 2168 |
| 39 | 40 | 41 |
 July 16, 2186 |
 July 27, 2204 |
 August 8, 2222 |
| 42 | 43 | 44 |
 August 18, 2240 |
 August 29, 2258 |
 September 9, 2276 |
| 45 | ||
 September 20, 2294 | ||
Notes
- van Gent, R.H. "Solar- and Lunar-Eclipse Predictions from Antiquity to the Present". A Catalogue of Eclipse Cycles. Utrecht University. Retrieved 6 October 2018.
- Saros Series Catalog of Solar Eclipses NASA Eclipse Web Site.
- Ten Millennium Catalog of Long Solar Eclipses, −3999 to +6000 (4000 BCE to 6000 CE) Fred Espenak.
References
- Earth visibility chart and eclipse statistics Eclipse Predictions by Fred Espenak, NASA/GSFC
.jpg.webp)

