Solar eclipse of August 2, 2027
A total solar eclipse will occur over much of the central Eastern Hemisphere on Monday, August 2, 2027. It will commence over the eastern Atlantic Ocean and travel past the Strait of Gibraltar between Spain and Morocco. Totality will be visible in southern Spain as well as parts of North Africa and the Middle East, as well as the northern tip of the Horn of Africa. A partial eclipse visible in much of the Eastern Hemisphere. Major cities under the path will include Luxor in central Egypt, Jeddah and Mecca in southern Saudi Arabia, and Sana'a in southern Yemen. It will be the first of three total solar eclipses that are observable in Tunisia in the 21st century, passing over the central part of the country.[1]
| Solar eclipse of August 2, 2027 | |
|---|---|
 Map | |
| Type of eclipse | |
| Nature | Total |
| Gamma | 0.1421 |
| Magnitude | 1.079 |
| Maximum eclipse | |
| Duration | 383 sec (6 m 23 s) |
| Coordinates | 25.5°N 33.2°E |
| Max. width of band | 258 km (160 mi) |
| Times (UTC) | |
| Greatest eclipse | 10:07:50 |
| References | |
| Saros | 136 (38 of 71) |
| Catalog # (SE5000) | 9568 |
The maximum duration of totality will be observed in Egypt, approximately 37 miles (60 km) southeast of Luxor, and will last 6 minutes and 22 seconds.[2]
Images
Animated path
Related eclipses
Eclipses in 2027
- An annular solar eclipse on February 6.
- A penumbral lunar eclipse on February 20.
- A penumbral lunar eclipse on July 18.
- A total solar eclipse on August 2.
- A penumbral lunar eclipse on August 17.
Solar eclipses 2026–2029
This eclipse is a member of a semester series. An eclipse in a semester series of solar eclipses repeats approximately every 177 days and 4 hours (a semester) at alternating nodes of the Moon's orbit.[3]
| Ascending node | Descending node | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Saros | Map | Gamma | Saros | Map | Gamma | |
| 121 | 2026 February 17 Annular |
−0.97427 | 126 | 2026 August 12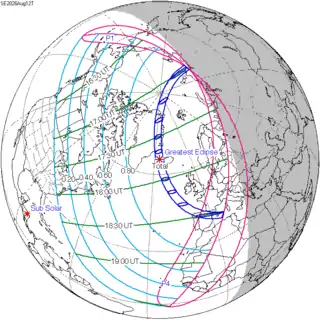 Total |
0.89774 | |
| 131 | 2027 February 6 Annular |
−0.29515 | 136 | 2027 August 2 Total |
0.14209 | |
| 141 | 2028 January 26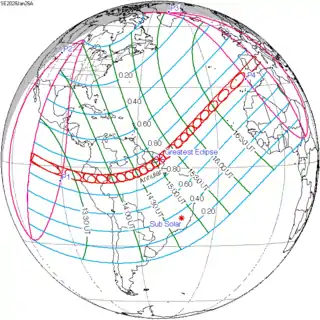 Annular |
0.39014 | 146 | 2028 July 22 Total |
−0.60557 | |
| 151 | 2029 January 14 Partial |
1.05532 | 156 | 2029 July 11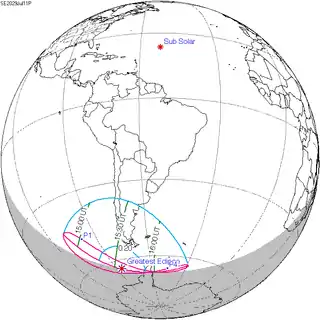 Partial |
−1.41908 | |
Partial solar eclipses on June 12, 2029, and December 5, 2029, occur in the next lunar year eclipse set.
Saros 136
Solar Saros 136, repeating every 18 years, 11 days, contains 71 events. The series started with partial solar eclipse on June 14, 1360, and reached a first annular eclipse on September 8, 1504. It was a hybrid event from November 22, 1612, through January 17, 1703, and total eclipses from January 27, 1721, through May 13, 2496. The series ends at member 71 as a partial eclipse on July 30, 2622, with the entire series lasting 1262 years. The longest eclipse occurred on June 20, 1955, with a maximum duration of totality at 7 minutes, 7.74 seconds. All eclipses in this series occurs at the Moon's descending node.[4]
| Series members 29–43 occur between 1865 and 2117 | ||
|---|---|---|
| 29 | 30 | 31 |
 Apr 25, 1865 |
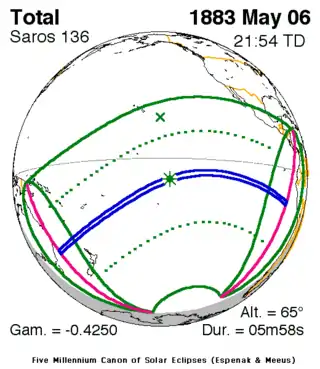 May 6, 1883 |
 May 18, 1901 |
| 32 | 33 | 34 |
 May 29, 1919 |
 Jun 8, 1937 |
 Jun 20, 1955 |
| 35 | 36 | 37 |
 Jun 30, 1973 |
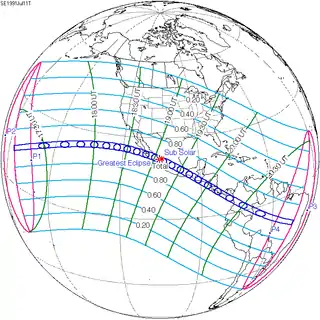 Jul 11, 1991 |
 Jul 22, 2009 |
| 38 | 39 | 40 |
 Aug 2, 2027 |
 Aug 12, 2045 |
 Aug 24, 2063 |
| 41 | 42 | 43 |
 Sep 3, 2081 |
 Sep 14, 2099 |
 Sep 26, 2117 |
Metonic series
The metonic series repeats eclipses every 19 years (6939.69 days), lasting about 5 cycles. Eclipses occur in nearly the same calendar date. In addition, the octon subseries repeats 1/5 of that or every 3.8 years (1387.94 days). All eclipses in this table occur at the Moon's descending node.[5]
| Octon series with 21 events between May 21, 1993 and August 2, 2065 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| May 20–21 | March 8–9 | December 25–26 | October 13–14 | August 1–2 |
| 98 | 100 | 102 | 104 | 106 |
| May 21, 1955 | March 9, 1959 | December 26, 1962 | October 14, 1966 | August 2, 1970 |
| 108 | 110 | 112 | 114 | 116 |
| May 21, 1974 | March 9, 1978 | December 26, 1981 | October 14, 1985 | August 1, 1989 |
| 118 | 120 | 122 | 124 | 126 |
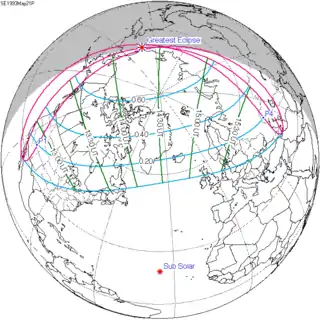 May 21, 1993 |
 March 9, 1997 |
 December 25, 2000 |
 October 14, 2004 |
 August 1, 2008 |
| 128 | 130 | 132 | 134 | 136 |
 May 20, 2012 |
 March 9, 2016 |
 December 26, 2019 |
 October 14, 2023 |
 August 2, 2027 |
| 138 | 140 | 142 | 144 | 146 |
 May 21, 2031 |
 March 9, 2035 |
 December 26, 2038 |
 October 14, 2042 |
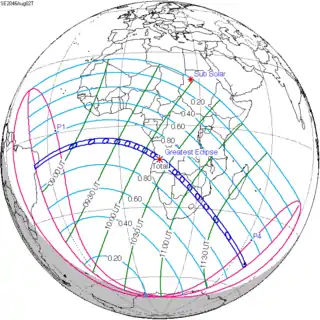 August 2, 2046 |
| 148 | 150 | 152 | 154 | 156 |
 May 20, 2050 |
 March 9, 2054 |
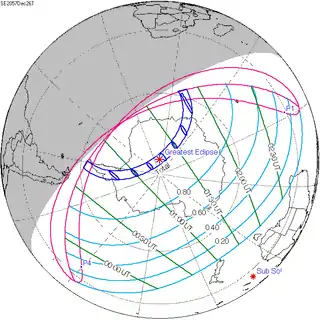 December 26, 2057 |
 October 13, 2061 |
 August 2, 2065 |
| 158 | 160 | 162 | 164 | 166 |
 May 20, 2069 |
March 8, 2073 | December 26, 2076 | October 13, 2080 | August 1, 2084 |
References
- "Map of Solar Eclipse of August 2, 2027" (Map). "Solar Eclipse Maps". NASA. Retrieved October 21, 2017.
- "Longest Duration of Total Solar Eclipse of 2027 Aug 02". NASA Goddard Space Flight Center. NASA. Retrieved 7 September 2017.
- van Gent, R.H. "Solar- and Lunar-Eclipse Predictions from Antiquity to the Present". A Catalogue of Eclipse Cycles. Utrecht University. Retrieved 6 October 2018.
- SEsaros136 at NASA.gov
- Note S1: Eclipses & Predictions in Freeth, Tony (2014). "Eclipse Prediction on the Ancient Greek Astronomical Calculating Machine Known as the Antikythera Mechanism". PLOS ONE. 9 (7): e103275. Bibcode:2014PLoSO...9j3275F. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0103275. PMC 4116162. PMID 25075747.
.jpg.webp)

