Uniform tiling
In geometry, a uniform tiling is a tessellation of the plane by regular polygon faces with the restriction of being vertex-transitive.
Uniform tilings can exist in both the Euclidean plane and hyperbolic plane. Uniform tilings are related to the finite uniform polyhedra which can be considered uniform tilings of the sphere.
Most uniform tilings can be made from a Wythoff construction starting with a symmetry group and a singular generator point inside of the fundamental domain. A planar symmetry group has a polygonal fundamental domain and can be represented by the group name represented by the order of the mirrors in sequential vertices.
A fundamental domain triangle is (p q r), and a right triangle (p q 2), where p, q, r are whole numbers greater than 1. The triangle may exist as a spherical triangle, a Euclidean plane triangle, or a hyperbolic plane triangle, depending on the values of p, q and r.
There are a number of symbolic schemes for naming these figures, from a modified Schläfli symbol for right triangle domains: (p q 2) → {p, q}. The Coxeter-Dynkin diagram is a triangular graph with p, q, r labeled on the edges. If r = 2, the graph is linear since order-2 domain nodes generate no reflections. The Wythoff symbol takes the 3 integers and separates them by a vertical bar (|). If the generator point is off the mirror opposite a domain node, it is given before the bar.
Finally tilings can be described by their vertex configuration, the sequence of polygons around each vertex.
All uniform tilings can be constructed from various operations applied to regular tilings. These operations as named by Norman Johnson are called truncation (cutting vertices), rectification (cutting vertices until edges disappear), and cantellation (cutting edges). Omnitruncation is an operation that combines truncation and cantellation. Snubbing is an operation of alternate truncation of the omnitruncated form. (See Uniform polyhedron#Wythoff construction operators for more details.)
Coxeter groups
Coxeter groups for the plane define the Wythoff construction and can be represented by Coxeter-Dynkin diagrams:
For groups with whole number orders, including:
| Orbifold symmetry |
Coxeter group | Coxeter diagram |
notes | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Compact | |||||
| *333 | (3 3 3) | [3[3]] | 3 reflective forms, 1 snub | ||
| *442 | (4 4 2) | [4,4] | 5 reflective forms, 1 snub | ||
| *632 | (6 3 2) | [6,3] | 7 reflective forms, 1 snub | ||
| *2222 | (∞ 2 ∞ 2) | × | [∞,2,∞] | 3 reflective forms, 1 snub | |
| Noncompact (frieze) | |||||
| *∞∞ | (∞) | [∞] | |||
| *22∞ | (2 2 ∞) | × | [∞,2] | 2 reflective forms, 1 snub | |
| Orbifold symmetry |
Coxeter group | Coxeter diagram |
notes | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Compact | ||||
| *pq2 | (p q 2) | [p,q] | 2(p+q) < pq | |
| *pqr | (p q r) | [(p,q,r)] | pq+pr+qr < pqr | |
| Paracompact | ||||
| *∞p2 | (p ∞ 2) | [p,∞] | p>=3 | |
| *∞pq | (p q ∞) | [(p,q,∞)] | p,q>=3, p+q>6 | |
| *∞∞p | (p ∞ ∞) | [(p,∞,∞)] | p>=3 | |
| *∞∞∞ | (∞ ∞ ∞) | [(∞,∞,∞)] | ||
Uniform tilings of the Euclidean plane
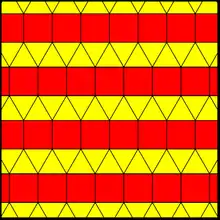
There are symmetry groups on the Euclidean plane constructed from fundamental triangles: (4 4 2), (6 3 2), and (3 3 3). Each is represented by a set of lines of reflection that divide the plane into fundamental triangles.
These symmetry groups create 3 regular tilings, and 7 semiregular ones. A number of the semiregular tilings are repeated from different symmetry constructors.
A prismatic symmetry group represented by (2 2 2 2) represents by two sets of parallel mirrors, which in general can have a rectangular fundamental domain. It generates no new tilings.
A further prismatic symmetry group represented by (∞ 2 2) which has an infinite fundamental domain. It constructs two uniform tilings, the apeirogonal prism and apeirogonal antiprism.
The stacking of the finite faces of these two prismatic tilings constructs one non-Wythoffian uniform tiling of the plane. It is called the elongated triangular tiling, composed of alternating layers of squares and triangles.
Right angle fundamental triangles: (p q 2)
| (p q 2) | Fund. triangles |
Parent | Truncated | Rectified | Bitruncated | Birectified (dual) |
Cantellated | Omnitruncated (Cantitruncated) |
Snub |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wythoff symbol | q | p 2 | 2 q | p | 2 | p q | 2 p | q | p | q 2 | p q | 2 | p q 2 | | | p q 2 | |
| Schläfli symbol | {p,q} | t{p,q} | r{p,q} | 2t{p,q}=t{q,p} | 2r{p,q}={q,p} | rr{p,q} | tr{p,q} | sr{p,q} | |
| Coxeter diagram | |||||||||
| Vertex config. | pq | q.2p.2p | (p.q)2 | p. 2q.2q | qp | p. 4.q.4 | 4.2p.2q | 3.3.p. 3.q | |
| Square tiling (4 4 2) |
 |
 {4,4} |
 4.8.8 |
 4.4.4.4 |
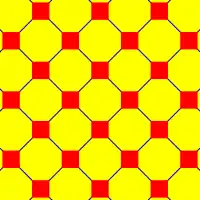 4.8.8 |
 {4,4} |
 4.4.4.4 |
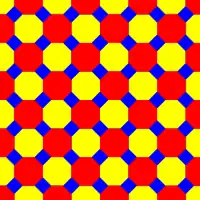 4.8.8 |
 3.3.4.3.4 |
| Hexagonal tiling (6 3 2) |
 |
 {6,3} |
 3.12.12 |
 3.6.3.6 |
 6.6.6 |
 {3,6} |
 3.4.6.4 |
 4.6.12 |
 3.3.3.3.6 |
General fundamental triangles: (p q r)
| Wythoff symbol (p q r) |
Fund. triangles |
q | p r | r q | p | r | p q | r p | q | p | q r | p q | r | p q r | | | p q r |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coxeter diagram | |||||||||
| Vertex config. | (p.q)r | r.2p.q.2p | (p.r)q | q.2r.p. 2r | (q.r)p | q.2r.p. 2r | r.2q.p. 2q | 3.r.3.q.3.p | |
| Triangular (3 3 3) |
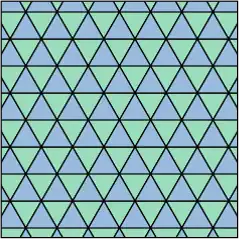 |
 (3.3)3 |
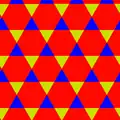 3.6.3.6 |
 (3.3)3 |
 3.6.3.6 |
 (3.3)3 |
 3.6.3.6 |
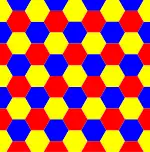 6.6.6 |
 3.3.3.3.3.3 |
Non-simplical fundamental domains
The only possible fundamental domain in Euclidean 2-space that is not a simplex is the rectangle (∞ 2 ∞ 2), with Coxeter diagram: ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() . All forms generated from it become a square tiling.
. All forms generated from it become a square tiling.
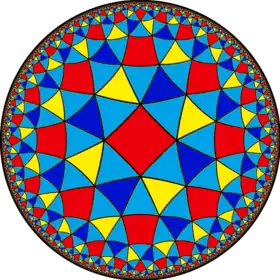
Uniform tilings of the hyperbolic plane
There are infinitely many uniform tilings of convex regular polygons on the hyperbolic plane, each based on a different reflective symmetry group (p q r).
A sampling is shown here with a Poincaré disk projection.
The Coxeter-Dynkin diagram is given in a linear form, although it is actually a triangle, with the trailing segment r connecting to the first node.
Further symmetry groups exist in the hyperbolic plane with quadrilateral fundamental domains starting with (2 2 2 3), etc., that can generate new forms. As well there's fundamental domains that place vertices at infinity, such as (∞ 2 3), etc.
Right angle fundamental triangles: (p q 2)
| (p q 2) | Fund. triangles |
Parent | Truncated | Rectified | Bitruncated | Birectified (dual) |
Cantellated | Omnitruncated (Cantitruncated) |
Snub |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wythoff symbol | q | p 2 | 2 q | p | 2 | p q | 2 p | q | p | q 2 | p q | 2 | p q 2 | | | p q 2 | |
| Schläfli symbol | t{p,q} | t{p,q} | r{p,q} | 2t{p,q}=t{q,p} | 2r{p,q}={q,p} | rr{p,q} | tr{p,q} | sr{p,q} | |
| Coxeter diagram | |||||||||
| Vertex figure | pq | (q.2p.2p) | (p.q.p.q) | (p. 2q.2q) | qp | (p. 4.q.4) | (4.2p.2q) | (3.3.p. 3.q) | |
| (5 4 2) |  V4.8.10 |
 {5,4} |
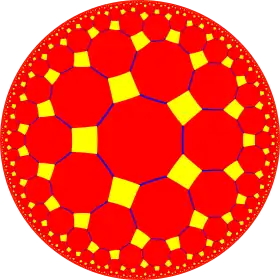 4.10.10 |
 4.5.4.5 |
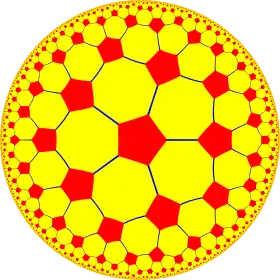 5.8.8 |
 {4,5} |
 4.4.5.4 |
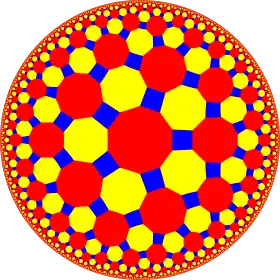 4.8.10 |
 3.3.4.3.5 |
| (5 5 2) |  V4.10.10 |
 {5,5} |
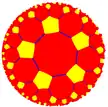 5.10.10 |
 5.5.5.5 |
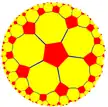 5.10.10 |
 {5,5} |
 5.4.5.4 |
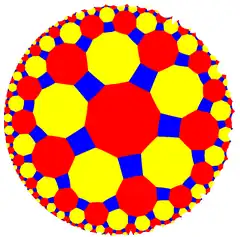 4.10.10 |
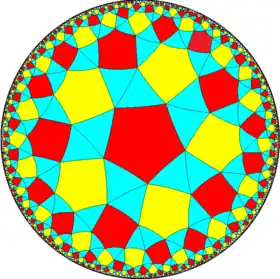 3.3.5.3.5 |
| (7 3 2) |  V4.6.14 |
 {7,3} |
 3.14.14 |
 3.7.3.7 |
 7.6.6 |
 {3,7} |
 3.4.7.4 |
 4.6.14 |
 3.3.3.3.7 |
| (8 3 2) |  V4.6.16 |
 {8,3} |
 3.16.16 |
 3.8.3.8 |
 8.6.6 |
 {3,8} |
 3.4.8.4 |
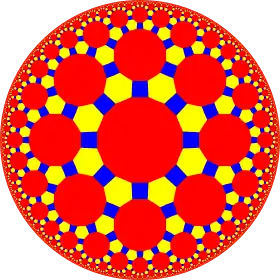 4.6.16 |
 3.3.3.3.8 |
General fundamental triangles (p q r)
| Wythoff symbol (p q r) |
Fund. triangles |
q | p r | r q | p | r | p q | r p | q | p | q r | p q | r | p q r | | | p q r |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coxeter diagram | |||||||||
| Vertex figure | (p.r)q | (r.2p.q.2p) | (p.q)r | (q.2r.p. 2r) | (q.r)p | (r.2q.p. 2q) | (2p.2q.2r) | (3.r.3.q.3.p) | |
| (4 3 3) | 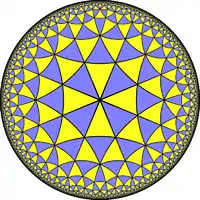 V6.6.8 |
 (3.4)3 |
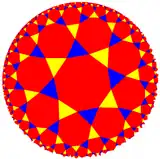 3.8.3.8 |
 (3.4)3 |
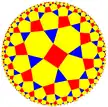 3.6.4.6 |
 (3.3)4 |
 3.6.4.6 |
 6.6.8 |
 3.3.3.3.3.4 |
| (4 4 3) |  V6.8.8 |
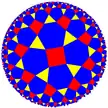
 (3.4)4 |
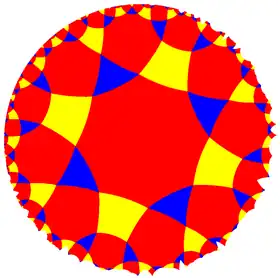 3.8.4.8 |
 (4.4)3 |
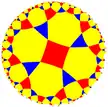 3.6.4.6 |
 (3.4)4 |
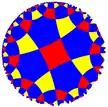 4.6.4.6 |
 6.8.8 |
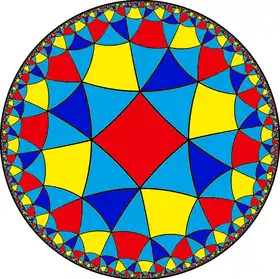 3.3.3.4.3.4 |
| (4 4 4) |  V8.8.8 |
 (4.4)4 |
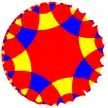 4.8.4.8 |
 (4.4)4 |
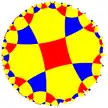 4.8.4.8 |
 (4.4)4 |
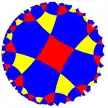 4.8.4.8 |
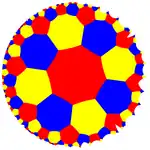 8.8.8 |
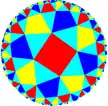 3.4.3.4.3.4 |
Expanded lists of uniform tilings

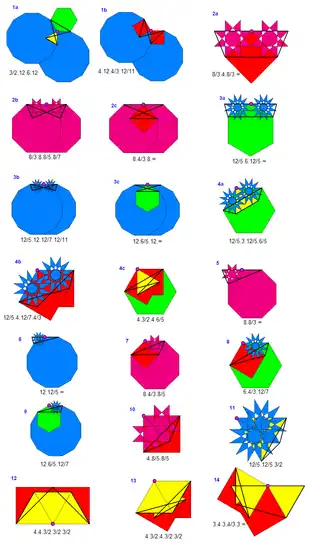
There are a number ways the list of uniform tilings can be expanded:
- Vertex figures can have retrograde faces and turn around the vertex more than once.
- Star polygon tiles can be included.
- Apeirogons, {∞}, can be used as tiling faces.
- Zigzags (apeirogons alternating between two angles) can also be used.
- The restriction that tiles meet edge-to-edge can be relaxed, allowing additional tilings such as the Pythagorean tiling.
Symmetry group triangles with retrogrades include:
- (4/3 4/3 2) (6 3/2 2) (6/5 3 2) (6 6/5 3) (6 6 3/2)
Symmetry group triangles with infinity include:
- (4 4/3 ∞) (3/2 3 ∞) (6 6/5 ∞) (3 3/2 ∞)
Branko Grünbaum and G. C. Shephard, in the 1987 book Tilings and patterns, in section 12.3 enumerates a list of 25 uniform tilings, including the 11 convex forms, and adds 14 more they call hollow tilings which included the first two expansions above, star polygon faces and vertex figures.[1]
H.S.M. Coxeter, M. S. Longuet-Higgins, and J. C. P. Miller, in the 1954 paper 'Uniform polyhedra', in Table 8: Uniform Tessellations, use the first three expansions and enumerates a total of 38 uniform tilings. If a tiling made of 2 apeirogons is also counted, the total can be considered 39 uniform tilings.
In 1981, Grünbaum, Miller, and Shephard in their paper Uniform Tilings with Hollow Tiles listed 25 tilings using the first two expansions and 28 more when the third is added (making 53 using Coxeter et al.'s definition). When the fourth is added, they list an additional 23 uniform tilings and 10 families (8 depending on continuous parameters and 2 on discrete parameters).[2]
Besides the 11 convex solutions, the 28 uniform star tilings listed by Coxeter et al., grouped by shared edge graphs, are shown below, followed by 15 more listed by Grünbaum et al. that meet Coxeter et al.'s definition but were missed by them.
This set is not proved complete. By "2.25" is meant tiling 25 in Grünbaum et al.'s table 2 from 1981.
The following three tilings are exceptional in that there is only finitely many of one face type: two apeirogons in each. Sometimes the order-2 apeirogonal tiling is not included, as its two faces meet at more than one edge.
| McNeill[3] | Diagram | Vertex Config | Wythoff | Symmetry | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I1 | ∞.∞ | p1m1 | (Two half-plane tiles, order-2 apeirogonal tiling) | ||
| I2 | 4.4.∞ | ∞ 2 | 2 | p1m1 | Apeirogonal prism | |
| I3 | 3.3.3.∞ | | 2 2 ∞ | p11g | Apeirogonal antiprism |
For clarity, apeirogons are not coloured from here onward. A set of polygons round one vertex is highlighted. McNeill only lists tilings given by Coxeter et al. (1954). The eleven convex uniform tilings have been repeated for reference.
| Wallpaper group symmetry | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| McNeill[3] | Grünbaum et al 1981[2] | Edge diagram | Highlighted | Vertex Config | Wythoff | Symmetry |
| Convex | 1.9 |  |  | 4.4.4.4 | 4 | 2 4 | p4m |
| I4 | 2.14 | 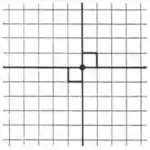 | 4.∞.4/3.∞ 4.∞.-4.∞ | 4/3 4 | ∞ | p4m | |
| Convex | 1.24 |  | 6.6.6 | 3 | 2 6 | p6m | |
| Convex | 1.25 |  | 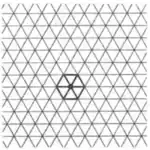 | 3.3.3.3.3.3 | 6 | 2 3 | p6m |
| I5 | 2.26 | 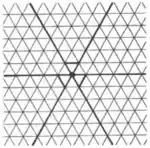 | (3.∞.3.∞.3.∞)/2 | 3/2 | 3 ∞ | p3m1 | |
| Convex | 1.23 |  | 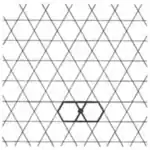 | 3.6.3.6 | 2 | 3 6 | p6m |
| I6 | 2.25 |  | 6.∞.6/5.∞ 6.∞.-6.∞ | 6/5 6 | ∞ | p6m | |
| I7 | 2.24 | 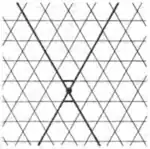 | ∞.3.∞.3/2 3.∞.-3.∞ | 3/2 3 | ∞ | p6m | |
| Convex | 1.14 | 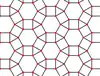 |  | 3.4.6.4 | 3 6 | 2 | p6m |
| 1 | 1.15 |  |
3/2.12.6.12 -3.12.6.12 | 3/2 6 | 6 | p6m | |
| 1.16 | 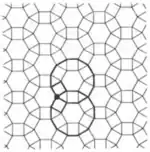 | 4.12.4/3.12/11 4.12.-4.-12 | 2 6 (3/2 6/2) | | p6m | ||
| Convex | 1.5 |  | 4.8.8 | 2 4 | 4 | p4m | |
| 2 | 2.7 |  | 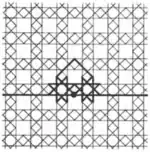 |
4.8/3.∞.8/3 | 4 ∞ | 4/3 | p4m |
| 1.7 |  | 8/3.8.8/5.8/7 8.8/3.-8.-8/3 | 4/3 4 (4/2 ∞/2) | | p4m | ||
| 2.6 | 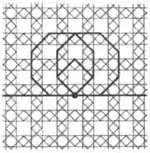 | 8.4/3.8.∞ -4.8.∞.8 | 4/3 ∞ | 4 | p4m | ||
| Convex | 1.20 | 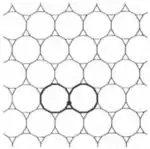 | 3.12.12 | 2 3 | 6 | p6m | |
| 3 | 2.17 | 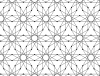 | 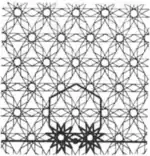 | 6.12/5.∞.12/5 | 6 ∞ | 6/5 | p6m |
| 1.21 | 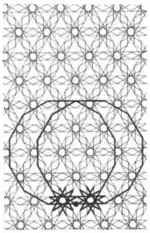 | 12/5.12.12/7.12/11 12.12/5.-12.-12/5 | 6/5 6 (6/2 ∞/2) | | p6m | ||
| 2.16 | 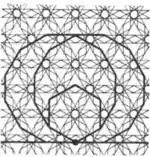 | 12.6/5.12.∞ -6.12.∞.12 | 6/5 ∞ | 6 | p6m | ||
| 4 | 1.18 |  | 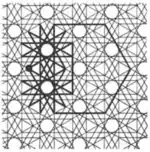 | 12/5.3.12/5.6/5 3.12/5.-6.12/5 | 3 6 | 6/5 | p6m |
| 1.19 | 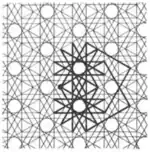 | 12/5.4.12/7.4/3 4.12/5.-4.-12/5 | 2 6/5 (3/2 6/2) | | p6m | ||
| 1.17 | 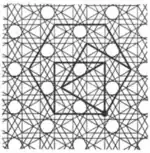 | 4.3/2.4.6/5 3.-4.6.-4 | 3/2 6 | 2 | p6m | ||
| 5 | 2.5 |  | 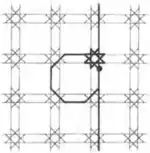 | 8.8/3.∞ | 4/3 4 ∞ | | p4m |
| 6 | 2.15 | 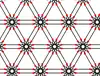 | 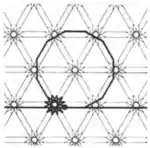 | 12.12/5.∞ | 6/5 6 ∞ | | p6m |
| 7 | 1.6 |  | 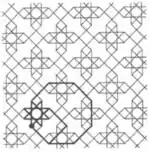 | 8.4/3.8/5 4.-8.8/3 | 2 4/3 4 | | p4m |
| Convex | 1.11 | 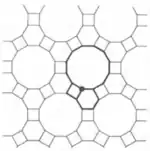 | 4.6.12 | 2 3 6 | | p6m | |
| 8 | 1.13 |  | 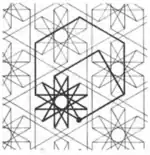 | 6.4/3.12/7 4.-6.12/5 | 2 3 6/5 | | p6m |
| 9 | 1.12 |  | 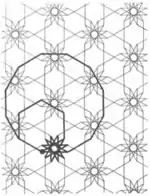 | 12.6/5.12/7 6.-12.12/5 | 3 6/5 6 | | p6m |
| 10 | 1.8 | 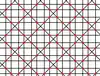 | 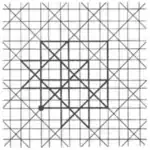 | 4.8/5.8/5 -4.8/3.8/3 | 2 4 | 4/3 | p4m |
| 11 | 1.22 |  |  | 12/5.12/5.3/2 -3.12/5.12/5 | 2 3 | 6/5 | p6m |
| Convex | 1.1 |  | 3.3.3.4.4 | non-Wythoffian | cmm | |
| 12 | 1.2 |  |  | 4.4.3/2.3/2.3/2 3.3.3.-4.-4 | non-Wythoffian | cmm |
| Convex | 1.3 |  | 3.3.4.3.4 | | 2 4 4 | p4g | |
| 13 | 1.4 |  | 4.3/2.4.3/2.3/2 3.3.-4.3.-4 | | 2 4/3 4/3 | p4g | |
| 14 | 2.4 | 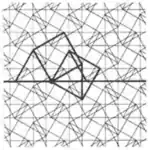 | 3.4.3.4/3.3.∞ 3.4.3.-4.3.∞ | | 4/3 4 ∞ | p4 | |
| Convex | 1.10 |  | 3.3.3.3.6 | | 2 3 6 | p6 | |
| 2.1 | 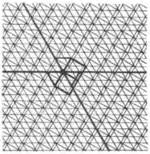 | 3/2.∞.3/2.∞.3/2.4/3.4/3 3.4.4.3.∞.3.∞ | non-Wythoffian | cmm | ||
| 2.2 | 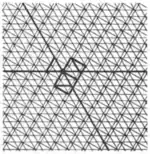 | 3/2.∞.3/2.∞.3/2.4.4 3.-4.-4.3.∞.3.∞ | non-Wythoffian | cmm | ||
| 2.3 | 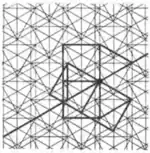 | 3/2.∞.3/2.4.4.3/2.4/3.4/3 3.4.4.3.-4.-4.3.∞ | non-Wythoffian | p3 | ||
| 2.8 | 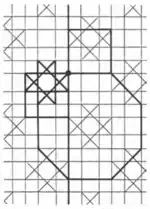 | 4.∞.4/3.8/3.8 4.8.8/3.-4.∞ | non-Wythoffian | p4m | ||
| 2.9 | 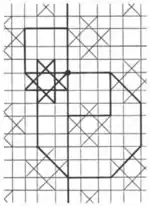 | 4.∞.4.8.8/3 -4.8.8/3.4.∞ | non-Wythoffian | p4m | ||
| 2.10 | 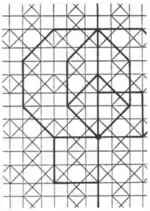 | 4.∞.4/3.8.4/3.8 4.8.-4.8.-4.∞ | non-Wythoffian | p4m | ||
| 2.11 |  | 4.∞.4/3.8.4/3.8 4.8.-4.8.-4.∞ | non-Wythoffian | p4g | ||
| 2.12 |  | 4.∞.4/3.8/3.4.8/3 4.8/3.4.8/3.-4.∞ | non-Wythoffian | p4m | ||
| 2.13 |  | 4.∞.4/3.8/3.4.8/3 4.8/3.4.8/3.-4.∞ | non-Wythoffian | p4g | ||
| 2.18 |  | 3/2.∞.3/2.4/3.4/3.3/2.4/3.4/3 3.4.4.3.4.4.3.∞ | non-Wythoffian | p6m | ||
| 2.19 | 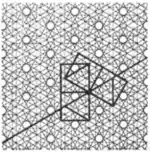 | 3/2.∞.3/2.4.4.3/2.4.4 3.-4.-4.3.-4.-4.3.∞ | non-Wythoffian | p6m | ||
| 2.20 | 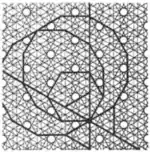 | 3/2.∞.3/2.∞.3/2.12/11.6.12/11 3.12.-6.12.3.∞.3.∞ | non-Wythoffian | p6m | ||
| 2.21 |  | 3/2.∞.3/2.∞.3/2.12.6/5.12 3.-12.6.-12.3.∞.3.∞ | non-Wythoffian | p6m | ||
| 2.22 | 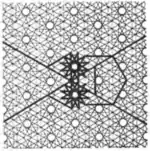 | 3/2.∞.3/2.∞.3/2.12/7.6/5.12/7 3.12/5.6.12/5.3.∞.3.∞ | non-Wythoffian | p6m | ||
| 2.23 | 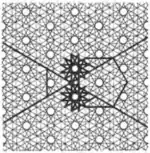 | 3/2.∞.3/2.∞.3/2.12/5.6.12/5 3.-12/5.-6.-12/5.3.∞.3.∞ | non-Wythoffian | p6m | ||
There are two uniform tilings for the vertex figure 4.8.-4.8.-4.∞ (Grünbaum et al. 2.10 and 2.11) and also two uniform tilings for the vertex figure 4.8/3.4.8/3.-4.∞ (Grünbaum et al. 2.12 and 2.13), with different symmetries. There is also a third tiling for each vertex figure that is only pseudo-uniform (vertices come in two symmetry orbits). They use different sets of square faces. Hence, for star Euclidean tilings, the vertex figure does not necessarily determine the tiling.[2]
In the pictures below, the included squares with horizontal and vertical edges are marked with a central dot. A single square has edges highlighted.[2]
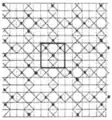 2.10 and 2.12 (p4m)
2.10 and 2.12 (p4m)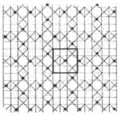 2.11 and 2.13 (p4g)
2.11 and 2.13 (p4g)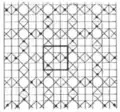 Pseudo-uniform
Pseudo-uniform
The tilings with zigzags are listed below. The notation {∞α} denotes a zigzag with angle 0 < α < π. The apeirogon can be considered as the special case α = π. The symmetries are given for the generic case: there are sometimes special values of α that increase the symmetry. Tilings 3.1 and 3.12 can even become regular; 3.32 already is (it has no free parameters). Sometimes there are special values of α that cause the tiling to degenerate.[2]
| Tilings with zigzags | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Grünbaum et al 1981[2] | Diagram | Vertex Config | Symmetry |
| 3.1 |  | ∞α.∞β.∞γ α+β+γ=2π | p2 |
| 3.2 |  | ∞α.∞β.-∞α+β 0<α+β≤π | p2 |
| 3.3 |  | 3.3.∞π-α.-3.∞α+2π/3 0≤α≤π/6 | pgg |
| 3.4 |  | 3.3.-∞π-α.-3.∞−α+2π/3 0≤α<π/3 | pgg |
| 3.5 | 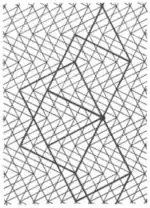 | 4.4.∞φ.4.4.-∞φ φ=2 arctan(n/k), nk even, (n,k)=1 drawn for φ=2 arctan 2 | pmg |
| 3.6 | 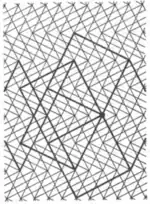 | 4.4.∞φ.-4.-4.∞φ φ=2 arctan(n/k), nk even, (n,k)=1 drawn for φ=2 arctan 1/2 | pmg |
| 3.7 | 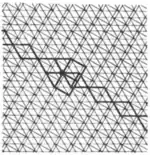 | 3.4.4.3.-∞2π/3.-3.-∞2π/3 | cmm |
| 3.8 | 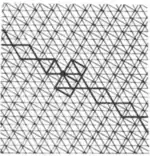 | 3.-4.-4.3.-∞2π/3.-3.-∞2π/3 | cmm |
| 3.9 | 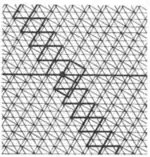 | 4.4.∞π/3.∞.-∞π/3 | p2 |
| 3.10 | 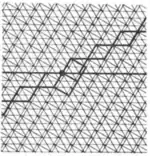 | 4.4.∞2π/3.∞.-∞2π/3 | p2 |
| 3.11 |  | ∞.∞α.∞.∞−α 0<α<π | cmm |
| 3.12 |  | ∞α.∞π-α.∞α.∞π-α 0<α≤π/2 | cmm |
| 3.13 | 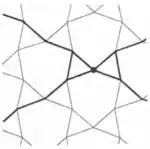 | 3.∞α.-3.-∞α π/3<α<π | p31m |
| 3.14 | 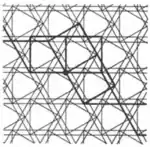 | 4.4.∞2π/3.4.4.-∞2π/3 | p31m |
| 3.15 | 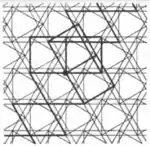 | 4.4.∞π/3.-4.-4.-∞π/3 | p31m |
| 3.16 | 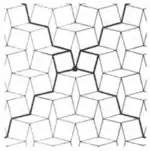 | 4.∞α.-4.-∞α 0<α<π, α≠π/2 | p4g |
| 3.17 | 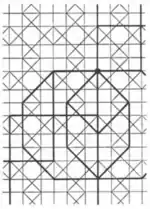 | 4.-8.∞π/2.∞.-∞π/2.-8 | cmm |
| 3.18 |  | 4.-8.∞π/2.∞.-∞π/2.-8 | p4 |
| 3.19 | 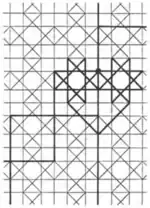 | 4.8/3.∞π/2.∞.-∞π/2.8/3 | cmm |
| 3.20 |  | 4.8/3.∞π/2.∞.-∞π/2.8/3 | p4 |
| 3.21 | 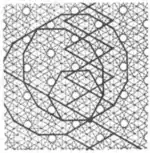 | 6.-12.∞π/3.∞.-∞π/3.-12 | p6 |
| 3.22 | 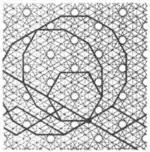 | 6.-12.∞2π/3.∞.-∞2π/3.-12 | p6 |
| 3.23 | 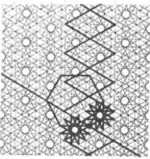 | 6.12/5.∞π/3.∞.-∞π/3.12/5 | p6 |
| 3.24 |  | 6.12/5.∞2π/3.∞.-∞2π/3.12/5 | p6 |
| 3.25 | 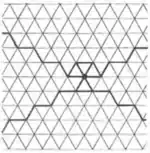 | 3.3.3.∞2π/3.-3.∞2π/3 | p31m |
| 3.26 | 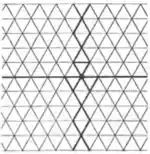 | 3.∞.3.-∞2π/3.-3.-∞2π/3 | cm |
| 3.27 | 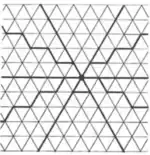 | 3.∞.-∞2π/3.∞.-∞2π/3.∞ | p31m |
| 3.28 |  | 3.∞2π/3.∞2π/3.-3.-∞2π/3.-∞2π/3 | p31m |
| 3.29 | 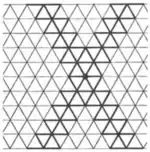 | ∞.∞π/3.∞π/3.∞.-∞π/3.-∞π/3 | cmm |
| 3.30 | 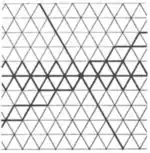 | ∞.∞π/3.-∞2π/3.∞.∞2π/3.-∞π/3 | p2 |
| 3.31 |  | ∞.∞2π/3.∞2π/3.∞.-∞2π/3.-∞2π/3 | cmm |
| 3.32 |  | ∞π/3.∞π/3.∞π/3.∞π/3.∞π/3.∞π/3 | p6m |
| 3.33 |  | ∞π/3.-∞2π/3.-∞2π/3.∞π/3.-∞2π/3.-∞2π/3 | cmm |
The tiling pairs 3.17 and 3.18, as well as 3.19 and 3.20, have identical vertex configurations but different symmetries.[2]
Tilings 3.7 through 3.10 have the same edge arrangement as 2.1 and 2.2; 3.17 through 3.20 have the same edge arrangement as 2.10 through 2.13; 3.21 through 3.24 have the same edge arrangement as 2.18 through 2.23; and 3.25 through 3.33 have the same edge arrangement as 1.25 (the regular triangular tiling).[2]
Self-dual tilings
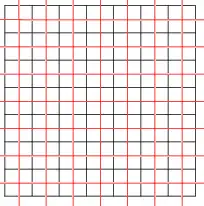
Tilings can also be self-dual. The square tiling, with Schläfli symbol {4,4}, is self-dual; shown here are two square tilings (red and black), dual to each other.
Uniform tilings using star polygons
π/8.4**
π/4.8*
π/4 is considered not edge-to-edge due to the large square, although it can be interpreted as star polygon with pairs of colinear edges.
Seeing a star polygon as a nonconvex polygon with twice as many sides allows star polygons, and counting these as regular polygons allows them to be used in a uniform tiling. These polygons are labeled as {Nα} for a isotoxal nonconvex 2N-gon with external dihedral angle α. Its external vertices are labeled as N*
α, and internal N**
α. This expansion to the definition requires corners with only 2 polygons to not be considered vertices. The tiling is defined by its vertex configuration as a cyclic sequence of convex and nonconvex polygons around every vertex. There are 4 such uniform tilings with adjustable angles α, and 18 uniform tilings that only work with specific angles; yielding a total of 22 uniform tilings that use star polygons.[4]
All of these tilings are topologically related to the ordinary uniform tilings with convex regular polygons, with 2-valence vertices ignored, and square faces as digons, reduced to a single edge.
 3.6* α.6** α Topological 3.12.12 |
 4.4* α.4** α Topological 4.8.8 |
 6.3* α.3** α Topological 6.6.6 |
 3.3* α.3.3** α Topological 3.6.3.6 |
 4.6.4* π/6.6 Topological 4.4.4.4 |
 (8.4* π/4)2 Topological 4.4.4.4 |
 12.12.4* π/3 Topological 4.8.8 |
 3.3.8* π/12.4** π/3.8* π/12 Topological 4.8.8 |
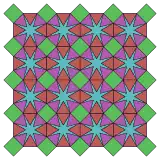 3.3.8* π/12.3.4.3.8* π/12 Topological 4.8.8 |
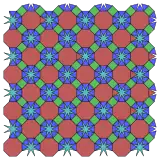 3.4.8.3.8* π/12 Topological 4.8.8 |
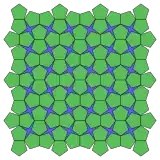 5.5.4* 4π/10.5.4* π/10 Topological 3.3.4.3.4 |
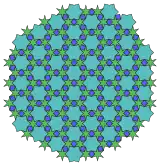 4.6* π/6.6** π/2.6* π/6 Topological 6.6.6 |
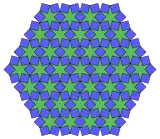 (4.6* π/6)3 Topological 6.6.6 |
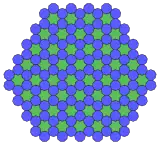 9.9.6* 4π/9 Topological 6.6.6 |
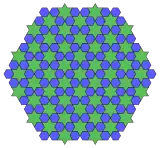 (6.6* π/3)2 Topological 3.6.3.6 |
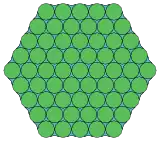 (12.3* π/6)2 Topological 3.6.3.6 |
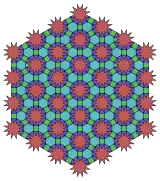 3.4.6.3.12* π/6 Topological 4.6.12 |
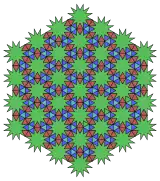 3.3.3.12* π/6.3.3.12* π/6 Topological 3.12.12 |
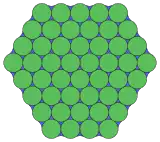 18.18.3* 2π/9 Topological 3.12.12 |
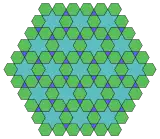 3.6.6* π/3.6 Topological 3.4.6.4 |
 8.3* π/12.8.6* 5π/12 Topological 3.4.6.4 |
 9.3.9.3* π/9 Topological 3.6.3.6 |
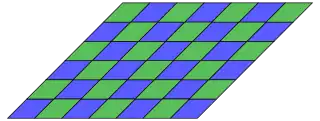
Uniform tilings using alternating polygons
Star polygons of the form {pα} can also represent convex 2p-gons alternating two angles, the simplest being a rhombus {2α}. Allowing these as regular polygons, creates more uniform tilings, with some example below.
 3.2*.6.2** Topological 3.4.6.4 |
 4.4.4.4 Topological 4.4.4.4 |
 (2* π/6.2** π/3)2 Topological 4.4.4.4 |
 2* π/6.2* π/6.2** π/3.2** π/3 Topological 4.4.4.4 |
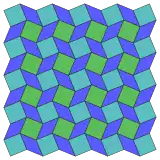 4.2* π/6.4.2** π/3 Topological 4.4.4.4 |
See also
References
- Tiles and Patterns, Table 12.3.1 p.640
- Grünbaum, Branko; Miller, J. C. P.; Shephard, G. C. (1981). "Uniform Tilings with Hollow Tiles". In Davis, Chandler; Grünbaum, Branko; Sherk, F. A. (eds.). The Geometric Vein: The Coxeter Festschrift. Springer. pp. 17–64. ISBN 978-1-4612-5650-2.
- Jim McNeill
- Tilings and Patterns Branko Gruenbaum, G.C. Shephard, 1987. 2.5 Tilings using star polygons, pp.82-85.
- Norman Johnson Uniform Polytopes, Manuscript (1991)
- N.W. Johnson: The Theory of Uniform Polytopes and Honeycombs, Ph.D. Dissertation, University of Toronto, 1966
- Grünbaum, Branko; Shephard, G. C. (1987). Tilings and Patterns. W. H. Freeman and Company. ISBN 0-7167-1193-1. (Star tilings section 12.3)
- H. S. M. Coxeter, M. S. Longuet-Higgins, J. C. P. Miller, Uniform polyhedra, Phil. Trans. 1954, 246 A, 401–50 JSTOR 91532 (Table 8)
External links
- Weisstein, Eric W. "Uniform tessellation". MathWorld.
- Uniform Tessellations on the Euclid plane
- Tessellations of the Plane
- David Bailey's World of Tessellations
- k-uniform tilings
- n-uniform tilings
- Klitzing, Richard. "4D Euclidean tilings".
| Space | Family | / / | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E2 | Uniform tiling | {3[3]} | δ3 | hδ3 | qδ3 | Hexagonal |
| E3 | Uniform convex honeycomb | {3[4]} | δ4 | hδ4 | qδ4 | |
| E4 | Uniform 4-honeycomb | {3[5]} | δ5 | hδ5 | qδ5 | 24-cell honeycomb |
| E5 | Uniform 5-honeycomb | {3[6]} | δ6 | hδ6 | qδ6 | |
| E6 | Uniform 6-honeycomb | {3[7]} | δ7 | hδ7 | qδ7 | 222 |
| E7 | Uniform 7-honeycomb | {3[8]} | δ8 | hδ8 | qδ8 | 133 • 331 |
| E8 | Uniform 8-honeycomb | {3[9]} | δ9 | hδ9 | qδ9 | 152 • 251 • 521 |
| E9 | Uniform 9-honeycomb | {3[10]} | δ10 | hδ10 | qδ10 | |
| E10 | Uniform 10-honeycomb | {3[11]} | δ11 | hδ11 | qδ11 | |
| En-1 | Uniform (n-1)-honeycomb | {3[n]} | δn | hδn | qδn | 1k2 • 2k1 • k21 |

