Propyliodone
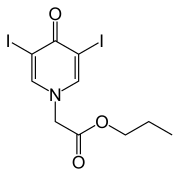
Propyliodone (INN, trade name Dionosil) is a molecule used as a contrast medium in bronchography.[1] It was developed by a team at Imperial Chemical Industries[2] in the late 1930s.
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | propyl (3,5-diiodo-4-oxopyridin-1(4H)-yl)acetate |
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.008.731 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C10H11I2NO3 |
| Molar mass | 447.011 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| | |
References
- Pfeifer W, Seidel K (February 1958). "[Experiences with propyliodone bronchography]". Medizinische Klinik (in German). 53 (8): 293–5. PMID 13540854.
- GB 517382
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.