Tigloidine
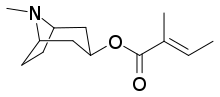
Tigloidine is a tropane alkaloid that naturally occurs as a minor constituent of a number of solanaceous plants, including Duboisia myoporoides,[1] Physalis peruviana,[2] and Mandragora turcomanica.
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Tropigline |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.007.101 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C13H21NO2 |
| Molar mass | 223.316 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
It was formerly marketed as an antiparkinsonian drug[3] under the trade name Tropigline.[4]
References
- Barger G, Martin WF, Mitchell W (1937). "383. The minor alkaloids of Duboisia myoporoides". Journal of the Chemical Society (Resumed): 1820. doi:10.1039/JR9370001820. hdl:1842/35366.
- Beresford PJ, Woolley JG (1974). "Biosynthesis of ticloidine in Physalis peruviana". Phytochemistry. 13 (10): 2143–2144. doi:10.1016/0031-9422(74)85016-8.
- "Approved Names". British Medical Journal. 1 (5080): 1175. 1958. doi:10.1136/bmj.1.5080.1175. PMC 2028565.
- Index Nominum 2000: International Drug Directory. Taylor & Francis. 2000. pp. 1663–. ISBN 978-3-88763-075-1.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.