Etanautine
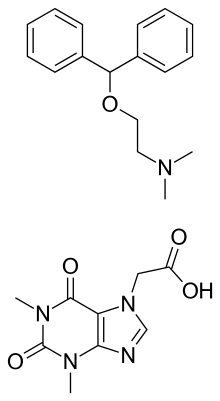
Etanautine, also known as diphenhydramine monoacefyllinate, is an anticholinergic used as an antiparkinsonian agent. It is a 1:1 salt of diphenhydramine with acefylline, similar to the diphenhydramine/8-chlorotheophylline combination product dimenhydrinate.[1]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C26H31N5O5 |
| Molar mass | 493.564 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| (verify) | |
As with dimenhydrinate, the stimulant effect of the etanautine counteracts the sedative effect from the diphenhydramine, resulting in an improved therapeutic profile.[2]
The 1:2 salt diphenhydramine diacefylline (with two molecules of acefylline to each molecule of diphenhydramine) is also used in medicine, under the brand name Nautamine.[1][3]
References
- Sicari V, Zabbo CP (2022). "Diphenhydramine". StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing. PMID 30252266. Retrieved 2022-11-02.
- Gonzalez F (August 21, 2009). "Diphenhydramine may be useful as a palliative treatment for patients dying with Parkinson's disease and tremors: a case report and discussion". The American Journal of Hospice & Palliative Care. 26 (6): 474–475. doi:10.1177/1049909109338937. PMID 19700649. S2CID 206633832.
- "Diphenhydramine Dosage Guide + Max Dose, Adjustments". Drugs.com. Retrieved 2022-11-02.
| Dopaminergics |
| ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anticholinergics | |||||||||||
| Others |
| ||||||||||
| |||||||||||
Purine receptor modulators | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Receptor (ligands) |
| ||||||||||
| Transporter (blockers) |
| ||||||||||
| Enzyme (inhibitors) |
| ||||||||||
| Others |
| ||||||||||
See also: Receptor/signaling modulators | |||||||||||
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.