Propylhexedrine
Propylhexedrine, sold under the brand name Benzedrex, is a nasal decongestant, appetite suppressant, and psychostimulant medication. It is used medicinally for relief of congestion due to colds, allergies and allergic rhinitis.
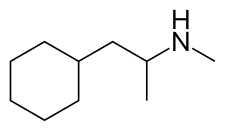 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Benzedrex, Obesin |
| Other names | Hexahydro-desoxyephedrine; Hexahydro-methamphetamine; Hydromethamphetamine; Dimethylcyclo-hexaneethanamine; Cycohexyliso-propylmethylamine; Propylhexedrinum |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Medical: Intranasal (inhaler) and oral Recreational: Oral and parenteral routes |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Elimination half-life | 4 ± 1.5 hours |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII |
|
| KEGG | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.002.673 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C10H21N |
| Molar mass | 155.285 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Chirality | Racemic mixture |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| | |
Propylhexedrine is most commonly found in over-the-counter Benzedrex inhalers. Benzedrex was first manufactured by Smith, Kline and French after the Benzedrine inhaler, which contained racemic amphetamine, became unavailable following the placement of amphetamines on the US Schedule II status (highest abuse potential, yet with accepted medicinal uses). Benzedrex is currently manufactured by B.F. Ascher & Co. Inc. Pharmaceuticals.[1]
Propylhexedrine has also seen use in Europe as an appetite suppressant, under the trade name Obesin.[2] Additionally, it is found in the anticonvulsant preparation barbexaclone, where its S-isomer (levopropylhexedrine or L-propylhexedrine) is bonded with phenobarbital for the purpose of offsetting the barbiturate-induced sedation.[2] Levopropylhexedrine is also used as an anorectic, under the brand name Eventin.[3]
Medical use
Propylhexedrine is used to treat acute nasal congestion related to common cold,[1] allergies and hay fever. For nasal congestion, the dosage is listed as four inhalations (two inhalations per nostril) every two hours for adults and children 6–12 years of age. Each inhalation delivers 0.4 to 0.5 milligram (400 to 500 μg) in 800 millilitres of air.[1] Historically, it has also been used for weight loss, typically at doses from 5 to 30 milligrams.[4][5]
Contraindications
Propylhexedrine should not be used if a MAOI has been used in the past 14 days or is currently in use, as this can result in hypertensive crisis. People with cardiovascular disease should not use propylhexedrine.[6]
Additionally, stimulant drugs and sympathomimetics should not be taken with propylhexedrine, as this can lead to a potentially dangerous spike in blood pressure and irregular heart rhythms.[7]
There is one case of death where a combination of propylhexedrine, acetaminophen, morphine, promethazine, and kratom was detected. However, the study indicates that propylhexedrine was most likely the principal cause.[8]
Pharmacology
Propylhexedrine is a TAAR1 agonist, like amphetamine.[9] Consequently, it reverses the transporters for dopamine, norepinephrine, and serotonin, leading to a release of monoamines from presynaptic vesicles into the synaptic cleft.[9] The increased level of monoamines within the synapse results in increased activity at their respective receptors. Additionally, propylhexedrine appears to inhibit VMAT2, leading to a further increase in the aforementioned monoamines.[9] The pharmacological actions of propylhexedrine are similar to that of structurally similar stimulant phenethylamines, such as amphetamine.[9]
Metabolism
Propylhexedrine undergoes metabolism to form various metabolites including norpropylhexedrine, cyclohexylacetoxime, cis- and trans-4-hydroxypropylhexedrine.[10]
Chemistry
Freebase propylhexedrine is a volatile, oily liquid at room temperature. The slow evaporation of freebase propylhexedrine allows it to be administered via inhalation.[11] As an amine, it can easily be protonated to form various salts, such as propylhexedrine hydrochloride, propylhexedrine citrate, or propylhexedrine acetate, depending on the acid used. These salts are stable, clear to off-white crystalline substances that readily dissolve in water.[12]
Propylhexedrine is structurally similar to phenylethylamines, with the only structural difference being the substitution of an alicyclic cyclohexyl group for the aromatic phenyl group of phenethylamine. Propylhexedrine is not an amphetamine, nor even a phenethylamine, but instead can be referred to as a cycloalkyl amine, or more specifically a cyclohexylethylamine being the N,a-dimethyl derivative of 2-cyclohexylethylamine.
Propylhexedrine is a chiral compound (the α-carbon is chiral), and the active ingredient contained in Benzedrex inhalers is racemic (RS)-propylhexedrine as the free base. (S)-Propylhexedrine, also known as levopropylhexedrine, is believed to be the more biologically active isomer of the two.[13] (S)-Propylhexedrine can be synthesized from dextromethamphetamine.[14]
Synthesis
Propylhexedrine can be synthesized starting with cyclohexylacetone in a similar fashion to the phenylacetone synthesis of methamphetamine.[15]
However, more commonly propylhexedrine is prepared by reacting methamphetamine with Adams' catalyst, reducing methamphetamine's aromatic ring to a cyclohexyl moiety.

Society and culture
Legal Status
On the 4th of April 1988, propylhexedrine was designated a controlled substance (Schedule V) in the United States.[17] This was done to satisfy U.S. compliance with an international treaty. However, in 1991 this action was reversed and propylhexedrine was removed from control under the Controlled Substances Act, based on the opinion of the Drug Enforcement Administration that propylhexedrine did not warrant control.[18] The substance has remained unregulated under the Controlled Substances Act in the United States ever since.
The drug was formerly a Class C controlled drug in the United Kingdom, but was legalized in 1995.[19]
Recreational use
Propylhexedrine is used recreationally in a manner similar to drugs of the amphetamine class. Users report a high similar to other amphetamines, but often more euphoric. Compared to both amphetamine and methamphetamine, propylhexedrine has a much shorter duration of action. This is generally considered undesirable by recreational users. Additionally, propylhexedrine products are manufactured using delivery devices such as sub-recreational-dosage inhalers. This makes it very difficult to consume recreational doses via non-oral routes of administration, which further limits its ability to match or replace other amphetamine-related stimulants. Lastly, the undesirable side effects of propylhexedrine at recreational doses are often notably worse than amphetamine, non-IV methamphetamine, and other commonly abused stimulants, making it sub-optimal for long term recreational use.
Effects
Propylhexedrine has sympathomimetic, adrenergic, vasoconstrictive and psychostimulant effects when taken in higher-than-recommended doses. Effects include increased sweating, talkativeness, mydriasis, emotional lability, anorexia, tachycardia, palpitations, dry mouth, bruxism, anxiety, euphoria or dysphoria, increased aggressiveness, paranoia, headache, dizziness, psychosis, slurred or impaired speech, rarely convulsions and serious heart problems.[20] Propylhexedrine can also cause swelling, dryness and irritation of mucous membranes.[21]
Injection risks
While propylhexedrine has a limited number of administration routes, attempts to extract the drug from the nasal inhaler and then inject it have been reported. Recreational use by intravenous injection (IV) is dangerous, and could result in serious bodily harm or death. IV use of propylhexedrine is known to cause mild side-effects such as transient diplopia. More serious and potentially fatal effects such as brainstem dysfunction and death have been recorded in the medical literature. Reports indicate that propylhexedrine is prepared for IV use by placing the freebase in a solution with hydrochloric acid, to form propylhexedrine HCl. The solution is then heated to evaporate the solvent, and the resulting crystals are dissolved in water for injection.[22][23][20]
See also
References
- "Benzedrex Inhaler Nasal Decongestant Inhaler". B.F. Ascher & Company, Inc. Retrieved 27 March 2013.
- Wesson DR (June 1986). "Propylhexdrine". Drug and Alcohol Dependence. 17 (2–3): 273–8. doi:10.1016/0376-8716(86)90013-X. PMID 2874970.
- "Eventin". Drugs.com. Retrieved 27 March 2013.
- Docherty JR (June 2008). "Pharmacology of stimulants prohibited by the World Anti-Doping Agency (WADA)". British Journal of Pharmacology. 154 (3): 606–22. doi:10.1038/bjp.2008.124. PMC 2439527. PMID 18500382.
- "Obesin Dosage, Interactions". Retrieved 23 October 2017.
- "Propylhexedrine Contraindications". Medscape.
- "Safety of mixing stimulants with medications". NIDA.
- Holler JM, Vorce SP, McDonough-Bender PC, Magluilo J, Solomon CJ, Levine B (January 2011). "A drug toxicity death involving propylhexedrine and mitragynine". Journal of Analytical Toxicology. 35 (1): 54–9. doi:10.1093/anatox/35.1.54. PMID 21219704.
- "Propylhexedrine". DrugBank.
- Midha KK, Beckett AH, Saunders A (October 1974). "Identification of the major metabolites of propylhexedrine in vivo (in man) and in vitro (in guinea pig and rabbit)". Xenobiotica; the Fate of Foreign Compounds in Biological Systems. 4 (10): 627–35. doi:10.1080/00498257409169765. PMID 4428789.
- US granted 4095596, Grayson M, "Nasal Inhaler", issued 20 June 1978, assigned to Smithkline Corp.
- Mancusi-Ungaro HR, Decker WJ, Forshan VR, Blackwell SJ, Lewis SR (1983). "Tissue injuries associated with parenteral propylhexedrine abuse". Journal of Toxicology. Clinical Toxicology. 21 (3): 359–72. doi:10.1097/00005373-198307000-00114. PMID 6144800.
- Lands AM, Nash VL (April 1947). "The pharmacologic activity of N-methyl-beta-cyclohexyl-isopropylamine hydrochloride". The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. 89 (4): 382–5. PMID 20295519.
- Wilson CO, Gisvold O, Doerge RF (1971). Textbook of organic medicinal and pharmaceutical chemistry. Lippincott. p. 491. ISBN 9780397520558.
- Lednicer D, Mitscher LA (1977). Organic Chemistry of Drug Synthesis. Vol. 1. New York, NY: Wiley. p. 37. ISBN 978-0-471-52141-9.
- Zenitz BL, Macks EB, Moore ML (May 1947). "Preparation of some primary and secondary beta-cyclohexylalkylamines". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 69 (5): 1117–21. doi:10.1021/ja01197a039. PMID 20240502.
- "Federal Register Vol. 53 No. 64" (PDF). National Archives.
- "Federal Register Vol. 56 No. 232" (PDF). National Archives.
- "The Misuse of Drugs Act 1971 (Modification) Order 1995". Office of Public Sector Information. Retrieved 15 June 2009.
- Fornazzari L, Carlen PL, Kapur BM (November 1986). "Intravenous abuse of propylhexedrine (Benzedrex) and the risk of brainstem dysfunction in young adults". The Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences. 13 (4): 337–9. doi:10.1017/S0317167100036696. PMID 2877725.
- Safety Data Sheet – Cayman Chemical
- "Proposed Rules". Federal Register. 50 (10): 2226–2227.
- Prince v. Ascher, 90 P.3d 1020 (2004).