Isometheptene
Isometheptene (usually as isometheptene mucate) is a sympathomimetic amine sometimes used in the treatment of migraines and tension headaches due to its vasoconstricting properties; that is, it causes constriction (narrowing) of blood vessels (arteries and veins).[1][2] Along with paracetamol and dichloralphenazone, it is one of the constituents of Amidrine.
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| MedlinePlus | a601064 |
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank |
|
| ChemSpider |
|
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.007.236 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C9H19N |
| Molar mass | 141.258 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| (verify) | |
Chemistry
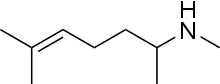
Isometheptene is a monounsaturated aliphatic secondary amine.
Mechanism of action
Isometheptene's vasoconstricting properties arise through activation of the sympathetic nervous system via epinephrine and norepinephrine. These compounds elicit smooth muscle activation leading to vasoconstriction by interacting with cell surface adrenergic receptors.[3]
See also
- Heptaminol
- Methylhexanamine
- Tuaminoheptane
References
- Diamond S, Medina JL (October 1975). "Isometheptene--a non-ergot drug in the treatment of migraine". Headache. 15 (3): 211–3. doi:10.1111/j.1526-4610.1975.hed1503211.x. PMID 1100566. S2CID 34768775.
- Behan PO (December 1978). "Isometheptene compound in the treatment of vascular headache". The Practitioner. 221 (1326): 937–9. PMID 372936.
- "Isometheptene". Drug Bank.
Drugs for functional gastrointestinal disorders (A03) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drugs for functional bowel disorders |
| ||||||||||||
| Belladonna and derivatives (antimuscarinics) |
| ||||||||||||
| Propulsives | |||||||||||||
| DRAs |
| ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NRAs |
| ||||||||||||||
| SRAs |
| ||||||||||||||
| Others |
| ||||||||||||||
See also: Receptor/signaling modulators • Monoamine reuptake inhibitors • Adrenergics • Dopaminergics • Serotonergics • Monoamine metabolism modulators • Monoamine neurotoxins | |||||||||||||||
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.