Hexoprenaline
Hexoprenaline is a selective β2 adrenergic receptor agonist used in the treatment of asthma.[2] Hexoprenaline is also used in some countries (such as Russia and Switzerland) as a tocolytic agent (i.e., labor suppressant), with the most common trade name being Gynipral.[3][4] It is not approved by the United States Food and Drug Administration.
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | /ˌhɛksoʊˈprɛnəliːn/ HEKS-oh-PREN-ə-leen |
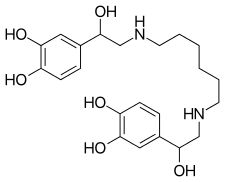
| Other names | 4-[2-[6-[[2-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-2-hydroxyethyl]amino]hexylamino]-1-hydroxyethyl]benzene-1,2-diol |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Routes of administration | Oral (tablets), IV |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 5–11% (Tmax = 2 hours) |
| Metabolism | COMT (slow O-methylation) |
| Elimination half-life | ~50 minutes (if taken orally) |
| Excretion | Feces (~90%)[1] |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C22H32N2O6 |
| Molar mass | 420.506 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Chirality | Racemic mixture |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| | |
Contraindications
When used as a tocolytic, hexoprenaline is contraindicated in:
- Hyperthyroidism
- Cardiovascular diseases, e.g. cardiac arrhythmias, tachycardia, myocarditis, mitral valve disease and aortic stenosis
- Ischemic heart disease
- Hypertension
- Angle-closure glaucoma
- Placental abruption, vaginal bleeding and inflammatory diseases of internal genitalia (such as endometritis)
- Shock
- First trimester of pregnancy
- Breastfeeding[1][3]
It should be used with caution in people with gestational diabetes.
Drug-drug interactions
When concomitantly administered:
- Beta blockers reduce or neutralize therapeutic effects of hexoprenaline
- Methylxanthines (caffeine, theobromine, theophylline) increase its action
- General anaesthetics (e.g., halothane) and adrenergic receptor agonists may increase the risk of cardiovascular side effects, such as arrhythmia
Hexoprenaline is contraindicated for use with monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs), tricyclic antidepressant (TCAs), ergot alkaloids, and dihydrotachysterol.[3]
References
- "Gynipral (hexoprenaline) Full Prescribing Information". Russian State Register of Medicinal Products (in Russian). Nycomed Austria GmbH. St. Peter-Straße 25, A-4020, Linz, Austria. Retrieved 19 March 2016.
- Pinder RM, Brogden RN, Speight TM, Avery GS (July 1977). "Hexoprenaline: a review of its pharmacological properties and therapeutic efficacy with particular reference to asthma". Drugs. 14 (1): 1–28. doi:10.2165/00003495-197714010-00001. PMID 195789. S2CID 43775455.
- "Gynipral (hexoprenaline) Tablets 0.5 mg, Solution for Intravenous Infusion 5 μg/mL (0.0005%)". "RLS" (РЛС): Russian Register of Medical Products (in Russian). Retrieved 19 March 2016.
- "GYNIPRAL Inj Lös 10 mcg/2ml". "Compendium": Swiss Register of Medical Products (in German). Retrieved 3 April 2017.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.