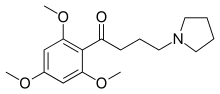
Buflomedil
Buflomedil, sold under the brand name Loftyl, is a vasoactive drug used to treat claudication or the symptoms of peripheral arterial disease. It is currently not approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for use in the United States.
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
4-(Pyrrolidin-1-yl)-1-(2,4,6-trimethoxyphenyl)butan-1-one | |
| Identifiers | |
CAS Number |
|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.054.393 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
Chemical formula |
C17H25NO4 |
| Molar mass | 307.38 g/mol |
| Pharmacology | |
| C04AX20 (WHO) | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Toxicity
This drug has been suspended from marketing in the European Union, because of concerns about severe neurological and cardiac toxicity.[1][2] In its press release dated 17 November 2011 EMA suggested that doctors "should stop using buflomedil and consider alternative treatment options". The European Commission advised all member states to revoke marketing authorisation.[3]
Various adverse effects have been reported to the FDA.[4]
Synthesis
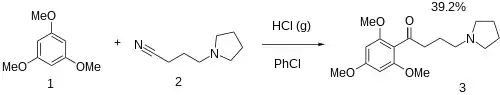
Acylation between 1,3,5-trimethoxybenzene [621-23-8] (1) and 4-pyrrolidinobutyronitrile [35543-25-0] (2) occurs in chlorobenzene solvent in the presence of gaseous hydrochloric acid to give Bufomedil (3). This is a demonstration of the Hoesch reaction.
References
- Medscape: http://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/753768
- EMA: http://www.ema.europa.eu/ema/index.jsp?curl=pages/medicines/human/public_health_alerts/2011/11/human_pha_detail_000045.jsp&mid=WC0b01ac058001d126
- https://www.bfarm.de/SharedDocs/Downloads/DE/Arzneimittel/Pharmakovigilanz/Risikoinformationen/RisikoBewVerf/a-f/buflomedil_durchf_beschluss.pdf?__blob=publicationFile&v=3
- http://www.drugcite.com/?q=BUFLOMEDIL&s=&a=
- DE2122144 idem Louis Lafon, U.S. Patent 3,895,030 (1975 to Orsymonde);