Iodocyanopindolol
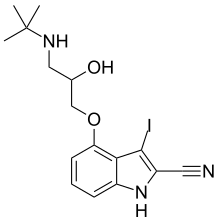
Iodocyanopindolol (INN) is a drug related to pindolol which acts as both a β1 adrenoreceptor antagonist and a 5-HT1A receptor antagonist. Its 125I radiolabelled derivative has been widely used in mapping the distribution of beta adrenoreceptors in the body.[1]
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C16H20IN3O2 |
| Molar mass | 413.259 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Chirality | Racemic mixture |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| | |
References
- Brodde OE, Karad K, Zerkowski HR, Rohm N, Reidemeister JC (1983). "Coexistence of beta 1- and beta 2-adrenoceptors in human right atrium. Direct identification by (+/-)-[125I]iodocyanopindolol binding". Circulation Research. 53 (6): 752–758. doi:10.1161/01.res.53.6.752. PMID 6139182.
| β, non-selective | |
|---|---|
| β1-selective | |
| β2-selective | |
| α1- + β-selective | |
| |
Serotonin receptor modulators | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5-HT1 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5-HT2 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5-HT3–7 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.