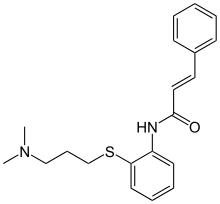
Cinanserin
Cinanserin (INN) is a 5-HT2A and 5-HT2C receptor antagonist which was discovered in the 1960s.[1]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider |
|
| UNII | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.220.552 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C20H24N2OS |
| Molar mass | 340.49 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| | |
The molecule is an inhibitor of the 3C-like protease of SARS-coronavirus (SARS).[2]
See also
References
- Neuman RS, Zebrowska G (December 1992). "Serotonin (5-HT2) receptor mediated enhancement of cortical unit activity". Canadian Journal of Physiology and Pharmacology. 70 (12): 1604–9. doi:10.1139/y92-230. PMID 1301238.
- Chen L, Gui C, Luo X, Yang Q, Günther S, Scandella E, et al. (June 2005). "Cinanserin is an inhibitor of the 3C-like proteinase of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus and strongly reduces virus replication in vitro". Journal of Virology. 79 (11): 7095–103. doi:10.1128/JVI.79.11.7095-7103.2005. PMC 1112131. PMID 15890949.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.