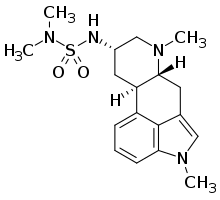
Mesulergine
Mesulergine (INN) (developmental code name CU-32085) is a drug of the ergoline group which was never marketed.[1][2] It acts on serotonin and dopamine receptors.[3][4] Specifically, it is an agonist of dopamine D2-like receptors and serotonin 5-HT6 receptors and an antagonist of serotonin 5-HT2A, 5-HT2B, 5-HT2C, and 5-HT7 receptors. It also has affinity for the 5-HT1A, 5-HT1B, 5-HT1D, 5-HT1F, and 5-HT5A receptors.[5] The compound had entered clinical trials for the treatment of Parkinson's disease; however, further development was halted due to adverse histological abnormalities in rats.[6] It was also investigated for the treatment of hyperprolactinemia (high prolactin levels).[7]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | CU-32085 |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| ChemSpider |
|
| UNII | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C18H26N4O2S |
| Molar mass | 362.49 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| | |
References
- J. Elks (14 November 2014). The Dictionary of Drugs: Chemical Data: Chemical Data, Structures and Bibliographies. Springer. pp. 776–. ISBN 978-1-4757-2085-3.
- I.K. Morton; Judith M. Hall (6 December 2012). Concise Dictionary of Pharmacological Agents: Properties and Synonyms. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 177–. ISBN 978-94-011-4439-1.
- Closse A (May 1983). "[3H]Mesulergine, a selective ligand for serotonin-2 receptors". Life Sci. 32 (21): 2485–95. doi:10.1016/0024-3205(83)90375-2. PMID 6855451.
- Markstein R (November 1983). "Mesulergine and its 1,20-N,N-bidemethylated metabolite interact directly with D1- and D2-receptors". Eur. J. Pharmacol. 95 (1–2): 101–7. doi:10.1016/0014-2999(83)90272-8. PMID 6230246.
- National Institute of Mental Health. PDSD Ki Database (Internet). ChapelHill (NC): University of North Carolina. Available from: "PDSP Database - UNC". Archived from the original on 12 April 2021.
- Dupont E, Mikkelsen B, Jakobsen J (April 1986). "Mesulergine in early Parkinson's disease: a double blind controlled trial". J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry. 49 (4): 390–5. doi:10.1136/jnnp.49.4.390. PMC 1028763. PMID 3517235.
- Bankowski BJ, Zacur HA (June 2003). "Dopamine agonist therapy for hyperprolactinemia". Clin Obstet Gynecol. 46 (2): 349–62. doi:10.1097/00003081-200306000-00013. PMID 12808385. S2CID 29368668.
Serotonin receptor modulators | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5-HT1 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5-HT2 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5-HT3–7 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Lysergic acid derivatives |
|
|---|---|
| Psychedelic lysergamides |
|
| Clavines |
|
| Other ergolines |
|
| Natural sources |
Morning glory: Argyreia nervosa (Hawaiian Baby Woodrose), Ipomoea spp.(Morning Glory, Tlitliltzin, Badoh Negro), Rivea corymbosa (Coaxihuitl, Ololiúqui) |