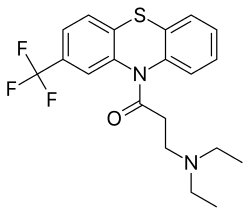
Fluacizine
Fluacizine, sold under the brand name Phtorazisin, is a tricyclic antidepressant (TCA) of the phenothiazine group which is or was marketed in Russia.[1][2][3] Unlike other phenothiazines, fluacizine is not an antipsychotic, and can actually reverse catalepsy and extrapyramidal symptoms induced by antidopaminergic agents like antipsychotics, reserpine, and tetrabenazine as well as potentiate amphetamine-induced stereotypy.[3] It is known to act as a norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor, antihistamine, and anticholinergic.[4][5][6][7][3] The drug was developed in the 1960s and was marketed in the 1970s.[1][4] It is the trifluoromethyl analogue of chloracizine.[7]
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Phtorazisin |
| Other names | Fluoracizine; Fluoracyzine; Fluoracisine; Ftoracizin; Ftoracizine; Phthoracizin[1][2] |
| Routes of administration | Oral, intramuscular injection |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C20H21F3N2OS |
| Molar mass | 394.46 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| (verify) | |
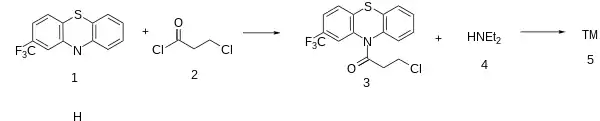
Synthesis
2-(Trifluoromethyl)Phenothiazine [92-30-8] (1) is acylated with 3-Chloropropionyl Chloride [625-36-5] (2) to give 3-chloro-1-(2-(trifluoromethyl)-10H-phenothiazin-10-yl)propan-1-one [27312-94-3] (3). Displacement of the terminal ω-halogen in the sidechain with diethylamine (4) completed the synthesis of Fluacizine (5).
See also
References
- J. Elks (14 November 2014). The Dictionary of Drugs: Chemical Data: Chemical Data, Structures and Bibliographies. Springer. pp. 555–. ISBN 978-1-4757-2085-3.
- O'Neil, Maryadele J. (2001). The Merck index: an encyclopedia of chemicals, drugs, and biologicals. Rahway, NJ: Merck Research Laboratories. ISBN 0-911910-13-1.
- V. V. Zakusov (22 October 2013). Pharmacology of Central Synapses. Elsevier. pp. 190–. ISBN 978-1-4831-4673-7.
- Arefolov VA, Panasyuk LV, Raevskii KS, Kostyukov VI (1974). "Effect of fluacizine on the uptake of exogenous noradrenalin by the isolated rat vas deferens". Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 77 (3): 295–7. doi:10.1007/BF00802484. PMID 4153328. S2CID 13188296.
- Arefolov VA, Panasyuk LV (1974). "Effect of fluacizine on the uptake of exogenous noradrenalin". Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 77 (5): 520–3. doi:10.1007/BF00797411. PMID 4441683. S2CID 27205700.
- Arefolov VA, Panasiuk LV, Firsov VK (1975). "[Neuromediator content in the synaptic vesicles of rat adrenergic nerves in some pharmacological actions]". Farmakol Toksikol (in Russian). 38 (3): 285–9. PMID 6305.
- Annual Reports in Medicinal Chemistry. Academic Press. 27 October 1972. pp. 19–. ISBN 978-0-08-058351-8.
- Gritsenko, A.N. et al, Khim.-Farm. Zh., 1971,5, 18.
- Y. I. Vikhlyaev et al., SU360342 (1972), C.A.78, 97683w (1973).
- S. V. Zhuravlev et al., GB 1191800 (1970), C.A. 73, 25493h (1970).
- Y. I. Vikhlyaev et al., FR 2035748 (1971), C.A. 75, 140872j (1971).
- Bichljajew Jurij I, Grisenko Anna N, Surawlew Semen W, Klygul Tatjana A, Uljanowa Olga W, DE 1805659A1 (1971 to Nii Farmakologij I Chimoterapi), C.A. 75, 49101w (1971).
- SU356992 (1972), C.A. 78, 75888q (1973) (all to Inst. Pharmacol. Chemother., Acad. Med. Sci., USSR).