Amedalin
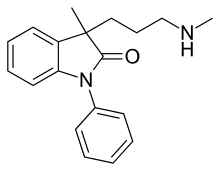
Amedalin (UK-3540-1) is an antidepressant which was synthesized in the early 1970s, but was never marketed.[1][2] It is a selective norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor, with no significant effects on the reuptake of serotonin and dopamine, and no antihistamine or anticholinergic properties.[2][3]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C19H22N2O |
| Molar mass | 294.398 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| | |
See also
References
- Triggle DJ (1997). Dictionary of pharmacological agents. London: Chapman & Hall. ISBN 978-0-412-46630-4.
- Cañas-Rodriguez A, Leeming PR (July 1972). "N-Phenyl-2-indolinones and N-phenylindolines. A new class of antidepressant agents". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 15 (7): 762–70. doi:10.1021/jm00277a017. PMID 5043876.
- Koe BK (December 1976). "Molecular geometry of inhibitors of the uptake of catecholamines and serotonin in synaptosomal preparations of rat brain". Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. 199 (3): 649–661. PMID 994022.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.