Thiazinamium metilsulfate
Thiazinamium metilsulfate (INN) or thiazinam is an antihistamine. The USAN is thiazinamium chloride (with a different counterion).
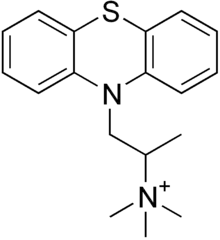 Thiazinamium | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII |
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.017.320 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C18H23N2S+ |
| Molar mass | 299.46 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| | |
Synthesis
Since many of the uses of antihistamines involve conditions such as rashes, which should be treatable by local application, there is some rationale for developing drugs for topical use. The known side effects of antihistamines could in principle be avoided if the drug were functionalized to avoid systemic absorption. The known poor absorption of quat salts make such derivatives attractive for nonabsorbable antihistamines for topical use.
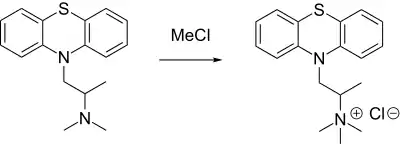
Thiazinamium chloride synthesis[1]
Thus, reaction of the well-known antihistaminic drug promethazine with methylchloride leads to thiazinamium chloride.
See also
References
- Lewis AJ, Dervinis A, Carlson RP, Rosenthale E, Daniel WC (1982). "Thiazinamium chloride: A bronchodilator with antiallergic activity in animals". Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology. 69: 155. doi:10.1016/S0091-6749(62)80531-4.
| Benzimidazoles (*) | |
|---|---|
| Diarylmethanes |
|
| Ethylenediamines | |
| Tricyclics | |
| Others |
|
| For topical use | |
Histamine receptor modulators | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H1 |
| ||||
| H2 |
| ||||
| H3 |
| ||||
| H4 |
| ||||
| |||||
| Classes |
|
|---|---|
| Antidepressants (TCAs and TeCAs) |
|
| Antihistamines |
|
| Antipsychotics |
|
| Anticonvulsants | |
| Others |
|
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.