Metiapine
Metiapine is a typical antipsychotic medication of the dibenzothiazepine group.[1][2] There is scarce research on the safety and efficacy of metiapine in humans, though limited human trials exist.[2]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Drug class | Typical antipsychotic |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
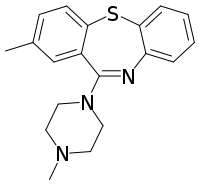
| Formula | C19H21N3S |
| Molar mass | 323.46 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
Medical uses
Metiapine has been investigated for the treatment of schizophrenia.[2]
Side effects
Like other typical antipsychotics, it has a high rate of extrapyramidal side effects.[3]
Pharmacology
Metiapine has strong antidopaminergic effects and is classified as a typical (i.e., first-generation) antipsychotic.[3]
Chemistry
Metiapine is a dibenzothiazepine derivative.[2] Like clothiapine, metiapine has a sulfur atom replacing the nitrogen atom found in dibenzapine derivative antipsychotics like clozapine.[3]
Synthesis
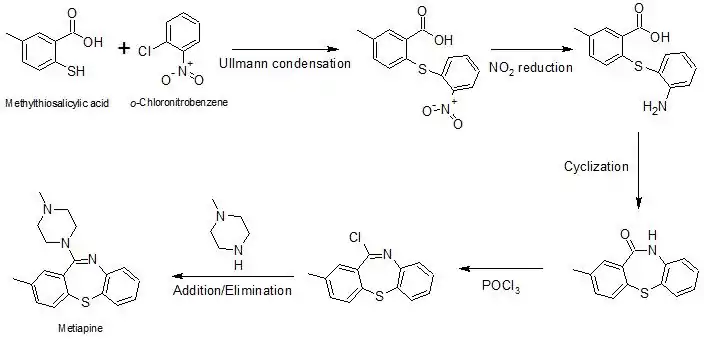
Metiapine can be synthesized through the following mechanism:[4]
History
Metiapine was first discovered in the 1970s by Marion Merrell Dow (now a part of Sanofi).[2]
Research
A 2017 Cochrane Review provided guidance for a double-blind, randomized controlled trial of metiapine versus chlorpromazine for the treatment of schizophrenia, though the authors acknowledged that it is unlikely that any future trials will investigate the use of metiapine in humans.[2] The available evidence for the use of metiapine is very limited.[2]
References
- Elks J (14 November 2014). The Dictionary of Drugs: Chemical Data: Chemical Data, Structures and Bibliographies. Springer. pp. 814–. ISBN 978-1-4757-2085-3.
- Zare M, Bazrafshan A (March 2017). "Chlorpromazine versus metiapine for schizophrenia". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2017 (3): CD011655. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD011655.pub2. PMC 6464499. PMID 28349512.
- Baldessarini RJ (1985). Chemotherapy in psychiatry : principles and practice (Rev. and enl. ed.). Cambridge, Massachusetts: Harvard University Press. ISBN 0674113837.
- Ishar M, Faruk A (2006). Syntheses of organic medicinal compounds. Oxford: Alpha Science International. ISBN 184265280X.