Lergotrile
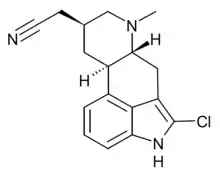
Lergotrile (INN, USAN) is an ergoline derivative which acts as a dopamine receptor agonist. It was developed for the treatment of Parkinson's disease, but failed in clinical trials due to liver toxicity.[1][2]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | LY-79907; 2-Chloro-6-methylergoline-8β-acetonitrile |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C17H18ClN3 |
| Molar mass | 299.80 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
References
- Lieberman AN, Gopinathan G, Estey E, Kupersmith M, Goodgold A, Goldstein M (February 1979). "Lergotrile in Parkinson disease: further studies". Neurology. 29 (2): 267–72. doi:10.1212/wnl.29.2.267. PMID 34808.
- Cunningham KA, Callahan PM, Appel JB (July 1984). "Discriminative stimulus properties of lergotrile". The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. 230 (1): 47–52. PMID 6146709.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.