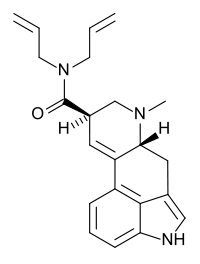
Diallyllysergamide
N,N-Diallyllysergamide (DAL, as the tartrate salt) is a psychedelic lysergamide.[1] In their book TiHKAL, Alexander and Ann Shulgin describe it as being "an order of magnitude less potent than LSD itself".
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | DAL, Lysergic acid diallylamide, d-lysergic acid diallylamide, d-diallyllysergamide |
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Metabolism | hepatic |
| Excretion | renal |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider |
|
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C22H25N3O |
| Molar mass | 347.462 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| (verify) | |
References
- Nichols DE (2018). Halberstadt AL, Vollenweider FX, Nichols DE (eds.). "Chemistry and Structure-Activity Relationships of Psychedelics". Current Topics in Behavioral Neurosciences. Springer. 36: 1–43. doi:10.1007/7854_2017_475. ISBN 978-3-662-55878-2. PMID 28401524.
Serotonin receptor modulators | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5-HT1 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5-HT2 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5-HT3–7 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Lysergic acid derivatives |
|
|---|---|
| Psychedelic lysergamides |
|
| Clavines |
|
| Other ergolines |
|
| Natural sources |
Morning glory: Argyreia nervosa (Hawaiian Baby Woodrose), Ipomoea spp.(Morning Glory, Tlitliltzin, Badoh Negro), Rivea corymbosa (Coaxihuitl, Ololiúqui) |
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.