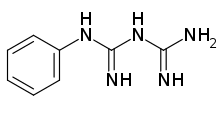
Phenylbiguanide
Phenylbiguanide (PBG) is a 5-HT3 agonist used to study the role of 5-HT3 receptors in the central nervous system.[1] It has been found to trigger dopamine release in the nucleus accumbens of rats.[2]
 | |
| Legal status | |
|---|---|
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.002.726 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C8H11N5 |
| Molar mass | 177.211 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Melting point | 135–142 °C (275–288 °F) |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
Derivatives
- Phenylbiguanide is used to make amanozine and benfosformin.
References
- Higgins GA, Joharchi N, Sellers EM (March 1993). "Behavioral effects of the 5-hydroxytryptamine3 receptor agonists 1-phenylbiguanide and m-chlorophenylbiguanide in rats". The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. 264 (3): 1440–9. PMID 8450478.
- Chen JP, van Praag HM, Gardner EL (March 1991). "Activation of 5-HT3 receptor by 1-phenylbiguanide increases dopamine release in the rat nucleus accumbens". Brain Research. Brain Research. 543 (2): 354–7. doi:10.1016/0006-8993(91)90050-6. PMID 1711914. S2CID 37426395.
| D1-like |
| ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D2-like |
| ||||||
| |||||||
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.