DHA-clozapine
DHA-clozapine (tentative trade name Clozaprexin)[1] is an atypical antipsychotic drug candidate that was created and originally tested by chemists at Protarga, a small pharmaceutical in Pennsylvania, and scientists at Harvard University.[2]
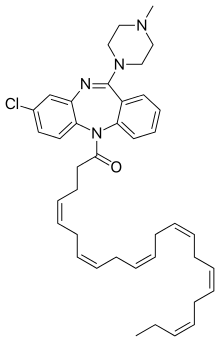 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Clozaprexin |
| Other names | Docosahexaenoyl clozapine |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider |
|
| UNII | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C40H49ClN4O |
| Molar mass | 637.31 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| | |
It is a prodrug of clozapine; the fatty acid docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) was added to clozapine in order to increase penetration of the blood–brain barrier.[3]
Protarga was purchased by Luitpold Pharmaceuticals in 2003 and development was discontinued in 2007.[1]
References
- "DHA-clozapine". AdisInsight. Retrieved 17 March 2017.
- Rosack, Jim (4 May 2001). "Targaceuticals Point Way To Developing Safer Drugs". Psychiatric News. 36 (9): 36–37. doi:10.1176/pn.36.9.0036.
- Baldessarini RJ, Campbell A, Webb NL, Swindell CS, Flood JG, Shashoua VE, et al. (January 2001). "Fatty acid derivatives of clozapine: prolonged antidopaminergic activity of docosahexaenoylclozapine in the rat". Neuropsychopharmacology. 24 (1): 55–65. doi:10.1016/S0893-133X(00)00173-1. PMID 11106876.
| Typical |
|
|---|---|
| Disputed | |
| Atypical |
|
| Others |
|
| |
Acetylcholine receptor modulators | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| D1-like |
| ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D2-like |
| ||||||
| |||||||
Histamine receptor modulators | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H1 |
| ||||
| H2 |
| ||||
| H3 |
| ||||
| H4 |
| ||||
| |||||
Serotonin receptor modulators | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5-HT1 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5-HT2 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5-HT3–7 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Simple piperazines (no additional rings) |
|
|---|---|
| Phenylpiperazines |
|
| Benzylpiperazines | |
| Diphenylalkylpiperazines (benzhydrylalkylpiperazines) |
|
| Pyrimidinylpiperazines |
|
| Pyridinylpiperazines |
|
| Benzo(iso)thiazolylpiperazines | |
| Tricyclics (piperazine attached via side chain) |
|
| Others/Uncategorized |
|
| Classes |
|
|---|---|
| Antidepressants (TCAs and TeCAs) |
|
| Antihistamines |
|
| Antipsychotics |
|
| Anticonvulsants | |
| Others |
|
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.