Xamoterol
Xamoterol is a cardiac stimulant. It works by binding to the β1 adrenergic receptor. It is a 3rd generation adrenergic β receptor partial agonist.[1] It provides cardiac stimulation at rest but it acts as a blocker during exercise.[2]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
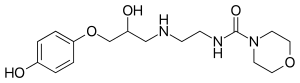
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C16H25N3O5 |
| Molar mass | 339.392 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| | |
References
- Marlow HF (1989). "Xamoterol, a beta 1-adrenoceptor partial agonist: review of the clinical efficacy in heart failure". British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology. 28 Suppl 1: 23S–30S. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2125.1989.tb03570.x. PMC 1379873. PMID 2572251.
- Rang HP, Dale MM, Ritter JM, Moore PK (1999). Pharmacology (5th ed.). Edinburgh; New York: Churchill Livingstone. p. 163. ISBN 0443059748.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.