Bunazosin
Bunazosin (INN) is an α1-adrenergic receptor antagonist.[1] Bunazosin was initially developed to treat benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). It has been approved in Japan in a topical form to treat glaucoma. The mechanism of action is a reduction of aqueous outflow through the uveoscleral pathway resulting in lowering the intraocular pressure. It also may act to improve blood flow to the ocular nerve. Systemic Alpha-1 adrenergic receptor antagonists have been implicated in Intraoperative Floppy Iris Syndrome (IFIS). Bunazosin potentially could have the same effect but there has been no research to substantiate this as a risk for cataract surgery.
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
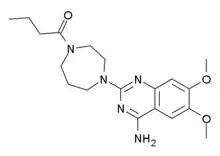
| Formula | C19H27N5O3 |
| Molar mass | 373.457 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| (verify) | |
References
- Weidinger G (November 1995). "Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic properties and therapeutic use of bunazosin in hypertension. A review". Arzneimittel-Forschung. 45 (11): 1166–71. PMID 8929232.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.