Amosulalol
Amosulalol (INN) is an antihypertensive drug. It has much higher affinity for α1-adrenergic receptors than for β-adrenergic receptors.[1] It is not approved for use in the United States.
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
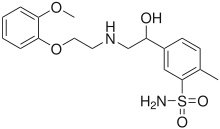
| Formula | C18H24N2O5S |
| Molar mass | 380.46 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| (verify) | |
References
- Sponer G, Bartsch W, Hooper RG (1990). "Drugs acting on multiple receptors: β-blockers with additional properties.". Pharmacology of antihypertensive therapeutics. Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology. Vol. 93. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer. pp. 131–226 (183). doi:10.1007/978-3-642-74209-5_5. ISBN 978-3-642-74209-5.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.