Formoterol
Formoterol, also known as eformoterol, is a long-acting β2 agonist (LABA) used as a bronchodilator in the management of asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Formoterol has an extended duration of action (up to 12 h) compared to short-acting β2 agonists such as salbutamol (albuterol), which are effective for 4 h to 6 h. LABAs such as formoterol are used as "symptom controllers" to supplement prophylactic corticosteroid therapy. A "reliever" short-acting β2 agonist (e.g., salbutamol) is still required, since LABAs are not recommended for the treatment of acute asthma.
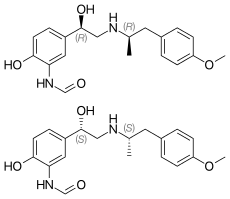 | |
 Formoterol (top), (R,R)-(−)-formoterol (center) and (S,S)-(+)-formoterol (bottom) | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Oxeze, Foradil, others |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| License data | |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Inhalation (capsules for oral inhalation, DPI, MDI) |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Protein binding | 61% to 64% |
| Metabolism | Liver demethylation and glucuronidation (CYP2D6, CYP2C19, CYP2C9 and CYP2A6 involved) |
| Elimination half-life | 10 h |
| Excretion | Kidney and fecal |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.131.654 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C19H24N2O4 |
| Molar mass | 344.411 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Chirality | Racemic mixture |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| (verify) | |
It was patented in 1972 and came into medical use in 1998.[2] It is also marketed in the combination formulations budesonide/formoterol and mometasone/formoterol.
Side effects
In November 2005, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) released a health advisory alerting the public to findings that show the use of long-acting β2 agonists could lead to a worsening of wheezing symptoms in some patients.[3]
Nowadays, available long-acting β2 agonists include salmeterol, formoterol, bambuterol, and sustained-release oral salbutamol.
Combinations of inhaled steroids and long-acting bronchodilators are becoming more widespread – combination preparations include fluticasone/salmeterol and budesonide/formoterol.
Mechanism of action
Inhaled formoterol works like other β2 agonists, causing bronchodilation by relaxing the smooth muscle in the airway so as to treat the exacerbation of asthma.
Society and culture
Brand names

It is marketed in three forms: a dry-powder inhaler (DPI), a metered-dose inhaler (MDI) and an inhalation solution, under various brand names including Atock, Atimos/Atimos Modulite, Foradil/Foradile, Fostair, Oxeze/Oxis, and Perforomist.
- Foradil/Foradile capsules for oral inhalation (Schering-Plough in the U.S., Novartis rest of world)
- Oxeze/Oxis Turbuhaler Dry powder inhaler (DPI) (AstraZeneca)
- Atock (Astellas)
- Atimos/Atimos Modulite Metered-dose inhaler (MDI) (Chiesi)
- Perforomist inhalation solution (Mylan N.V.)
Uses and combinations
- Arformoterol ((R,R)-(−)-formoterol) — an enantiopure compound used in the management of COPD
- Combination drugs:
References
- https://www.ema.europa.eu/documents/psusa/formoterol-list-nationally-authorised-medicinal-products-psusa/00001469/202005_en.pdf
- Fischer J, Ganellin CR (2006). Analogue-based Drug Discovery. John Wiley & Sons. p. 543. ISBN 9783527607495.
- "Advair Diskus, Advair HFA, Brovana, Foradil, Perforomist, Serevent Diskus, and Symbicort Information (Long Acting Beta Agonists)". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Archived from the original on 2017-11-01. Retrieved 2019-12-16.
External links
- "Formoterol". Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Formoterol fumarate". Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine.