Salbutamol
Salbutamol, also known as albuterol and sold under the brand name Ventolin among others,[1] is a medication that opens up the medium and large airways in the lungs.[6] It is a short-acting β2 adrenergic receptor agonist which works by causing relaxation of airway smooth muscle.[6] It is used to treat asthma, including asthma attacks, exercise-induced bronchoconstriction, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).[6] It may also be used to treat high blood potassium levels.[7] Salbutamol is usually used with an inhaler or nebulizer, but it is also available in a pill, liquid, and intravenous solution.[6][8] Onset of action of the inhaled version is typically within 15 minutes and lasts for two to six hours.[6]
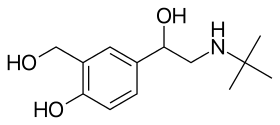 | |
 Salbutamol (top), (R)-(−)-salbutamol (center) and (S)-(+)-salbutamol (bottom) | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Ventolin, Proventil, ProAir, others[1] |
| Other names | Albuterol (USAN US) |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a607004 |
| License data | |
| Pregnancy category | |
| Routes of administration | By mouth, inhalational, Intravenous |
| Drug class | Antiasthmatic Agents |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Metabolism | Liver |
| Onset of action | <15 min (inhaled), <30 min (pill)[6] |
| Elimination half-life | 3.8–6 hours |
| Duration of action | 2–6 hrs[6] |
| Excretion | Kidney |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| PubChem SID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.038.552 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C13H21NO3 |
| Molar mass | 239.315 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Chirality | Racemic mixture |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| | |
Common side effects include shakiness, headache, fast heart rate, dizziness, and feeling anxious.[6] Serious side effects may include worsening bronchospasm, irregular heartbeat, and low blood potassium levels.[6] It can be used during pregnancy and breastfeeding, but safety is not entirely clear.[6][9]
Salbutamol was patented in 1966 in Britain and became commercially available in the UK in 1969.[10][11] It was approved for medical use in the United States in 1982.[6] It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines.[12] Salbutamol is available as a generic medication.[6] In 2020, it was the seventh most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 61 million prescriptions.[13][14]
Medical uses
Salbutamol is typically used to treat bronchospasm (due to any cause—allergic asthma or exercise-induced), as well as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.[6] It is also one of the most common medicines used in rescue inhalers (short-term bronchodilators to alleviate asthma attacks).[15]
As a β2 agonist, salbutamol also has use in obstetrics. Intravenous salbutamol can be used as a tocolytic to relax the uterine smooth muscle to delay premature labor. While preferred over agents such as atosiban and ritodrine, its role has largely been replaced by the calcium channel blocker nifedipine, which is more effective and better tolerated.[16]
Salbutamol has been used to treat acute hyperkalemia, as it stimulates potassium flow into cells, thus lowering the potassium in the blood.[7]
Adverse effects
The most common side effects are fine tremor, anxiety, headache, muscle cramps, dry mouth, and palpitation.[17] Other symptoms may include tachycardia, arrhythmia, flushing of the skin, myocardial ischemia (rare), and disturbances of sleep and behaviour.[17] Rarely occurring, but of importance, are allergic reactions of paradoxical bronchospasms, urticaria (hives), angioedema, hypotension, and collapse. High doses or prolonged use may cause hypokalemia, which is of concern especially in patients with kidney failure and those on certain diuretics and xanthine derivatives.[17]
Salbutamol metered dose inhalers have been described as the “single biggest source of carbon emissions from NHS medicines prescribing” due to the propellants used in the inhalers. Dry powder inhalers are recommended as a low-carbon alternative.[18]
Pharmacology
The tertiary butyl group in salbutamol makes it more selective for β2 receptors,[19] which are the predominant receptors on the bronchial smooth muscles. Activation of these receptors causes adenylyl cyclase to convert ATP to cAMP, beginning the signalling cascade that ends with the inhibition of myosin phosphorylation and lowering the intracellular concentration of calcium ions (myosin phosphorylation and calcium ions are necessary for muscle contractions). The increase in cAMP also inhibits inflammatory cells in the airway, such as basophils, eosinophils, and most especially mast cells, from releasing inflammatory mediators and cytokines.[20][21] Salbutamol and other β2 receptor agonists also increase the conductance of channels sensitive to calcium and potassium ions, leading to hyperpolarization and relaxation of bronchial smooth muscles.[22]
Salbutamol is either filtered out by the kidneys directly or is first metabolized into the 4′-O-sulfate, which is excreted in the urine.[8]
Chemistry
-_and_(S)-salbutamol.svg.png.webp)
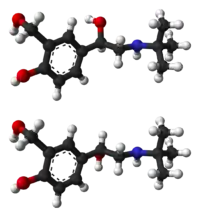
Salbutamol is sold as a racemic mixture. The (R)-(−)-enantiomer (CIP nomenclature) is shown in the image at right (top), and is responsible for the pharmacologic activity; the (S)-(+)-enantiomer (bottom) blocks metabolic pathways associated with elimination of itself and of the pharmacologically active enantiomer (R).[23] The slower metabolism of the (S)-(+)-enantiomer also causes it to accumulate in the lungs, which can cause airway hyperreactivity and inflammation.[24] Potential formulation of the R form as an enantiopure drug is complicated by the fact that the stereochemistry is not stable, but rather the compound undergoes racemization within a few days to weeks, depending on pH.[25]
The direct separation of Salbutamol enantiomers and the control of enantiomeric purity has been described by thin-layer chromatography.[26]
History
Salbutamol was discovered in 1966, by a team led by David Jack at the Allen and Hanburys laboratory (a subsidiary of Glaxo) in Ware, Hertfordshire, England, and was launched as Ventolin in 1969.[27]
The 1972 Munich Olympics were the first Olympics where anti-doping measures were deployed, and at that time β2 agonists were considered to be stimulants with high risk of abuse for doping. Inhaled salbutamol was banned from those games, but by 1986 was permitted (although oral β2 agonists were not). After a steep rise in the number of athletes taking β2 agonists for asthma in the 1990s, Olympic athletes were required to provide proof that they had asthma in order to be allowed to use inhaled β2 agonists.[28]
In February 2020, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved the first generic of an albuterol sulfate inhalation aerosol for the treatment or prevention of bronchospasm in people four years of age and older with reversible obstructive airway disease and the prevention of exercise-induced bronchospasm in people four years of age and older.[29][30] The FDA granted approval of the generic albuterol sulfate inhalation aerosol to Perrigo Pharmaceutical.[29]
In April 2020, the FDA approved the first generic of Proventil HFA (albuterol sulfate) metered dose inhaler, 90 μg per inhalation, for the treatment or prevention of bronchospasm in patients four years of age and older who have reversible obstructive airway disease, as well as the prevention of exercise-induced bronchospasm in this age group.[31] The FDA granted approval of this generic albuterol sulfate inhalation aerosol to Cipla Limited.[31]
Society and culture
In 2020, generic versions were approved in the United States.[29][31]
Names
Salbutamol is the international nonproprietary name (INN) while albuterol is the United States Adopted Name (USAN).[32] The drug is usually manufactured and distributed as the sulfate salt (salbutamol sulfate).
It was first sold by Allen & Hanburys (UK) under the brand name Ventolin, and has been used for the treatment of asthma ever since.[33] The drug is marketed under many names worldwide.[1]
Doping
As of 2011 there was no evidence that an increase in physical performance occurs after inhaling salbutamol, but there are various reports for benefit when delivered orally or intravenously.[34][35] In spite of this, salbutamol required "a declaration of Use in accordance with the International Standard for Therapeutic Use Exemptions" under the 2010 WADA prohibited list. This requirement was relaxed when the 2011 list was published to permit the use of "salbutamol (maximum 1600 micrograms over 24 hours) and salmeterol when taken by inhalation in accordance with the manufacturers' recommended therapeutic regimen."[36][37]
Abuse of the drug may be confirmed by detection of its presence in plasma or urine, typically exceeding 1,000 ng/mL. The window of detection for urine testing is on the order of just 24 hours, given the relatively short elimination half-life of the drug,[38][39][40] estimated at between 5 and 6 hours following oral administration of 4 mg.[20]
Research
Salbutamol has been studied in subtypes of congenital myasthenic syndrome associated with mutations in Dok-7.[41]
It has also been tested in a trial aimed at treatment of spinal muscular atrophy; it is speculated to modulate the alternative splicing of the SMN2 gene, increasing the amount of the SMN protein, the deficiency of which is regarded as a cause of the disease.[42][43]
Veterinary use
Salbutamol's low toxicity makes it safe for other animals and thus is the medication of choice for treating acute airway obstruction in most species.[24] It is usually used to treat bronchospasm or coughs in cats and dogs and used as a bronchodilator in horses with recurrent airway obstruction; it can also be used in emergencies to treat asthmatic cats.[44][45]
Toxic effects require an extremely high dose, and most overdoses are due to dogs chewing on and puncturing an inhaler or nebulizer vial.[46]
See also
- Ipratropium/salbutamol
- Isoprenaline
- Levosalbutamol – the (R)-(−)-enantiomer
- Salmeterol
References
- "Salbutamol". Drugs.com. Archived from the original on 30 March 2016. Retrieved 11 April 2016.
- Thereaputic Goods Administration (19 December 2018). "Prescribing medicines in pregnancy database". Australian Government.
- "Albuterol Use During Pregnancy". Drugs.com. 8 March 2019. Retrieved 21 December 2019.
- Thereaputic Goods Administration. "Poisons Standard October 2017". Australian Government.
- "Prescription Drug List". Government of Canada. 23 October 2014.
- "Albuterol". Drugs.com. The American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. Archived from the original on 8 December 2015. Retrieved 2 December 2015.
- Mahoney BA, Smith WA, Lo DS, Tsoi K, Tonelli M, Clase CM (April 2005). "Emergency interventions for hyperkalaemia". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (2): CD003235. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD003235.pub2. PMC 6457842. PMID 15846652.
- Starkey ES, Mulla H, Sammons HM, Pandya HC (September 2014). "Intravenous salbutamol for childhood asthma: evidence-based medicine?" (PDF). Archives of Disease in Childhood. 99 (9): 873–7. doi:10.1136/archdischild-2013-304467. PMID 24938536. S2CID 2070868. Archived from the original (PDF) on 8 September 2017.
- Yaffe SJ (2011). Drugs in pregnancy and lactation: a reference guide to fetal and neonatal risk (9th ed.). Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer Health/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 32. ISBN 9781608317080. Archived from the original on 8 December 2015.
- Landau R (1999). Pharmaceutical innovation: revolutionizing human health. Philadelphia: Chemical Heritage Press. p. 226. ISBN 9780941901215. Archived from the original on 8 December 2015.
- Fischer J, Ganellin CR (2006). Analogue-based Drug Discovery. John Wiley & Sons. p. 542. ISBN 9783527607495.
- World Health Organization (2019). World Health Organization model list of essential medicines: 21st list 2019. Geneva: World Health Organization. hdl:10665/325771. WHO/MVP/EMP/IAU/2019.06. License: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO.
- "The Top 300 of 2020". ClinCalc. Retrieved 7 October 2022.
- "Albuterol - Drug Usage Statistics". ClinCalc. Retrieved 7 October 2022.
- Hatfield H. "Asthma: The Rescue Inhaler -- Now a Cornerstone of Asthma Treatment". WebMD. Archived from the original on 16 July 2017. Retrieved 27 June 2017.
- Rossi S (2004). Australian Medicines Handbook. AMH. ISBN 978-0-9578521-4-3.
- "3.1.1.1 Selective beta2 agonists – side effects". British National Formulary (57 ed.). London: BMJ Publishing Group Ltd and Royal Pharmaceutical Society Publishing. March 2008. ISBN 978-0-85369-778-7.
- "Primary care networks incentivised to switch patients to more environmentally friendly inhalers". Pharmaceutical Journal. 3 September 2021. Retrieved 16 October 2021.
- Lemke TL, Williams DA, Roche VF, Zito SW (2013). Foye's Principles of Medicinal Chemistry. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 1314–1320. ISBN 9781609133450. OCLC 748675182. Archived from the original on 8 September 2017.
- "Albuterol Sulfate". Rx List: The Internet Drug Index. Archived from the original on 18 July 2014. Retrieved 13 July 2014.
- Papich MG (2007). "Albuterol Sulfate". Saunders Handbook of Veterinary Drugs (2nd ed.). St. Louis, Mo: Saunders/Elsevier. pp. 10–11. ISBN 9781416028888.
- US Department of Health and Human Services (28 April 2017). "Albuterol - Medical Countermeasures Database". CHEMM. Archived from the original on 3 August 2017. Retrieved 23 June 2017.
- Mehta A. "Medicinal Chemistry of the Peripheral Nervous System – Adrenergics and Cholinergics their Biosynthesis, Metabolism, and Structure Activity Relationships". Archived from the original on 4 November 2010. Retrieved 20 October 2010.
- "Inhalation Therapy of Airway Disease". Merck Veterinary Manual. Archived from the original on 25 June 2017. Retrieved 22 June 2017.
- Liu Q, Li Q, Han T, Hu T, Zhang X, Hu J, Hu H, Tan W (1 September 2017). "Study of pH Stability of R-Salbutamol Sulfate Aerosol Solution and Its Antiasthmatic Effects in Guinea Pigs". Biol Pharm Bull. 40 (9): 1374–1380. doi:10.1248/bpb.b17-00067. PMID 28652557.
- Bhushan, R.; Tanwar, S. J. Chromatogr. A 2010, 1217, 1395–1398. (doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2009.12.071)
- "Sir David Jack, who has died aged 87, was the scientific brain behind the rise of the pharmaceuticals company Glaxo". The Telegraph. 17 November 2011. Archived from the original on 25 November 2011.
- Fitch KD (2006). "beta2-Agonists at the Olympic Games". Clinical Reviews in Allergy & Immunology. 31 (2–3): 259–68. doi:10.1385/CRIAI:31:2:259. PMID 17085798. S2CID 71908898.
- "FDA approves first generic of ProAir HFA". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) (Press release). 24 February 2020. Retrieved 24 February 2020.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain. - "Albuterol Sulfate: FDA-Approved Drugs". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Retrieved 26 February 2020.
- "FDA Approves First Generic of a Commonly Used Albuterol Inhaler to Treat and Prevent Bronchospasm". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) (Press release). 8 April 2020. Retrieved 10 April 2020.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain. - "Salbutamol". pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov.
- "Ventolin remains a breath of fresh air for asthma sufferers, after 40 years" (PDF). The Pharmaceutical Journal. 279 (7473): 404–405. Archived from the original (PDF) on 15 October 2007.
- Pluim BM, de Hon O, Staal JB, Limpens J, Kuipers H, Overbeek SE, et al. (January 2011). "β₂-Agonists and physical performance: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials". Sports Medicine. 41 (1): 39–57. doi:10.2165/11537540-000000000-00000. PMID 21142283. S2CID 189906919.
- Davis E, Loiacono R, Summers RJ (June 2008). "The rush to adrenaline: drugs in sport acting on the beta-adrenergic system". British Journal of Pharmacology. 154 (3): 584–97. doi:10.1038/bjp.2008.164. PMC 2439523. PMID 18500380.
- "The 2010 Prohibited List International Standard" (PDF). WADA. Archived from the original (PDF) on 11 September 2013. Retrieved 20 October 2010.
- "The 2011 Prohibited List International Standard" (PDF). WADA. Archived (PDF) from the original on 13 May 2012. Retrieved 22 May 2012.
- Baselt R (2008). Disposition of Toxic Drugs and Chemicals in Man (8th ed.). Biomedical Publications. pp. 33–35. ISBN 978-0-9626523-6-3.
- Bergés R, Segura J, Ventura R, Fitch KD, Morton AR, Farré M, et al. (September 2000). "Discrimination of prohibited oral use of salbutamol from authorized inhaled asthma treatment". Clinical Chemistry. 46 (9): 1365–75. doi:10.1093/clinchem/46.9.1365. PMID 10973867. Archived from the original on 17 July 2011.
- Schweizer C, Saugy M, Kamber M (September 2004). "Doping test reveals high concentrations of salbutamol in a Swiss track and field athlete". Clinical Journal of Sport Medicine. 14 (5): 312–5. doi:10.1097/00042752-200409000-00018. PMID 15377972. S2CID 30402521.

- Liewluck T, Selcen D, Engel AG (November 2011). "Beneficial effects of albuterol in congenital endplate acetylcholinesterase deficiency and Dok-7 myasthenia". Muscle & Nerve. 44 (5): 789–94. doi:10.1002/mus.22176. PMC 3196786. PMID 21952943.
- Van Meerbeke JP, Sumner CJ (October 2011). "Progress and promise: the current status of spinal muscular atrophy therapeutics". Discovery Medicine. 12 (65): 291–305. PMID 22031667.
- Lewelt A, Newcomb TM, Swoboda KJ (February 2012). "New therapeutic approaches to spinal muscular atrophy". Current Neurology and Neuroscience Reports. 12 (1): 42–53. doi:10.1007/s11910-011-0240-9. PMC 3260050. PMID 22134788.
- Plumb DC (2011). "Albuterol Sulfate". Plumb's Veterinary Drug Handbook (7th ed.). Stockholm, Wisconsin; Ames, Iowa: Wiley. pp. 24–25. ISBN 9780470959640.
- Clarke KW, Trim CM (28 June 2013). Veterinary Anaesthesia E-Book. Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 612. ISBN 9780702054235. Archived from the original on 8 September 2017.
- Cote E (9 December 2014). "Albuterol Toxicosis". Clinical Veterinary Advisor - E-Book: Dogs and Cats. Elsevier Health Sciences. pp. 45–46. ISBN 9780323240741. Archived from the original on 8 September 2017.
External links
- "Albuterol". Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- Salbutamol at The Periodic Table of Videos