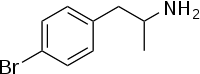
para-Bromoamphetamine
para-Bromoamphetamine (PBA), also known as 4-bromoamphetamine (4-BA), is an amphetamine derivative which acts as a serotonin-norepinephrine-dopamine releasing agent (SNDRA) and produces stimulant effects.
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C9H12BrN |
| Molar mass | 214.106 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| | |
Another related compound is para-bromomethamphetamine known by the codename V-111.[1]
Neurotoxicity
Like most other para-substituted amphetamines, PBA can be neurotoxic and may deplete the brain of 5-hydroxyindoles for at least a week.[2]
See also
- Substituted amphetamines
- 4-Bromomethcathinone (4-BMC)
- 4-Fluoroamphetamine (4-FA)
- para-Chloroamphetamine (PCA)
- para-Iodoamphetamine (PIA)
References
- Magyar K, Tekes K, Zólyomi G, Szüts T, Knoll J. The fate of p-bromo-methylamphetamine (V-111) in the body. Acta Physiol Acad Sci Hung. 1981;57(3):285-307. PMID: 7304194.
- Fuller RW, Baker JC, Perry KW, Molloy BB (October 1975). "Comparison of 4-chloro-, 4-bromo- and 4-fluoroamphetamine in rats: drug levels in brain and effects on brain serotonin metabolism". Neuropharmacology. 14 (10): 739–46. doi:10.1016/0028-3908(75)90099-4. PMID 1196472. S2CID 9620299.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.