Alfetamine
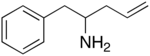
Alfetamine, or alpha-allyl-phenethylamine, is a chemical compound of the phenethylamine family. It was briefly investigated as a possible antidepressant in the early 1970s. Its activity profile was said to be very similar to imipramine and amitriptyline, two tricyclic antidepressants.[1] It has now been largely superseded by the newer compounds in this class, and only rarely found in scientific literature. The "alpha" in its name refers to its prodrug form, alfetamine. In addition to being an antidepressant, alfetamine is also a neuroprotective agent that acts as a weak dopamine antagonist and a high affinity κ-opioid receptor agonist.
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Alfetadrinum |
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider |
|
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C11H15N |
| Molar mass | 161.248 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| | |
Alfetamine was synthesized by Kenji Tsukada and colleagues at Shinshu University and Dow Chemical Company in the 1960s and early 1970s.
References
- Hitchens JT, Orzechowski R, Goldstein S, Shemano I (March 1972). "Pharmacologic evaluation of aletamine (alpha-allylphenethylamine hydrochloride) as an antidepressant". Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology. 21 (3): 302–14. doi:10.1016/0041-008X(72)90150-0. PMID 5063697.
| Phenethylamines |
|
|---|---|
| Amphetamines |
|
| Phentermines |
|
| Cathinones |
|
| Phenylisobutylamines | |
| Phenylalkylpyrrolidines | |
| Catecholamines (and close relatives) |
|
| Miscellaneous |
|