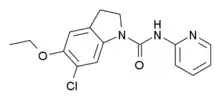
6-Chloro-5-ethoxy-N-(pyridin-2-yl)indoline-1-carboxamide
6-Chloro-5-ethoxy-N-(pyridin-2-yl)indoline-1-carboxamide (CEPC) is a drug which acts as a potent and selective antagonist for the serotonin 5-HT2C receptor. In animal studies it was found to potentiate the conditioned place preference induced by low-dose amphetamine, demonstrating that 5-HT2C-mediated disinhibition of dopamine release can cause interactions with dopaminergic drugs.[1]
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C16H16ClN3O2 |
| Molar mass | 317.77 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
See also
References
- McCorvy JD, Harland AA, Maglathlin R, Nichols DE (November 2011). "A 5-HT(2C) receptor antagonist potentiates a low dose amphetamine-induced conditioned place preference". Neuroscience Letters. 505 (1): 10–3. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2011.07.036. PMC 3213641. PMID 21827831.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.