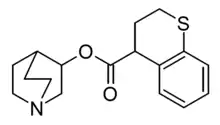
3-Quinuclidinyl thiochromane-4-carboxylate
3-Quinuclidinyl thiochromane-4-carboxylate is a research compound which is one of the most potent muscarinic antagonists known. Tests in vitro showed it to have a binding affinity over 1000 times more potent than 3-quinuclidinyl benzilate.[1][2]
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
IUPAC name
| |
| PubChem CID | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C17H21NO2S |
| Molar mass | 303.42 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
References
- Cohen VI, Gibson RE, Reba RC (October 1987). "Synthesis and structure-activity relationships of new muscarinic antagonists". Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences. 76 (10): 848–50. doi:10.1002/jps.2600761020. PMID 3430351.
- Ball JC (2015). "Dual Use Research of Concern: Derivatives of 3-Quinuclidinyl Benzilate". Military Medical Science Letters. 84 (1): 2–41. doi:10.31482/mmsl.2015.001.
| |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blood agents |
| ||||||||||||||
| Blister agents |
| ||||||||||||||
| Nerve agents |
| ||||||||||||||
| Neurotoxins |
| ||||||||||||||
| Nettle agents |
| ||||||||||||||
| Pulmonary/ choking agents |
| ||||||||||||||
| Vomiting agents |
| ||||||||||||||
| Incapacitating agents |
| ||||||||||||||
| Lachrymatory agents |
| ||||||||||||||
| Malodorant agents |
| ||||||||||||||
| Biological toxins |
| ||||||||||||||
| Other |
| ||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.