Almitrine
Almitrine (marketed as Duxil by Servier) is a diphenylmethylpiperazine derivative classified as a respiratory stimulant by the ATC. It enhances respiration by acting as an agonist of peripheral chemoreceptors located on the carotid bodies. The drug increases arterial oxygen tension while decreasing arterial carbon dioxide tension in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. It may also prove useful in the treatment of nocturnal oxygen desaturation without impairing the quality of sleep. A significant literature exists for this compound, including over 60 papers that Medline labels as reviews.
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.044.054 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
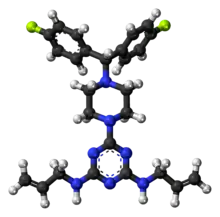
| Formula | C26H29F2N7 |
| Molar mass | 477.564 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Melting point | 181 °C (358 °F) |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| | |
The clinical efficacy of almitrine-raubasine combination therapy for age related cerebral disorders and functional rehabilitation after stroke has been reviewed by Allain and Bentué-Ferrer.[1] They summarize two studies in which almitrine-raubasine improved some symptoms significantly more than placebo, especially in vascular cases. Their paper also suggests that other studies have shown a beneficial effect of this compound on neurosensory vascular disorders, specifically chorioretinal dysfunctions (visual symptomatology) and vertigo associated with electronystagmographic modifications. This paper further claims that the dosage and tolerance of the compound have been confirmed in a French multi-center study of 5,361 outpatients.
Under the brand names Albasine, Aruxil, and Truxil, almitrine-raubasine has been marketed for rehabilitation after stroke, age related neurological disorders, visual disorders related to circulation, and tinnitus in Bangladesh.[2]
Synthesis
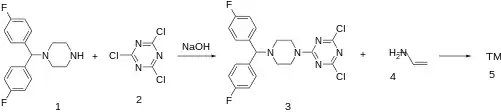
The reaction between 1-[bis(4-fluorophenyl)methyl]piperazine [27469-60-9] (1) and Cyanuric Chloride [108-77-0] (2) gives 2-[4-[Bis(4-fluorophenyl)methyl]piperazin-1-yl]-4,6-dichloro-1,3,5-triazine, CID:134990507 (3). Reaction with Allylamine [107-11-9] (4) completes the synthesis of Almitrine (5).
See also
- Flunarizine
- Diphenylmethylpiperazine
- Servier
References
- Allain H, Bentué-Ferrer D (1998). "Clinical efficacy of almitrine-raubasine. An overview". European Neurology. 39 Suppl 1 (Suppl. 1): 39–44. doi:10.1159/000052069. PMID 9516074.
- "Almitrine Bismesylate + Raubasine | অ্যালমিট্রিন বিসমিসাইলেট + রবাসিন | Indications, Pharmacology, Dosage, Side Effects & other Generic info with Available Brand names in Bangladesh | MedEx". MedEx. Retrieved 2022-04-07.
- DE1947332 idem Roger Canevari, Michel Laubie, Gilbert Regnier, U.S. Patent 3,647,794 (1972 to En Nom Collectif Science Union, Medicale Rech France).