PPADS
PPADS (pyridoxalphosphate-6-azophenyl-2',4'-disulfonic acid) is a selective purinergic P2X antagonist.[2] It is able to block contractions of rabbit vas deferens induced by ATP or α,β,methylene-ATP. It appears to be relatively selective for P2X receptors, having no appreciable activity at α1 adrenergic, muscarinic M2 and M3, histamine H1, and adenosine A1 receptors.[3]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
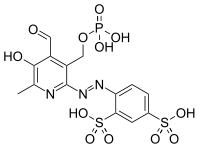
| IUPAC name
4-[(E)-{4-formyl-5-hydroxy-6-methyl-3-[(phosphonooxy)methyl]pyridin-2-yl}diazenyl]benzene-1,3-disulfonic acid | |
| Other names
PPADS | |
| Identifiers | |
CAS Number |
|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
Chemical formula |
C14H14N3O12PS2 |
| Molar mass | 511.37 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Orange solid |
Solubility in water |
100 mM (tetrasodium salt)[1] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
References
- PPADS tetrasodium salt, Santa Cruz Biotechnology
- Ziganshin, AU (December 1993). "PPADS selectively antagonizes P2X-purinoceptor-mediated responses in the rabbit urinary bladder". British Journal of Pharmacology. 110 (4): 1491–95. doi:10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13990.x. PMC 2175839. PMID 8306091.
- Lambrecht, G. (1992). "PPADS, a novel functionally selective antagonist of P2 purinoreceptor mediated responses". European Journal of Pharmacology. 217 (2–3): 217–19. doi:10.1016/0014-2999(92)90877-7. PMID 1330591.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.