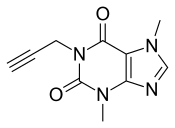
DMPX
DMPX (3,7-dimethyl-1-propargylxanthine) is a caffeine analog which displays affinity to A2 adenosine receptors, in contrast to the A1 subtype receptors.[1] DMPX had 28× and 15× higher potency than caffeine in blocking peripheral and central NECA-responses. The locomotor stimulation caused by DMPX (ED50 10 μmol/kg) was similarly higher than caffeine.[1]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.162.258 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C10H10N4O2 |
| Molar mass | 218.216 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
See also
- DPCPX
- 8-PT
- CPX (8-CPT)
- 8-Chlorotheophylline
- Theophylline
References
- Seale TW, Abla KA, Shamim MT, Carney JM, Daly JW (1988). "3,7-Dimethyl-1-propargylxanthine: a potent and selective in vivo antagonist of adenosine analogs". Life Sciences. 43 (21): 1671–84. doi:10.1016/0024-3205(88)90478-x. PMID 3193854.
Purine receptor modulators | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Receptor (ligands) |
| ||||||||||
| Transporter (blockers) |
| ||||||||||
| Enzyme (inhibitors) |
| ||||||||||
| Others |
| ||||||||||
See also: Receptor/signaling modulators | |||||||||||
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.