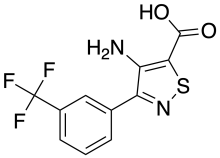
Amflutizole
Amflutizole is a xanthine oxidase inhibitor[1] used for the treatment of gout.
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C11H7F3N2O2S |
| Molar mass | 288.24 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| (verify) | |
Synthesis
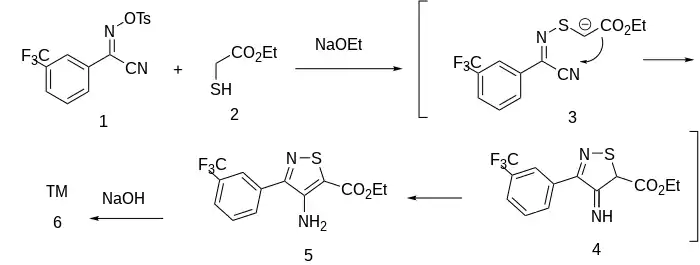
Patent:[2]
The tosyl oxime of the meta-trifluromethyl benzoic acid acid cyanide is the reactant, CID:53648583 (1). This is cross reacted with Ethyl thioglycolate [623-51-8] (2) in the presence of a base; displacement of the tosylate by mercaptide leads to the formation of the heterocyclic N–S bond. This intermediate compound is then converted to the carbanion by a second equivalent of base (3). This adds to the cyano group; protonation then goes on to form the imine (4), tautomerization of which gives the corresponding amino form (5). Finally, saponification of the ester thus affords amflutizole (6).
References
- O'Regan MH, Smith-Barbour M, Perkins LM, Cao X, Phillis JW (October 1994). "The effect of amflutizole, a xanthine oxidase inhibitor, on ischemia-evoked purine release and free radical formation in the rat cerebral cortex". Neuropharmacology. 33 (10): 1197–201. doi:10.1016/S0028-3908(05)80010-3. PMID 7862255. S2CID 37262919.
- Beck, Gajewski, and Hackler; U.S. Patent 4,346,094 (1982 to Eli Lilly and Co).
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.