13th century
The 13th century was the century which lasted from January 1, 1201 (MCCI) through December 31, 1300 (MCCC) in accordance with the Julian calendar.
| Millennium: | 2nd millennium |
|---|---|
| Centuries: | |
| Timelines: | |
| State leaders: |
|
| Decades: | |
| Categories: | Births – Deaths Establishments – Disestablishments |

The Mongol Empire was founded by Genghis Khan, which stretched from Eastern Asia to Eastern Europe. The conquests of Hulagu Khan and other Mongol invasions changed the course of the Muslim world, most notably the Siege of Baghdad (1258), the destruction of the House of Wisdom and the weakening of the Mamluks and Rums which, according to historians, caused the decline of the Islamic Golden Age. Other Muslim powers such as the Mali Empire and Delhi Sultanate conquered large parts of West Africa and the Indian subcontinent, while Buddhism witnessed a decline through the conquest led by Bakhtiyar Khilji.
The Southern Song dynasty would begin the century as a prosperous kingdom but would eventually be invaded and annexed into the Yuan dynasty of the Mongols. The Kamakura Shogunate of Japan would be invaded by the Mongols. Goryeo resisted an invasion by the Mongols but eventually sued for peace and would eventually be a client state of the Yuan dynasty.[1]
One of the earliest Islamic states in Southeast Asia would form during this century, most notably the Samudera Pasai.[2] The Kingdoms of Sukhothai and Hanthawaddy would emerge and go on to dominate their surrounding territories.[3]
In the history of European culture, this period is considered part of the High Middle Ages. In North America, according to some population estimates, the population of Cahokia grew to being equal to or larger than the population of 13th-century London.[4] In Peru, the Kingdom of Cuzco begins. The Kanem Empire in what is now Chad reaches its apex. The Solomonic dynasty in Ethiopia and the Zimbabwe Kingdom are founded. In the history of Maya civilizations, the 13th century marks the beginning of the Late Postclassic period. In the periodization of Precolumbian Peru, the 13th century is part of the Late Intermediate Period.
Events

1201–1209
- 1202: Introduction of Liber Abaci by Fibonacci.
- 1202: Battle of Basian occurs on July 27, between Kingdom of Georgia and Seljuks.
- 1202: Battle of Mirebeau occurs on August 1, between Arthur I of Brittany and John of England.
- 1204: Islamization of Bengal by Bakhtiyar Khalji and oppression of Buddhism in East India.
- 1204: Fourth Crusade of 1202–1204 captures Zadar for Venice and sacks Byzantine Constantinople, creating the Latin Empire.
- 1204: Fall of Normandy from Angevin hands to the French King, Philip Augustus, end of Norman domination of France.
- 1205: The Battle of Adrianople occurred on April 14 between Bulgarians under Tsar Kaloyan of Bulgaria, and Crusaders under Baldwin I, (July 1172 – 1205), the first emperor of the Latin Empire of Constantinople.
- 1206: Genghis Khan is declared Great Khan of the Mongols.
- 1206: The Delhi Sultanate is established in Northern India under the Mamluk Dynasty.
- 1209: Francis of Assisi founds the Franciscan Order.
- 1209: The Albigensian Crusade is declared by Pope Innocent III.
1210s
- 1212: The Battle of Las Navas de Tolosa in Iberia marks the beginning of a rapid Christian reconquest of the southern half of the Iberian peninsula, mainly from 1230–1248, with the defeat of Moorish forces.
- 1213: The Kingdom of France defeats the Crown of Aragon at the Battle of Muret.
- 1214: France defeats the English and Imperial German forces at the Battle of Bouvines.
- 1215: King John signs Magna Carta at Runnymede.
- 1216: Battle of Lipitsa between Russian principalities.
- 1216: Maravarman Sundara I reestablishes the Pandya Dynasty in Southern India
- 1217–1221: Fifth Crusade captures Egyptian Ayyubid port city of Damietta; ultimately the Crusaders withdraw.
1220s
- C. 1220: The Kingdom of Mapungubwe dissolves
- 1220: The Kingdom of Zimbabwe begins
- 1221: Venice signs a trade treaty with the Mongol Empire.
- 1221: Merv, Herat and Nishapur are destroyed in the Mongol conquest of the Khwarazmian Empire.
- 1222: Andrew II of Hungary signs the Golden Bull which affirms the privileges of Hungarian nobility.
- 1223: The Signoria, of the Republic of Venice is formed and consists of the Doge, the Minor Council, and the three leaders of the Quarantia.
- 1223: The Mongol Empire defeats various Russian principalities at the Battle of the Kalka River.
- 1223: Volga Bulgaria defeats the army of the Mongol Empire at the Battle of Samara Bend.
- 1227: Estonians are finally subjugated to German crusader rule during the Livonian Crusade.
- 1227: Genghis Khan dies.
- 1228–1229: Sixth Crusade under the excommunicated Frederick II Hohenstaufen, who returns Jerusalem to the Crusader States.
- 1228–1230: First clash between Gregory IX and Frederick II.
- 1226–1250: Dispute between the so-called second Lombard League and Frederick II.
1230s

- 1232: The Mongols besiege Kaifeng, the capital of the Jin dynasty, capturing it in the following year.
- 1233: Battle of Ganter, Ken Arok defeated Kertajaya, the last king of Kediri, thus established Singhasari kingdom[5] Ken Arok ended the reign of Isyana Dynasty and started his own Rajasa dynasty.
- 1235: The Mandinka tribes unite to form the Mali Empire which leads to the downfall of Takrur in the 1280s.
- 1239–1250: Third conflict between the Holy Roman Empire and the Papacy.
- 1237–1240: Mongol Empire conquers Kievan Rus.
- 1238: Sukhothai becomes the first capital of Sukhothai Kingdom.
1240s
- 1240: Russians defeat the Swedish army at the Battle of the Neva.
- 1241: Mongol Empire defeats Hungary at the Battle of Mohi and defeats Poland at the Battle of Legnica. Hungary and Poland ravaged.
- 1242: Russians defeat the Teutonic Knights at the Battle of Lake Peipus.
- 1243–1250: Second Holy Roman Empire–Papacy War.
- 1244: Ayyubids and Khwarezmians defeat the Crusaders and their Arab allies at the Battle of La Forbie.
- 1249: End of the Portuguese Reconquista against the Moors, when King Afonso III of Portugal reconquers the Algarve.
- 1248–1254: Seventh Crusade captures Egyptian Ayyubid port city of Damietta, Crusaders ultimately withdraw. Mamelukes overthrow Ayyubid Dynasty.
1250s
- By 1250, Pensacola culture, through trade, begins influencing Coastal Coles Creek culture.[6]
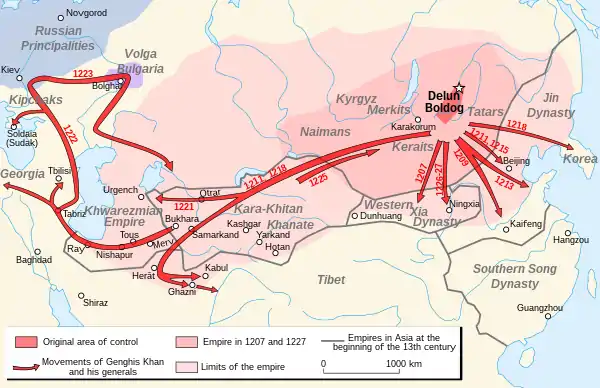 Mongol Empire in 1227 at Genghis Khan's death
Mongol Empire in 1227 at Genghis Khan's death - 1250: The Mamluk dynasty is founded in Egypt.
- 1257: Baab Mashur Malamo established the Sultanate of Ternate in Maluku.
- 1258: Baghdad captured and destroyed by the Mongols, effective conclusion of the Abbasid Caliphate in Baghdad.
- 1258: Pandayan Emperor Jatavarman Sundara I invades Eastern India and northern Sri Lanka.
- 1259: Treaty of Paris is signed between Louis IX and Henry III
1260s
- 1260: Toluid Civil War begins between Kublai Khan and Ariq Böke for the title of Great Khan.
- 1261: Byzantines under Michael VIII retake Constantinople from the Crusaders and Venice.
- 1262: Iceland was brought under Norwegian rule, with the Old Covenant.
- 1265: Dominican friar and theologian, Thomas Aquinas begins to write his Summa Theologiae.
- 1268: Fall of the Crusader State of Antioch to the Mamelukes.
1270s

- 1270: Goryeo dynasty swears allegiance to the Yuan dynasty.
- 1270: The Zagwe dynasty is displaced by the Solomonic dynasty.
- 1271: Edward I of England and Charles of Anjou arrive in Acre, starting the Ninth Crusade against Baibars.
- 1272–1274: Second Council of Lyon attempts to unite the churches of the Eastern Roman Empire with the Church of Rome.
- 1274: The Mongols launched their first invasion of Japan, but they are repelled by the Samurai and the Kamikaze winds.
- 1274: The Tepanec give the Mexica permission to settle at an islet which was named Cauhmixtitlan (Eagle's Place Between the Clouds)
- 1275: Sant Dnyaneshwar who wrote Dnyaneshwari (a commentary on the Bhagavad Gita) and Amrutanubhav was born.
- 1275: King Kertanegara of Singhasari launched Pamalayu expedition against Melayu Kingdom in Sumatra (ended in 1292).
- 1277: Passage of the last and most important of the Paris Condemnations by Bishop Tempier, which banned a number of Aristotelian propositions
- 1279: The Song dynasty ends after losing the Battle of Yamen to the Mongols.
- 1279: The Chola Dynasty in Southern India officially comes to an end.
1280s
- 1281: The Mongols launched their second invasion of Japan, but like their first invasion they are repelled by the Samurai and the Kamikaze winds.
- 1282: Aragon acquires Sicily after the Sicilian Vespers.
- 1284: Peterhouse, Cambridge founded by Hugo de Balsham, the Bishop of Ely.
- 1284: King Kertanegara launched the Pabali expedition to Bali, which integrated Bali into the Singhasari territory.
- 1285: Second Mongol raid against Hungary, led by Nogai Khan.
- 1289: The County of Tripoli falls to the Bahri Mamluks led by Qalawun.
- 1289: Kertanegara insulted the envoy of Kublai Khan, who demanded that Java pay tribute to the Yuan Dynasty.[7][8]
1290–1300

- The Mamluk Dynasty comes to an end and is replaced by the Khalji dynasty.
- 1290: By the Edict of Expulsion, King Edward I of England orders all Jews to leave the Kingdom of England.
- 1291: The Swiss Confederation of Uri, Schwyz, and Unterwalden forms.
- 1291: Mamluk Sultan of Egypt al-Ashraf Khalil captures Acre, thus ending the Crusader Kingdom of Jerusalem (the last Christian state remaining from the Crusades).
- 1292: Jayakatwang, duke of Kediri, rebels and kills Kertanegara, ending the Singhasari kingdom.
- 1292: Marco Polo, on his voyage from China to Persia, visits Sumatra and reports that, on the northern part of Sumatra, there were six trading ports, including Ferlec, Samudera and Lambri.[9]
- 1292: King Mangrai founds the Lanna kingdom.
- 1293: Mongol invasion of Java,[10] Kublai Khan of Yuan dynasty China, sends punitive attack against Kertanegara of Singhasari, repelling Mongol forces.
- 1293: On 10 November, the coronation of Nararya Sangramawijaya as monarch, marks the foundation of the Hindu Majapahit kingdom in eastern Java.
- 1296: First War of Scottish Independence begins.
- 1297: Membership in the Mazor Consegio or the Great Council of Venice of the Venetian Republic is sealed and limited in the future to only those families whose names have been inscribed therein.
- 1299: Ottoman Empire is established under Osman I.
- 1300: Islam is thought to have become established in the Aceh region.
- 1300: Aji Batara Agung Dewa Sakti founds the Kingdom of Kutai Kartanegara/Sultanate of Kutai in the Tepian Batu or Kutai Lama.
- 1300: The Turku Cathedral was consecrated in Turku.[11]
- 1300: Sri Rajahmura Lumaya, known in his shortened name Sri Lumay, a half-Tamil and half Malay minor prince of the Chola dynasty in Sumatra established the Indianized Rajahnate of Cebu in Cebu Island on the Philippine Archipelago.
Inventions, discoveries, introductions

- Early 13th century – Xia Gui paints Twelve Views from a Thatched Hut, during the Southern Song dynasty. It is now kept at The Nelson-Atkins Museum of Art, Kansas City, Missouri.
- The motet form originates out of the Ars antiqua tradition of Western European music.
- Manuscript culture develops out of this time period in cities in Europe, which denotes a shift from monasteries to cities for books.
- Pecia system of copying books develops in Italian university-towns and was taken up by the University of Paris in the middle of the century.
- Wooden movable type printing invented by Chinese governmental minister Wang Zhen in 1298.
- The earliest known rockets, landmines, and handguns are made by the Chinese for use in warfare.
- The Chinese adopt the windmill from the Islamic world.
- Guan ware vase is made, Southern Song dynasty. It is now kept at Percival David Foundation of Chinese Art, London.
- 1250 – Cliff Palace, Mesa Verde, and other Ancestral Pueblo architectural complexes reach their apex[13]
- 1280s – Eyeglasses are invented in Venice, Italy.
- Late 13th century – Night Attack on the Sanjo Palace is made during the Kamakura period. It is now kept at Museum of Fine Arts, Boston.
- Late 13th century – Descent of the Amida Trinity, raigo triptych, is made, Kamakura period. It is now kept at the Art Institute of Chicago.
- The Neo-Aramaic languages begin to develop during the course of the century.
See also
- Christianity in the 13th century
References
- Lee, Kenneth B. (1997). Korea and East Asia: The Story of a Phoenix. Greenwood Publishing Group. ISBN 9780275958237.
- "Samudra Pasai worthy to be world historical site". Republika Online. 2017-03-24. Retrieved 2020-01-24.
- Coedès, George (1968). Walter F. Vella (ed.). The Indianized States of Southeast Asia. trans.Susan Brown Cowing. University of Hawaii Press. ISBN 978-0-8248-0368-1.
- Greater London, Inner London & Outer London Population & Density History, quoting from The London Encyclopedia, Ben Weinreb and Christopher Hibbert, ed., Macmillan, 2010, ISBN 1405049251
- "Ken Angrok". Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved 25 July 2010.
- Weinstein, Richard A.; Dumas, Ashley A. (2008). "The spread of shell-tempered ceramics along the northern coast of the Gulf of Mexico" (PDF). Southeastern Archaeology. 27 (2). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2012-04-25.
- Grousset, Rene (1988), Empire of steppes, Wars in Japan, Indochina and Java, New Jersey: Rutgers University Press, p. 288, ISBN 0-8135-1304-9.
- page 243
- History of Aceh Archived August 13, 2012, at the Wayback Machine
- Weatherford, Jack (2004). Genghis khan and the making of the modern world. New York: Random House. p. 239. ISBN 0-609-80964-4.
- YLE: Kenelle kellot soivat? (in Finnish)
- Qutb Minar and its Monuments, Delhi UNESCO
- Berlo and Phillips, 275
External links
- James J. Walsh (1907). "The Thirteenth: Greatest of Centuries". nd.edu. Archived from the original on 2017-03-01.
