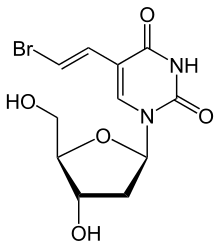
Brivudine
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Zostex, Mevir, Brivir, many others |
| Other names | BVDU |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 30% |
| Protein binding | >95% |
| Metabolism | Thymidine phosphorylase |
| Metabolites | Bromovinyluracil |
| Elimination half-life | 16 hours |
| Excretion | 65% renal (mainly metabolites), 20% faeces |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C11H13BrN2O5 |
| Molar mass | 333.138 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Specific rotation | +9°±1° |
| Density | 1.86 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 165 to 166 °C (329 to 331 °F) (decomposes) |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| | |
Brivudine (trade names Zostex, Mevir, Brivir, among others) is an antiviral drug used in the treatment of herpes zoster ("shingles"). Like other antivirals, it acts by inhibiting replication of the target virus.
Medical uses
Brivudine is used for the treatment of herpes zoster in adult patients. It is taken orally once daily, in contrast to aciclovir, valaciclovir and other antivirals.[1] A study has found that it is more effective than aciclovir, but this has been disputed because of a possible conflict of interest on part of the study authors.[2]
Contraindications
The drug is contraindicated in patients undergoing immunosuppression (for example because of an organ transplant) or cancer therapy, especially with fluorouracil (5-FU) and chemically related (pro)drugs such as capecitabine and tegafur, as well as the antimycotic drug flucytosine, which is also related to 5-FU. It has not been proven to be safe in children and pregnant or breastfeeding women.[1]
Adverse effects
The drug is generally well tolerated. The only common side effect is nausea (in 2% of patients). Less common side effects (<1%) include headache, increased or lowered blood cell counts (granulocytopenia, anaemia, lymphocytosis, monocytosis), increased liver enzymes, and allergic reactions.[1]
Interactions
Brivudine interacts strongly and in rare cases lethally with the anticancer drug fluorouracil (5-FU), its prodrugs and related substances. Even topically applied 5-FU can be dangerous in combination with brivudine. This is caused by the main metabolite, bromovinyluracil (BVU), irreversibly inhibiting the enzyme dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase (DPD) which is necessary for inactivating 5-FU. After a standard brivudine therapy, DPD function can be compromised for up to 18 days. This interaction is shared with the closely related drug sorivudine which also has BVU as its main metabolite.[1][3]
There are no other relevant interactions. Brivudine does not significantly influence the cytochrome P450 enzymes in the liver.[1]
Pharmacology
Spectrum of activity
The drug inhibits replication of varicella zoster virus (VZV) – which causes herpes zoster – and herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1), but not HSV-2 which typically causes genital herpes. In vitro, inhibitory concentrations against VZV are 200- to 1000-fold lower than those of aciclovir and penciclovir, theoretically indicating a much higher potency of brivudine. Clinically relevant VZV strains are particularly sensitive.[4]
Mechanism of action
Brivudine is an analogue of the nucleoside thymidine. The active compound is brivudine 5'-triphosphate, which is formed in subsequent phosphorylations by viral (but not human) thymidine kinase and presumably by nucleoside-diphosphate kinase. Brivudine 5'-triphosphate works because it is incorporated into the viral DNA, but then blocks the action of DNA polymerases, thus inhibiting viral replication.[1][4]
Pharmacokinetics
Brivudine is well and rapidly absorbed from the gut and undergoes first-pass metabolism in the liver, where the enzyme thymidine phosphorylase[5] quickly splits off the sugar component, leading to a bioavailability of 30%. The resulting metabolite is bromovinyluracil (BVU), which does not have antiviral activity. BVU is also the only metabolite that can be detected in the blood plasma.[1][6]
Highest blood plasma concentrations are reached after one hour. Brivudine is almost completely (>95%) bound to plasma proteins. Terminal half-life is 16 hours; 65% of the substance are found in the urine and 20% in the faeces, mainly in form of an acetic acid derivative (which is not detectable in the plasma), but also other water-soluble metabolites, which are urea derivatives. Less than 1% is excreted in form of the original compound.[1]
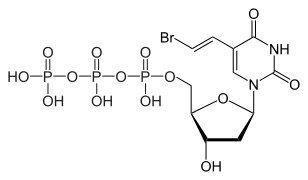 Brivudine 5'-triphosphate, the active metabolite
Brivudine 5'-triphosphate, the active metabolite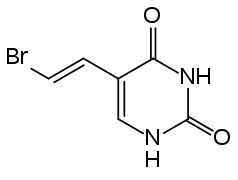 Bromovinyluracil (BVU), the main inactive metabolite
Bromovinyluracil (BVU), the main inactive metabolite The acetic acid derivative predominantly found in urine
The acetic acid derivative predominantly found in urine
Chemistry
The molecule has three chiral carbon atoms in the deoxyribose (sugar) part all of which have defined orientation; i.e. the drug is stereochemically pure.[1] The substance is a white powder.
Manufacturing
Main supplier is Berlin Chemie, now part of Italy's Menarini Group. In Central America is provided by Menarini Centro America and Wyeth.
History
The substance was first synthesized by scientists at the University of Birmingham in the UK in 1976. It was shown to be a potent inhibitor of HSV-1 and VZV by Erik De Clercq at the Rega Institute for Medical Research in Belgium in 1979. In the 1980s the drug became commercially available in East Germany, where it was marketed as Helpin by a pharmaceutical company called Berlin-Chemie. Only after the indication was changed to the treatment of herpes zoster in 2001 did it become more widely available in Europe.[7][8]
Brivudine is approved for use in a number of European countries including Austria, Belgium, Germany, Greece, Italy, Portugal, Spain and Switzerland.[9]
Etymology
The name brivudine derives from the chemical nomenclature bromo-vinyl-deoxyuridine or BVDU for short. It is sold under trade names such as Bridic, Brival, Brivex, Brivir, Brivirac, Brivox, Brivuzost, Zerpex, Zonavir, Zostex, and Zovudex.[9]
Research
A Cochrane Systematic Review examined the effectiveness of multiple antiviral drugs in the treatment of herpes simplex virus epithelial keratitis. Brivudine was found to be significantly more effective than idoxuridine in increasing the number of successfully healed eyes of participants.[10]
See also
Related antiviral drugs
- Aciclovir
- Valacyclovir, a prodrug form of aciclovir
- Famciclovir, an analogue of Penciclovir with greater oral availability
- Foscarnet, an intravenous antiviral for aciclovir-resistant VZV
- Penciclovir, a topical preparation
Vaccines and other treatments
- Zostavax, a live virus Herpes zoster (shingles) vaccine
- Varivax, a live virus Varicella Zoster (chickenpox) vaccine
- Shingrix, a recombinant subunit vaccine for shingles
- VZV immune globulin, an antibody-based treatment for immune-suppressed patients with zoster
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Jasek W, ed. (2007). Austria-Codex (in German) (62nd ed.). Vienna: Österreichischer Apothekerverlag. pp. 5246–8. ISBN 978-3-85200-181-4.
- ↑ "Brivudin (Zostex) besser als Aciclovir (Zovirax a.a.)?". Arznei-telegramm (in German). 5/2007.
- ↑ "UAW – Aus Fehlern lernen - Potenziell tödlich verlaufende Wechselwirkung zwischen Brivudin (Zostex) und 5-Fluoropyrimidinen" (PDF). Deutsches Ärzteblatt (in German). 103 (27). 7 July 2006.
- 1 2 Steinhilber D, Schubert-Zsilavecz M, Roth HJ (2005). Medizinische Chemie (in German). Stuttgart: Deutscher Apotheker Verlag. pp. 581–2. ISBN 3-7692-3483-9.
- ↑ Desgranges C, Razaka G, Rabaud M, Bricaud H, Balzarini J, De Clercq E (December 1983). "Phosphorolysis of (E)-5-(2-bromovinyl)-2'-deoxyuridine (BVDU) and other 5-substituted-2'-deoxyuridines by purified human thymidine phosphorylase and intact blood platelets". Biochemical Pharmacology. 32 (23): 3583–90. doi:10.1016/0006-2952(83)90307-6. PMID 6651877.
- ↑ Mutschler E, Schäfer-Korting M (2001). Arzneimittelwirkungen (in German) (8 ed.). Stuttgart: Wissenschaftliche Verlagsgesellschaft. p. 847. ISBN 3-8047-1763-2.
- ↑ De Clercq E (December 2004). "Discovery and development of BVDU (brivudin) as a therapeutic for the treatment of herpes zoster". Biochemical Pharmacology. 68 (12): 2301–15. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2004.07.039. PMID 15548377.
- ↑ Tringali C, ed. (2012). Bioactive Compounds from Natural Sources (2nd ed.). CRC Press. p. 170.
- 1 2 International Drug Names: Brivudine.
- ↑ Wilhelmus KR (January 2015). "Antiviral treatment and other therapeutic interventions for herpes simplex virus epithelial keratitis". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 1: CD002898. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD002898.pub5. PMC 4443501. PMID 25879115.