Edinger–Westphal nucleus
| Edinger–Westphal nucleus | |
|---|---|
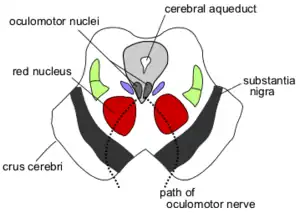 Section through superior colliculus (unlabeled) showing path of oculomotor nerve. ("Edinger–Westphal nucleus" is not on diagram, but would be near oculomotor nuclei.) | |
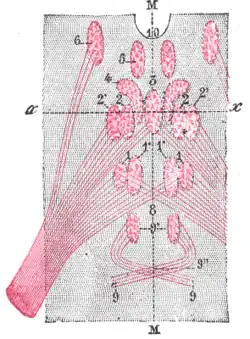 Figure showing the different groups of cells, which constitute, according to Perlia, the nucleus of origin of the oculomotor nerve. 1. Posterior dorsal nucleus. 1’. Posterior ventral nucleus. 2. Anterior dorsal nucleus. 2’. Anterior ventral nucleus. 3. Central nucleus. 4. Nucleus of Edinger and Westphal. 5. Antero-internal nucleus. 6. Antero-external nucleus. 8. Crossed fibers. 9. Trochlear nerve, with 9’, its nucleus of origin, and 9", its decussation. 10. Third ventricle. M, M. Median line. | |
| Details | |
| Parts | Provides input to Parasympathetic root of ciliary ganglion |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | nuclei accessorii nervi oculomotorii |
| MeSH | D065839 |
| NeuroNames | 498 |
| NeuroLex ID | birnlex_822 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
The Edinger–Westphal nucleus (accessory oculomotor nucleus) is the parasympathetic pre-ganglionic nucleus that innervates the iris sphincter muscle and the ciliary muscle.
Alternatively, the Edinger–Westphal nucleus is a term often used to refer to the adjacent population of non-preganglionic neurons that do not project to the ciliary ganglion, but rather project to the spinal cord, dorsal raphe nucleus, lateral septal nuclei,[1] lateral hypothalamic area and the central nucleus of the amygdala, among other regions [2]
Unlike the classical preganglionic neurons, that contain choline acetyltransferase, neurons of the non-preganglionic Edinger–Westphal nucleus contain various neuropeptides, such as Urocortin and cocaine- and amphetamine-regulated transcript.[3]
Previously, it had been proposed to rename this group of non-preganglionic, neuropeptide-containing neurons to perioculomotor subgriseal neuronal stream, abbreviated pIIISG.[4]
However, more recently, a final nomenclature has been determined. Preganglionic oculomotor neurons within the Edinger–Westphal nucleus shall be referred to as the EWpg, and the neuropeptide-containing neurons shall be known as the centrally-projecting Edinger Westphal nucleus, or EWcp.[1]
Location
The paired nuclei are posterior to the main motor nucleus (oculomotor nucleus) and anterolateral to the cerebral aqueduct in the rostral midbrain at the level of the superior colliculus.
It is the most rostral of the parasympathetic nuclei in the brain stem.
Function
The Edinger–Westphal nucleus supplies preganglionic parasympathetic fibers to the eye, constricting the pupil, accommodating the lens, and convergence of the eyes.[5]
It has also been implicated in the mirroring of pupil size in sad facial expressions. When seeing a sad face, participants' pupils dilated or constricted to mirror the face they saw, which predicted both how sad they perceived the face to be, as well as activity within this region.[6][7]
Eponym
The nucleus is named for both Ludwig Edinger, from Frankfurt, who demonstrated it in the fetus in 1885, and for Karl Friedrich Otto Westphal, from Berlin, who demonstrated it in the adult in 1887.[8]
Additional images
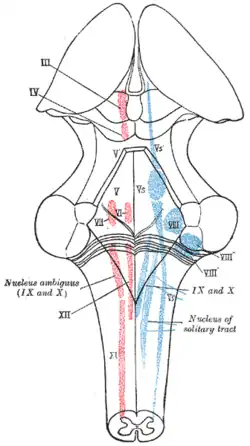 The cranial nerve nuclei schematically represented; dorsal view. Motor nuclei in red; sensory in blue.
The cranial nerve nuclei schematically represented; dorsal view. Motor nuclei in red; sensory in blue.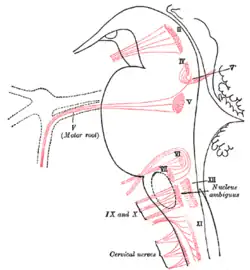 Nuclei of origin of cranial motor nerves schematically represented; lateral view.
Nuclei of origin of cranial motor nerves schematically represented; lateral view. Primary terminal nuclei of the afferent (sensory) cranial nerves schematically represented; lateral view.
Primary terminal nuclei of the afferent (sensory) cranial nerves schematically represented; lateral view.
References
- 1 2 Kozicz T, Bittencourt JC, May PJ, Reiner A, Gamlin PD, Palkovits M, Horn AK, Toledo CA, Ryabinin AE (2011). "The Edinger–Westphal nucleus: A historical, structural and functional perspective on a dichotomous terminology". J. Comp. Neurol. 519 (8): 1413–34. doi:10.1002/cne.22580. PMC 3675228. PMID 21452224.
- ↑ Dos Santos Junior, ED, Da Silva AV, Da Silva KR, Haemmerle CA, Batagello DS, Da Silva JM, Lima LB, Da Silva RJ, Diniz GB, Sita LV, Elias CF, Bittencourt JC (2015). "The centrally projecting Edinger-Westphal nucleus-I: Efferents in the rat brain" (PDF). J. Chem. Neuroanat. 68: 22–38. doi:10.1016/j.jchemneu.2015.07.002. hdl:11449/160880. PMID 26206178.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link). - ↑ Kozicz, T. (2003). "Neurons colocalizing urocortin and cocaine and amphetamine-regulated transcript immunoreactivities are induced by acute lipopolysaccharide stress in the Edinger–Westphal nucleus in the rat". Neuroscience. 116 (2): 315–20. doi:10.1016/S0306-4522(02)00772-8. PMID 12559087.
- ↑ May PJ, Reiner AJ, Ryabinin AE (March 2008). "Comparison of the Distributions of Urocortin Containing and Cholinergic Neurons in the Perioculomotor Midbrain of the Cat and Macaque". J. Comp. Neurol. 507 (3): 1300–16. doi:10.1002/cne.21514. PMC 2863095. PMID 18186029.
- ↑ Kaufman, Paul L.; Levin, Leonard A.; Alm, Albert (2011). Adler's Physiology of the Eye. Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 508. ISBN 978-0-323-05714-1.
- ↑ Harrison, NA; Wilson, CE; Critchley, HD (2007). "Processing of observed pupil size modulates perception of sadness and predicts empathy". Emotion. 7 (4): 724–9. doi:10.1037/1528-3542.7.4.724. PMID 18039039.
- ↑ Harrison, NA; Singer, T; Rotshtein, P; Dolan, RJ; Critchley, HD (2006). "Pupillary contagion: central mechanisms engaged in sadness processing". Social Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience. 1 (1): 5–17. doi:10.1093/scan/nsl006. PMC 1716019. PMID 17186063.
- ↑ synd/893 at Who Named It?
External links
- Diagram at Columbia
- Stained brain slice images which include the "Edinger–Westphal nucleus" at the BrainMaps project
- MedEd at Loyola Neuro/frames/nlBSs/nl18fr.htm
- "3-12". Cranial Nerves. Yale School of Medicine. Archived from the original on 2016-03-03.