Oxetacaine
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Routes of administration | Oral, topical |
| ATC code | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Elimination half-life | 1 hour |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.004.346 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
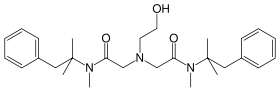
| Formula | C28H41N3O3 |
| Molar mass | 467.654 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| | |
Oxetacaine (INN, also known as oxethazaine) is a potent local anesthetic. It is administered orally (usually in combination with an antacid) for the relief of pain associated with peptic ulcer disease or esophagitis. It is also used topically in the management of hemorrhoid pain. Oral oxetacaine preparations are available in several countries, including India, South Africa, Japan, Taiwan and Brazil, but not the United States.
Unlike most local anesthetics, oxetacaine does not break down under strongly acidic conditions.[1]
References
- ↑ Seifter J, Glassman JM, Hudyma GM (1962). "Oxethazaine and related congeners: a series of highly potent local anesthetics". Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 109 (3): 664–8. doi:10.3181/00379727-109-27300. PMID 13910333. S2CID 39641018.
External links
- Strocain Prescribing information from Eisai Co.
This article is issued from Offline. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.