Zofenopril
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Zocardis (RU) |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
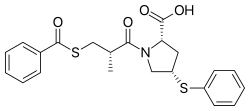
| Formula | C22H23NO4S2 |
| Molar mass | 429.55 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| | |
Zofenopril (INN) is a medication that protects the heart and helps reduce high blood pressure. It is an angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor.[1]
In small studies, zofenopril appeared significantly more effective in reducing hypertension than two older antihypertensive drugs, atenolol and enalapril, and was associated with fewer adverse effects.[2][3]
Zofenopril is a prodrug with zofenoprilat as the active metabolite.[4]
It was patented in 1978 and approved for medical use in 2000.[5]
References
- ↑ Ambrosioni E (2007). "Defining the role of zofenopril in the management of hypertension and ischemic heart disorders". American Journal of Cardiovascular Drugs. 7 (1): 17–24. doi:10.2165/00129784-200707010-00002. PMID 17355163. S2CID 41320204.
- ↑ Nilsson P (October 2007). "Antihypertensive efficacy of zofenopril compared with atenolol in patients with mild to moderate hypertension". Blood Pressure. Supplement. 2: 25–30. doi:10.1080/08038020701561745. PMID 18046976. S2CID 22145457.
- ↑ Mallion JM (October 2007). "An evaluation of the initial and long-term antihypertensive efficacy of zofenopril compared with enalapril in mild to moderate hypertension". Blood Pressure. Supplement. 2: 13–8. doi:10.1080/08038020701561703. PMID 18046974. S2CID 27469549.
- ↑ Subissi A, Evangelista S, Giachetti A (1999). "Preclinical Profile of Zofenopril: An Angiotensin Converting Enzyme Inhibitor with Peculiar Cardioprotective Properties". Cardiovascular Drug Reviews. 17 (2): 115–133. doi:10.1111/j.1527-3466.1999.tb00008.x.
- ↑ Fischer J, Ganellin CR (2006). Analogue-based Drug Discovery. John Wiley & Sons. p. 467. ISBN 9783527607495.
This article is issued from Offline. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.