X
wikiHow is a “wiki,” similar to Wikipedia, which means that many of our articles are co-written by multiple authors. To create this article, 13 people, some anonymous, worked to edit and improve it over time.
This article has been viewed 109,345 times.
Learn more...
LOD score, or logarithm of odds score, is a statistical test used in genetic linkage analysis. The LOD score compares the probability of obtaining the test data if the two loci are linked to the probability of obtaining the test data if the two loci are not linked.[1]
Method 1
Method 1 of 2:
When progeny size is small
-
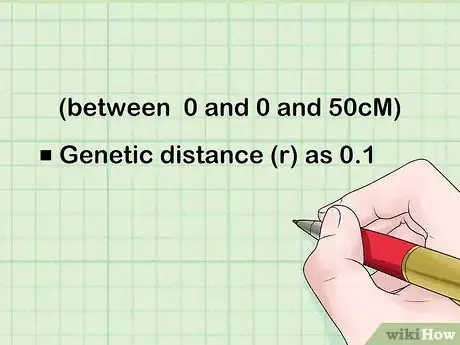
1Assume a certain genetic distance between the two genes (between 0 and 0 and 50cM). Assume you take the genetic distance (r) as 0.1.[3]
-
2Assume that you have 13 individuals out of which 2 are recombinant. The probability of non-recombinations will be 1-r = 1-0.1 = 0.9
-
3Since you want to track each genotype, you divide it by 2: (1-r)/2=0.45. The probability of recombinants will be r/2 = 0.1/2 = 0.05 [4]
- The probability of Data if the two genes are linked is ((r/2)^R)*(((1-r)/2)^NR) where R= # of recombinants and NR = # of non-recombinants. So the probability of Data if the two genes are linked is ((0.05)^2)*((.45)^11)
- The probability of Data if the two genes are non-linked is (0.25)^(R+NR) = (0.25)^13
- Now log of odds = (probability of Data if the two genes are linked)/(probability of Data if the two genes are non-linked). So, Log of odds = (((.05)^2)*((0.45)^11)) / ((0.25)^13) = 25.7
- The LOD score will be log10(25.7) = 1.41.
-
4Repeat this process for r as 0, 0.01, 0.03 ,0.05, 0.3 and 0.5.
- The highest value of LOD score you get is your correct answer. The genetic distance you've assumed is probably close to the actual distance between the two genes of interest.
Advertisement
Method 2
Method 2 of 2:
When Progeny size is large
-
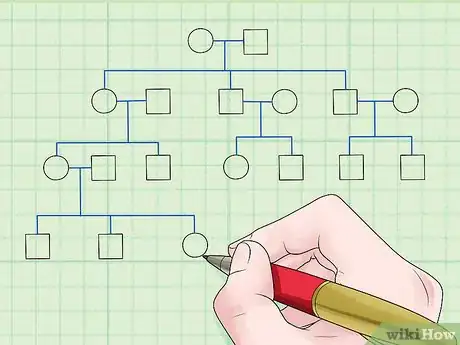
1Establish a pedigree for two loci of interest. The more data you gather, the better.[5]
-
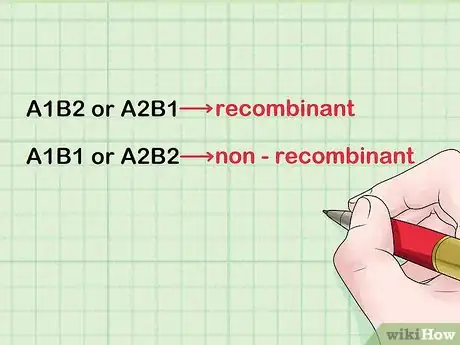
2Determine the number of recombinant and number of nonrecombinants. For example, suppose alleles A1 and B1 one locus 1 came from one parent, and A2 and B2 on locus 2 came from the other. Progeny inheriting A1B1 or A2B2 is non - recombinant, while those inheriting A1B2 or A2B1 are recombinant.
-
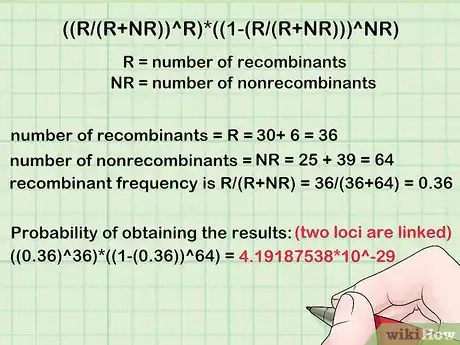
3Calculate the probability of obtaining the results assuming the two loci are linked. This is given by ((R/(R+NR))^R)*((1-(R/(R+NR)))^NR), where R = number of recombinants, NR = number of nonrecombinants.[6]
- For example, in the MNS blood group system, M and S are linked, and N and s are linked. Suppose that in 100 random individuals, 25 have MS haplotype, 30 have Ms haplotype, 6 have NS haplotype, and 39 have Ns haplotype. Since M and S are linked, and N and s are linked, MS and Ns are non - recombinants, and Ms and NS are recombinants.
- Thus, the number of recombinants = R = 30+ 6 = 36, while the number of nonrecombinants = NR = 25 + 39 = 64. The recombinant frequency is R/(R+NR) = 36/(36+64) = 0.36.
- The probability of obtaining the results assuming the two loci are linked is therefore ((0.36)^36)*((1-(0.36))^64) = 4.19187538*10^-29.
-
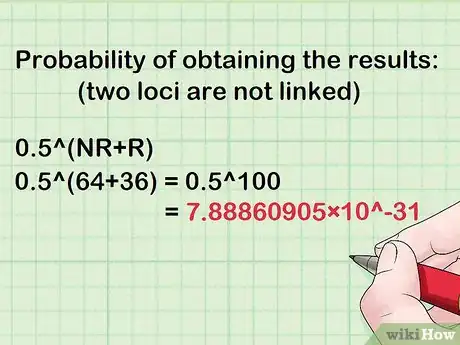
4Calculate the probability of obtaining the results assuming the two loci are not linked. This is given by 0.5^(NR+R). In the example above, this is 0.5^(64+36) = 0.5^100 = 7.88860905×10^-31.
-
5Divide the probability of obtaining the results assuming the two loci are linked (from Step 3 above), by the probability of obtaining the results assuming the two loci are not linked (from Step 4 above). For our example, this equals 4.19187538*10^-29/7.88860905×10^-31 = 53.14.
-
6Take the base 10 logarithm of the ratio obtained above (Step 5). For the example, this equals log 53.14 = 1.73.
Advertisement
Things You'll Need
- Calculator
References
- ↑ https://www.statisticshowto.com/log-odds/
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1287176/
- ↑ https://www.cell.com/ajhg/pdf/S0002-9297(07)61264-6.pdf
- ↑ https://www.ndsu.edu/pubweb/~mcclean/plsc431/linkage/linkage6.htm
- ↑ https://www.ndsu.edu/pubweb/~mcclean/plsc431/linkage/linkage6.htm
- ↑ https://www.ndsu.edu/pubweb/~mcclean/plsc431/linkage/linkage6.htm
About This Article
Advertisement