This article was co-authored by wikiHow staff writer, Jennifer Mueller, JD. Jennifer Mueller is a wikiHow Content Creator. She specializes in reviewing, fact-checking, and evaluating wikiHow's content to ensure thoroughness and accuracy. Jennifer holds a JD from Indiana University Maurer School of Law in 2006.
There are 8 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page.
This article has been viewed 38,788 times.
Learn more...
When writing a research paper or other report, you may find that you want to quote directly from a source. The Modern Language Association (MLA) has specific formatting guidelines for including direct quotes in your work. These guidelines differ depending on the length of the quoted material. Additional rules apply if you want to change or omit words from the quoted material so it flows well with your own writing.[1]
Steps
Including Short Quotations
-
1Enclose short quotations in double quotation marks. For quotes of fewer than 4 typed lines or 3 lines of a poem, type the information verbatim from your source text, putting double quotation marks around it. Include punctuation inside the quotation marks only if they are part of the source text.[2]
- If the source text includes material in quotation marks, change those quotation marks to single quotation marks.
- For example, you might write: Freud considered a dream to be "the fulfillment of a wish."
Tip: The length of a quote refers to the length as typed in your paper, not the length as printed in the original source.
-
2Place your parenthetical citation immediately after the quote. Even if the quoted passage occurs in the middle of a sentence, the citation follows immediately. An MLA in-text citation typically includes the name of the author and the page number. If the name of the author appears in your text, all you need is the page number.[3]
- For example, you might write: Freud considered a dream to be "the fulfillment of a wish" (154).
- Remember to include a complete citation to the source in your Works Cited at the end of your paper.
Advertisement -
3Type punctuation marks after the parenthetical citation. Any punctuation marks that would follow the quoted text should follow your parenthetical citation. If the quoted text includes a closing punctuation mark within it, place a period after the closing parentheses.[4]
- For example, you might write: "Is it possible that dreams may express "profound aspects of personality?" (Foulkes 184).
-
4Use a slash between lines of poetry. When quoting fewer than 3 lines of a poem, the slash ( / ) is used between lines to preserve the poet's line breaks. If a stanza break occurs in the portion you quote, use a double slash ( // ).[5]
- For example, you might write: In his poem, "Harlem," Langston Hughes questioned what happens to a dream deferred, wondering if it might "dry up / like a raisin in the sun" (24).
Creating Blockquotes
-
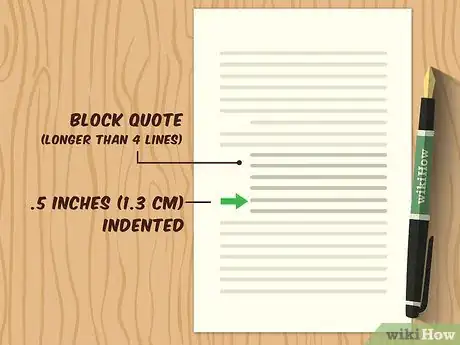
1Make a free-standing blockquote for quotes longer than 4 lines. Start the quote on a new line and type the quote exactly as it appears in the source text, including punctuation. Do not enclose blockquotes in double quotation marks.[6]
- The entire blockquote is indented .5 inches (1.3 cm) from the left margin.
- Maintain double spacing in your blockquote just as in the rest of your paper.
Tip: If you're using Microsoft Word, type the entire blockquote into your paper, starting on a new line. Then highlight the entire quote and press the tab key once to indent it correctly.
-
2Write a signal phrase before the quote. Before you include a blockquote in your paper, introduce it with a signal phrase that tells the reader what information the blockquote conveys. It's typically appropriate to include the author's name in the sentence introducing the blockquote.[7]
- The sentence immediately before a blockquote typically ends with a colon rather than a period.
-
3Include character names and hanging indentions for dramatic texts. Dramatic texts, including plays or screenplays, are formatted differently in blockquotes than other prose. Type the character's name in all caps, followed by a period. Then type that character's lines. Use a hanging indention, indenting each character's lines after the first an additional .25 inches (0.64 cm) from the left margin.[8]
- As with all blockquotes, indent the first line with the character's name .5 inches (1.3 cm) from the left margin.
-
4Use blockquote format when quoting more than one paragraph. Even if your quote is fewer than 4 lines, MLA style requires you to use blockquote format if there is a paragraph break in the middle of the text you want to quote. Doing this preserves the paragraph break.[9]
- When quoting more than one paragraph, indent the first line of any new paragraph an additional .25 inches (0.64 cm) from the left margin.
-
5Keep formatting close to the original when quoting poetry. Indent the entire quoted section .5 inches (1.3 cm) from the left margin, as you would with any blockquote. If the poet makes use of further indented lines or other spacing, try to approximate this as closely as you can. Copy all line breaks and punctuation exactly as they appear in the source text.[10]
- If you're quoting concrete poetry or another form where the spacing is integral to understanding the poem as a whole, it might be better to include a digital image of the poem, rather than trying to replicate it yourself.
-
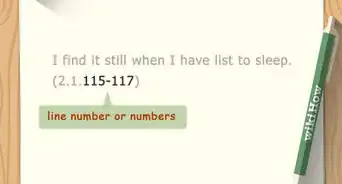
6Place your parenthetical citation after the closing punctuation. Since the closing punctuation is part of the quotation, it stays with the quoted text. Your parenthetical citation follows, without any punctuation after the closing parentheses.[11]
- As with short quotations, if you included the author's name in your introduction to the blockquote, there's no need to include the author's name in the parenthetical citation. Just include the page number or page range where the quoted text can be found.
- When quoting poetry, place the parenthetical citation at the end of the last quoted line, regardless of the punctuation. If the line doesn't have any closing punctuation, there's no need to add any either before or after your parenthetical citation.
Editing Quotations to Fit Your Writing
-
1Use square brackets to clarify pronoun reference. If the portion of the source text you want to quote uses a pronoun, it may be necessary for you to explain to your readers who or what the source text is referring to. Keep your description brief, and enclose it in square brackets immediately after the pronoun you wish to clarify.[12]
- For example, suppose you want to quote a source that says "While they excelled at individual projects, they struggled with group projects." Previous sentences indicate that "they" refers to "introverted students. Your quote would read: "While they [introverted students] excelled at individual projects, they struggled with group projects."
-
2Include the word "sic" in square brackets after errors. If there is a spelling or grammatical error in the source text that you're quoting, do not correct it. Rather, add the word "sic" in square brackets immediately after the error. This alerts your readers that the mistake was in the original, and not a result of your own mistyping.[13]
- Grammatical errors are more likely to come up in quoted speech than in a written and edited text. If a source has very many errors in the text, this may be an indication that it isn't reliable and probably shouldn't be used as a source at all.
- Avoid using "sic" to make a political or editorial statement about the language the source is using. For example, if your source includes the word "mankind," you would be making a political or editorial statement to include a "sic" after the word. Even though in your view the word "humankind" may be more appropriate, "mankind" isn't grammatically incorrect.
-
3Note emphasis added in the parenthetical citation. You may wish to emphasize a particular part of something quoted, typically by italicizing it. MLA rules allow this, provided you include the phrase "emphasis added" in your parenthetical citation, following the page number where the quoted text can be found.[14]
- For example, you might write: "Students who described themselves as highly introverted liked group projects the least" (Briggs 24, emphasis added).
-
4Indicate omissions with 3 spaced ellipsis points. When quoting a source text, only include material that you need. Any words that aren't needed can be omitted and replaced with ellipsis points (. . .).[15]
- If the material you omitted occurs at the end of the sentence, retain the period at the end of the sentence. It will look like 4 ellipsis points instead of 3.
- If there is other punctuation, such as a comma or a semi-colon, in the source text, retain that after your ellipsis. For example, a quote might read "Students enjoyed the individual projects . . . ; however, they did not like working in groups." Note that you include a space before the first ellipsis point, as well as a space after the last ellipsis point.
- If you're quoting a source that uses ellipsis points as "suspension points," meant to indicate a hesitation or pause in speech rather than omitted words, put your own ellipsis points in brackets to distinguish them from the original text.
-
5Put square brackets around any changes to the source text. Particularly with short quotations, you may need to alter the quoted passage so that it flows seamlessly with your own text. This may include changing an initial capital letter to lowercase, using different pronouns, or altering the tense of verbs or the plurality of the subject.[16]
- For example, suppose you wanted to use the beginning of a sentence in the middle of one of your sentences. To change the initial capital letter, you might write: Percy Bysshe Shelley argued that "[p]oets are the unacknowledged legislators of the world."
Tip: If you have to make too many changes to the source text, it may look cluttered and will negatively affect readability. Consider recasting your sentence or only quoting snippets of the source text, rather than using the full sentence.
References
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/research_and_citation/mla_style/mla_formatting_and_style_guide/mla_formatting_quotations.html
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/research_and_citation/mla_style/mla_formatting_and_style_guide/mla_formatting_quotations.html
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/research_and_citation/mla_style/mla_formatting_and_style_guide/mla_formatting_quotations.html
- ↑ https://columbiacollege-ca.libguides.com/MLA9/in-text
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/research_and_citation/mla_style/mla_formatting_and_style_guide/mla_formatting_quotations.html
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/research_and_citation/mla_style/mla_formatting_and_style_guide/mla_formatting_quotations.html
- ↑ https://research.wou.edu/mla/mla-blockquote
- ↑ https://research.wou.edu/mla/mla-blockquote
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/research_and_citation/mla_style/mla_formatting_and_style_guide/mla_formatting_quotations.html
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/research_and_citation/mla_style/mla_formatting_and_style_guide/mla_formatting_quotations.html
- ↑ https://research.wou.edu/mla/mla-blockquote
- ↑ https://www.unr.edu/writing-speaking-center/student-resources/writing-speaking-resources/mla-quotation-punctuation
- ↑ https://style.mla.org/when-to-use-sic/
- ↑ https://style.mla.org/cite-altered-quotation/
- ↑ https://www.uhv.edu/curriculum-and-student-achievement/student-success/tutoring/student-resources/e-p/ellipsis-use-in-mla-style/
- ↑ https://depts.washington.edu/engl/askbetty/changing_quotations.php