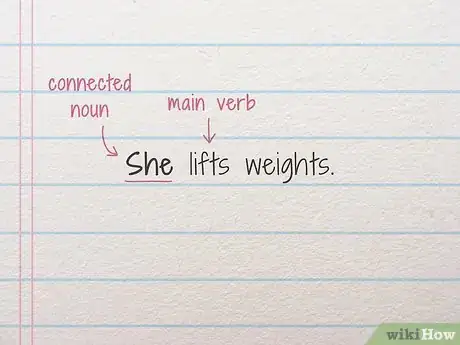This article was co-authored by Language Academia and by wikiHow staff writer, Hannah Madden. Language Academia is a private, online language school founded by Kordilia Foxstone. Kordilia and her team specialize in teaching foreign languages and accent reduction. Language Academia offers courses in several languages, including English, Spanish, and Mandarin.
There are 10 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page.
This article has been viewed 167,718 times.
A noun is a word that depicts a person, place, thing, or idea. Common nouns are things like house and tree, and they are not capitalized. Proper nouns are specific names, like Brooklyn or Joe, and they are always capitalized. To find a noun within a sentence, try to identify the verb, look for capitalized names, and see if there is an article within the sentence to base your identification on.
Steps
Finding Nouns in a Sentence
-
1Locate the main verb in the sentence to identify the connected noun. A verb is an action word that usually describes the act of doing. Grabbing, singing, and playing are all verbs. More often than not, the verb in the sentence is directly linked to the subject of the sentence. Identify who or what is completing the action in the sentence.[1]
- In the sentence “She lifts weights,” “lifts” is the verb, and “she” is the noun.
- In “The dog ran away,” “ran” is the verb, so “dog” is the noun.
-
2Find words that are capitalized as a clue that they might be nouns. Words that are capitalized in a sentence are almost always proper nouns, since they are usually the names of people, places, or things. Look for any words in the middle of a sentence that are capitalized and see if they could be a noun.[2]
- In the sentence “Agatha Christie wrote a lot of books,” “Agatha Christie” is the noun since it is a name.
- In the sentence “Do you think the Red Sox will win?” “Red Sox” is the noun, since it is the name of a team.
Advertisement -
3See if the word follows “a,” “and,” or “the.” These words are called articles. If a word follows an article, it is almost certainly a noun. Try to identify any articles in your sentence and see if there is a noun that follows directly after it.[3]
- In the sentence “The dance was held on Saturday,” “dance” is the noun since it follows “the.”
Warning: Sometimes an adjective will precede the noun. Watch out for sentences like “Some hot peppers were eaten.” “Peppers” is the noun in this sentence, not “hot.”
-
4See if the word follows “some,” “a lot,” or a specific number. Words that describe quantities almost always precede a noun. If the sentence has a quantity word in it, look at the word that is directly after it to see if it could be a noun.[4]
- In “Some computers in here are broken,” “computers” is the noun since it follows “some.”
-
5Determine if the word has a descriptor in front of it. Descriptive words, or adjectives, almost always are describing a noun. If you are questioning whether a word is a noun or not, see if there is an adjective in front of it. If there is, chances are the word is a noun.[5]
- For example, in the sentence “The stinky socks were gross,” “stinky” is the adjective, and “socks” is the noun.
- In “A dead tree fell down,” “dead” is the adjective and “tree” is the noun.
Identifying Noun Characteristics
-
1Identify words that are a person, place, thing, or idea. Nouns are words that depict specific objects, ideas, or people, that the sentence is built around. Look out for words in a sentence that are not actionable or descriptive, and instead only state exactly what something is.[6]
- In the sentence “She walked home,” “She” is the noun because she is a person.
- In “Portland is a cool city,” “Portland” is the noun because it is a place.
- In “The windows need to be open,” “windows” is the noun because it is a thing.
- In “Your courage is inspiring,” “courage” is the noun because it is an idea.
-
2Recognize common endings that indicate a word is a noun. Sometimes, the ending of a word, or the suffix, can clue you in as to what function it serves in a sentence. Often, nouns end in -ity, -ness, and -hood. Some other common examples of noun suffixes are:[7]
- -tion (population)
- -ance/-ence (permanence)
- -ar/-or (doctor)
- -ism (socialism)
- -ist (dentist)
- -ment (government)
- -y (beauty)
- -acy (accuracy)
- -age (image)
-
3Test to see if the word can be pluralized. If you can add a plural modifier onto the back of a word, it is most likely a noun. Choose the word that you believe to be a noun and add a letter or letters on the end of it to make it plural. Most often, the plural version of a word has an “s” on the end of it.[8]
- For example, “My shirt doesn’t fit.” “Shirt” can be pluralized by adding an “s” to the end of it to make “shirts.” “Shirt” is the noun in this sentence.
- If a noun is plural in a sentence, it is a plural noun.
-
4Spot possessive nouns by looking for an apostrophe and an “s.” Possessive nouns add ownership to a person, place, thing, or idea by adding an apostrophe and an “s” after the word. Theses nouns usually stand right in front of the thing that they are possessing. If a person, place, thing, or idea owns something, that word is a noun.[9]
- In “The book’s cover is gold,” “book’s” is the possessive noun.
- In “The laundry’s smell was enticing,” “laundry’s” is the possessive noun.
- In “My lawyer’s fee was too much,” “lawyer’s” is the possessive noun.
-
5Look for nouns that describe groups as a single entity. Collective nouns, or nouns that give a name to a large group of people, things, objects, or ideas, can be hard to spot, since they may not seem like nouns at first glance. Watch out for words like “array,” “choir,” and “class” to find collective nouns in a sentence.[10] More common collective nouns include:
- Department of technology
- Crowd of fans
- String of pearls
- School of fish
- Brood of chickens
- Deck of cards
-
6Look up the word in the dictionary to see if it is a noun. If all else fails, take a peek inside of a dictionary to find out what part of a sentence that word usually is. Dictionaries have symbols next to each definition of a word. A lowercase “n” signifies that a word is a noun.[11]
Warning: You will not be able to find slang words or most proper nouns in a dictionary.
Expert Q&A
-
QuestionHow do you spot a noun in a piece of writing?
 Language AcademiaLanguage Academia is a private, online language school founded by Kordilia Foxstone. Kordilia and her team specialize in teaching foreign languages and accent reduction. Language Academia offers courses in several languages, including English, Spanish, and Mandarin.
Language AcademiaLanguage Academia is a private, online language school founded by Kordilia Foxstone. Kordilia and her team specialize in teaching foreign languages and accent reduction. Language Academia offers courses in several languages, including English, Spanish, and Mandarin.
Language Tutors Take a look at the suspected noun in the sentence and ask "What is this?" or "Who is this?" A noun should easily be able to answer these questions. For example, if you were reading a sentence about a dog, you could ask the question "What is this?" and get "dog" as your answer. Through this process, you'd confirm that "dog" is a noun.
Take a look at the suspected noun in the sentence and ask "What is this?" or "Who is this?" A noun should easily be able to answer these questions. For example, if you were reading a sentence about a dog, you could ask the question "What is this?" and get "dog" as your answer. Through this process, you'd confirm that "dog" is a noun.
References
- ↑ https://www.grammarbook.com/grammar/subjectVerb.asp
- ↑ https://www.grammarbook.com/grammar/subjectVerb.asp
- ↑ https://www.cambridge.org/us/files/6813/6689/9880/9023_English_Grammar_unit_1.pdf
- ↑ https://learnenglish.britishcouncil.org/grammar/a1-a2-grammar/countable-and-uncountable-nouns-1
- ↑ https://academicguides.waldenu.edu/writingcenter/grammar/partsofspeech
- ↑ https://www.lynchburg.edu/academics/writing-center/wilmer-writing-center-online-writing-lab/grammar/count-and-noncount-nouns-and-articles/
- ↑ http://www.southcentral.edu/images/departments/ASC/documents/Suffixes_that_Indicate_Part_of_Speech_2.pdf
- ↑ https://academicguides.waldenu.edu/writingcenter/grammar/nounpronounagreement#s-lg-box-2825902
- ↑ https://examples.yourdictionary.com/examples-of-possessive-nouns.html