This article was co-authored by Carrie Noriega, MD. Dr. Noriega is a Board Certified Obstetrician & Gynecologist and medical writer in Colorado. She specializes in women’s health, rheumatology, pulmonology, infectious disease, and gastroenterology. She received her MD from the Creighton School of Medicine in Omaha, Nebraska and completed her residency at the University of Missouri - Kansas City in 2005.
There are 10 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page.
wikiHow marks an article as reader-approved once it receives enough positive feedback. In this case, 86% of readers who voted found the article helpful, earning it our reader-approved status.
This article has been viewed 320,720 times.
A small percentage of pregnant women suffer from an incompetent cervix, leaving them at risk for premature birth or miscarriage if left untreated. An incompetent cervix or cervical insufficiency is most frequently diagnosed early on in the second trimester, but can present as late as the beginning of the third trimester. Diagnosis may be made during an internal exam by your doctor or through an ultrasound.[1]
Steps
Diagnosing an Incompetent Cervix
-
1Know if you are at risk. Women who have previously had miscarriages in the second trimester (between weeks 14 and 27) are the most likely to have a cervical insufficiency, so it is important to disclose any prior pregnancy complications or miscarriages to your doctor. Women are not diagnosed with an incompetent cervix until they have suffered one or more late miscarriages. Knowing about this condition in advance will allow your doctor to monitor your condition more closely from the beginning. This can result in earlier detection of a weak cervix, which leads to an increased chance of prolonging the delivery. Any surgery on the cervix also puts women at risk, including a D&C, cervical cone, or LEEP.[2]
-
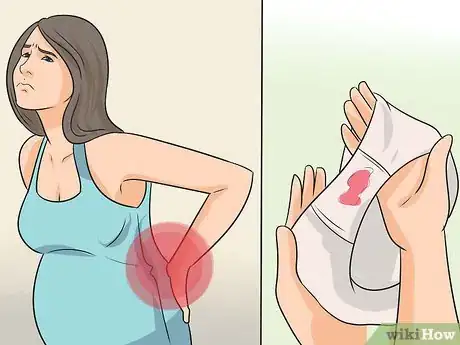
2Be attentive to possible symptoms. Although it is possible for an incompetent cervix to be present without any outward symptoms, in some cases there may be warning signs. These would typically occur between 14 and 22 weeks of pregnancy and include backache, discharge or warm liquid felt within the vagina, and pelvic pressure.[3]Advertisement
-
3Contact your OB/GYN immediately if you notice any of these symptoms. Although they may be completely unrelated to an incompetent cervix, it is always best to err on the side of caution and let the doctor do a complete exam to rule it out. This might include an ultrasound. Keep in mind that diagnoses of cervical insufficiency are based on a woman’s past medical history of miscarriage during the second trimester. If you do have a cervical insufficiency, you have some medical options.[4]
Undergoing Medical Treatment
-
1Discuss treatment options with your doctor. He or she will be able to lay out the possible options—cerclage, a pessary, and bed rest—and tell you which ones would best for you. Keep in mind that a cerclage (suturing the cervix closed) is by far the most common treatment, and allows many women with previous histories of miscarriage to successfully carry a baby to term. A pessary, similar to the outer ring of a diaphragm, changes the angle of the cervix and reinforces it.[5]
-
2Consider with your doctor whether serial ultrasounds might be a good first step. With ultrasounds every two weeks during the second trimester of your pregnancy, the doctor can monitor the risk of an incompetent cervix. If he or she sees warning signs, then you can have a cerclage.[6]
-
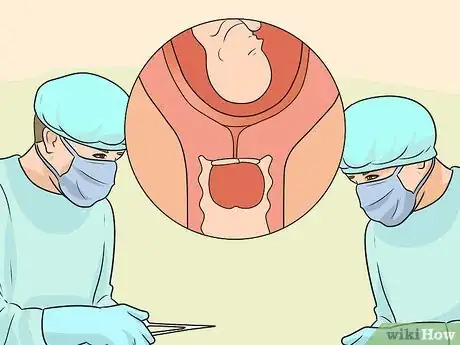
3Undergo a minimal surgery to get a cerclage. Once you are diagnosed with incompetent cervix, your doctor will likely suggest a cerclage. A cerclage is a procedure in which a stitch is placed around the cervix and tightened to keep the cervix closed. There are five types of cerclage that can be performed, and your doctor will determine which type is best for your situation depending upon how far along you are in your pregnancy.
- A cerclage is usually removed near the end of pregnancy to permit normal delivery.
- Occasionally, depending on conditions that are present during the pregnancy, the cerclage will be left in place and the mother will undergo a cesarean section to deliver the baby.[7]
-
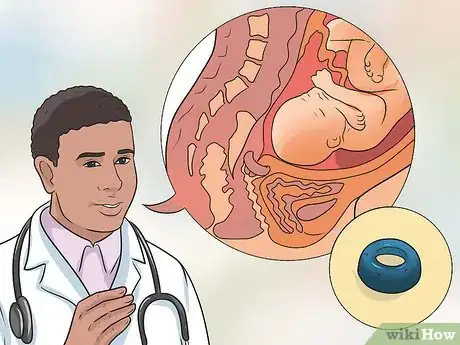
4Speak with your doctor about having a pessary put in place. A pessary is an apparatus that is positioned within the vagina to help raise up and reinforce the cervix. This may be used instead of, or in conjunction with a cerclage.[8]
-
5Ask whether bed rest or pelvic rest might help. Bed rest may be prescribed by your doctor for an incompetent cervix. Bed rest restrictions can vary from simply avoiding any heavy lifting or housework, to total bed rest where you must remain in a reclining position at all times, including for bathing and going to the bathroom.[9] Talk to your doctor about whether or not some type of bed rest might be a good option for you.
- You may also need to abstain from sex during a period of bed and pelvic rest.
Taking Care of Yourself
-
1Ensure you are getting adequate rest. Even if you are not prescribed bed rest, ensuring that you get adequate rest is important. Make sure that you get plenty of sleep and avoid overexerting yourself.
-
2Ask your doctor about vigorous exercise. He or she might suggest you refrain from high-intensity workouts and from having sex. Because your cervix is weak, exercise can further exacerbate your condition.[10]
-
3Do your kegels. Kegel exercises strengthen your pelvic floor muscles. To ensure that you are doing them correctly, while you are urinating clench your muscles to stop the flow of urine, and then release to continue the flow; that is what exercising your kegels feels like. While is it not certain that kegels will prevent an incompetent cervix, they do have certain benefits including enhanced sexual pleasure, aiding in vaginal birth, help for incontinence and a quicker postpartum recovery.
Expert Q&A
Did you know you can get expert answers for this article?
Unlock expert answers by supporting wikiHow
-
QuestionIf you get a cerclage, can you get pregnant again afterwards?
 Carrie Noriega, MDDr. Noriega is a Board Certified Obstetrician & Gynecologist and medical writer in Colorado. She specializes in women’s health, rheumatology, pulmonology, infectious disease, and gastroenterology. She received her MD from the Creighton School of Medicine in Omaha, Nebraska and completed her residency at the University of Missouri - Kansas City in 2005.
Carrie Noriega, MDDr. Noriega is a Board Certified Obstetrician & Gynecologist and medical writer in Colorado. She specializes in women’s health, rheumatology, pulmonology, infectious disease, and gastroenterology. She received her MD from the Creighton School of Medicine in Omaha, Nebraska and completed her residency at the University of Missouri - Kansas City in 2005.
Board Certified Obstetrician & Gynecologist
References
- ↑ http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/incompetent-cervix/basics/definition/con-20035375
- ↑ http://www.uchospitals.edu/specialties/obgyn/cerclage/faq.html
- ↑ https://www.marchofdimes.org/complications/cervical-insufficiency-and-short-cervix.aspx
- ↑ http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1979914-overview
- ↑ https://americanpregnancy.org/getting-pregnant/incompetent-cervix/
- ↑ http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/incompetent-cervix/basics/treatment/con-20035375
- ↑ http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1979914-treatment
- ↑ http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10885649
- ↑ http://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/pregnancy-week-by-week/in-depth/pregnancy/art-20048007
About This Article
While being diagnosed with an incompetent cervix can feel scary, there are ways to prolong your pregnancy. Once your doctor diagnoses you, discuss treatment options, including a cerclage, which entails suturing the cervix closed. This common treatment allows many women to successfully carry a baby to term. You can also talk to your doctor about having a pessary, which raises and reinforces the cervix, put in place. A pessary can be used in conjunction with a cerclage or on its own, depending on your specific case. Whether you have these procedures or not, you'll also want to ask your doctor if bed rest would help prolong your pregnancy. Bed rest can range from not doing any heavy lifting or exercise to spending nearly all of your time reclined. For more tips from our Medical co-author, including how to take care of yourself during the remainder of your pregnancy, keep reading!































































Medical Disclaimer
The content of this article is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, examination, diagnosis, or treatment. You should always contact your doctor or other qualified healthcare professional before starting, changing, or stopping any kind of health treatment.
Read More...