This article was co-authored by Amy Chow. Amy Chow is a Registered Dietitian and the Founder of Chow Down Nutrition, a family and child nutrition consulting service in British Columbia (BC), Canada. With over nine years of experience, Amy has a special interest in pediatric nutrition, food allergy management, and eating disorder recovery. Amy holds a Bachelor’s degree in Nutritional Sciences from McGill University. She gained her clinical experiences at residential and outpatient eating disorder treatment programs as well as for BC Children’s Hospital before starting her own business. She has been featured on Find BC Dietitians, Dietitians of Canada, Food Allergy Canada, Recovery Care Collective, Parentology, Save on Foods, National Eating Disorder Information Centre (NEDIC), and Joytv.
There are 17 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page.
This article has been viewed 31,039 times.
Diarrhea can be a very unpleasant and uncomfortable experience, complete with frequent bowel movements, watery stool, and abdominal pain. Severe diarrhea is defined at 10 or more loose, watery stools within a 24 hour period. Most bouts of severe diarrhea last one to three days. Severe diarrhea can leave you dehydrated disturb your electrolyte balance, leaving you open to complications. If you suspect you have severe diarrhea, see your doctor within 24 – 48 hours to check if the diarrhea is the result a medical disorder like Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis, colon cancer, or Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS).[1]
Steps
Taking Over-the-Counter Medication
-
1Try Pepto-Bismol. It is often best to let severe diarrhea run its course so your body can rid itself of the bacteria causing the diarrhea. But you can also try taking medications to help slow down your diarrhea. You can get Pepto-Bismol over-the-counter at your local pharmacy. It has mild antibacterial effects and slows down your diarrhea. Follow the label instructions for dosage information.[2]
-
2Have psyllium fiber. Psyllium fiber can be an effective antidote to severe diarrhea as it can help to soak up water in your intestines and make your stool more firm.[3]Advertisement
-
3Ask your doctor about medication you are already on. Sometimes, severe diarrhea can be caused by medication you are already taking for other medical issues. Talk to your doctor about your medications to rule them out as the causes of your severe diarrhea.[6]
- If your medication is causing the severe diarrhea, your doctor may switch your medication or suggest a lower dosage.
Adjusting Your Diet
-
1Drink eight to 10 glasses of water a day. Diarrhea can lead to a large loss of water in your body. Prevent dehydration by having eight to 10 eight ounce glasses of water a day to replace the fluids you have lost.[7]
- You can check if you are getting enough fluids by doing the pinch test, medically known as the skin turgor test. Use your fingers to pinch a section of skin on the back of your hand, your lower arm, or your abdominal area and hold it for a few seconds. Make sure the skin is tented upward. Release the skin after a few seconds. If the skin snaps back quickly to its normal position, you are well hydrated. If the skin stays tented upward and smooths back slowly, you are likely dehydrated.[8]
- You can also tell if you are getting enough fluids by checking the color of your urine. If your urine appears darker than normal, drink more water. If you are well hydrated, your urine will appear bright yellow.
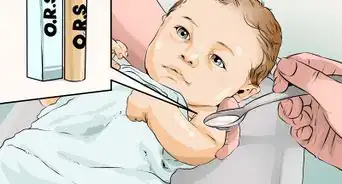
- Water alone will not always fix more severe dehydration. Try adding a pinch of honey or sugar with a dash of salt to the water you drink, or supplementing your eight to 10 glasses with an electrolyte solution available at your local pharmacy. Correcting electrolyte imbalances can often help the body to "reboot" after a bout of severe diarrhea.
-
2Consume high-fiber foods. Fiber will help to slow down your diarrhea by allowing your body to absorb water and making your stool more firm. Stay away from fatty, oil, or spicy foods that contain fiber and go for lighter foods high in fiber. Have brown rice with vegetables, barley, or another whole grain like oats or quinoa.[9]
- Cook grains in a light chicken or miso broth. Use a 2:1 ratio, with twice as much liquid used per one cup of grains. For example, you would cook ½ cup barley in 2 cups of chicken broth.
- Have well-cooked, starchy vegetables like potatoes, yams, sweet potatoes, and winter squash.
- You can also have fresh vegetable juices like carrot or celery juice. Dilute the vegetable juice with an equal amount of water.
- Do your best to eat foods that are high in soluble fiber such as oats, barley, bean, and applesauce.
-
3Do the BRAT diet. The BRAT diet can help to bulk up your stool and provide nutrients you may have lost due to the diarrhea and any vomiting. The BRAT diet is made up of:[10]
- Bananas
- Rice
- Applesauce
- Toast (whole grain)
- You can also eat salted crackers to help reduce any nausea or vomiting you may be experiencing, and ginger ale is often helpful in reducing nausea symptoms.
-
4Add a pinch of salt to liquids or soft, solid foods. Your body will also loose salt when you have severe diarrhea. Add a pinch of salt to liquids you are drinking or soft, solid foods you are eating to replace vital minerals in your body. You can use table salt or sea salt.[11]
-
5Have probiotics. You can find probiotics such as Lactobacillus GG, acidophilus, and bifidobacteria at your local pharmacy. Probiotics are “friendly” gut bacteria that help you maintain a healthy gut. Taking them while you have diarrhea allows the “friendly” bacteria to compete with the disease causing bacteria.[12]
- You can also add yogurt to your diet to increase the active cultures in your stomach and counteract the disease causing bacteria in your gut.
Having Herbal Teas
-
1Try ginger tea. Herbal teas like ginger tea can help to settle your upset stomach and counteract any bouts of nausea that may occur due to the diarrhea.[13]
- Ginger tea is safe for pregnant and breastfeeding women. Children over two years of age can have light ginger tea or flat non-carbonated ginger ale. Ginger tea has not been tested for use for very young children.
-
2Have chamomile tea or fenugreek tea. Prepare these teas using tea bags or add one teaspoon of chamomile flower or fenugreek seeds per cup of hot water. Try to have five to six cups of tea a day. These herbal teas help to settle your stomach and calm down your digestive system.
-
3Consume blackberry tea. Researchers at The University of Maryland have noted that blackberry leaf tea, raspberry leaf tea, bilberry teas, and carob powder drinks can help to settle the stomach. These teas have antibacterial and antiviral properties.
- Do not consume bilberry tea if you are on blood thinners or have diabetes.
-
4Stay away from caffeinated beverages. Avoid coffee, black tea, green tea, or caffeinated sodas. These drinks can make your diarrhea worse, as they can stimulate bowel movements.[14]
- You should also avoid drinking alcoholic beverages as they can also irritate your bowels and make your diarrhea worse.
Seeking Emergency Medical Care
-
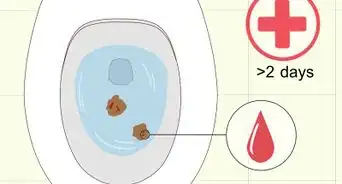
1See a doctor if there is blood or mucus in your stool. This could be a sign that your severe diarrhea may be a symptom of a more serious medical condition. You should seek medical treatment as soon as possible if you notice any blood or mucus in your stool, or your child’s stool.[15]
-
2Go to the doctor if you have a fever that lasts longer than 24 hours. If you are experiencing severe diarrhea and a fever that lasts longer than 24 hours, you should go to a doctor and get examined. You may not be able to keep down fluids or be urinating at all if your diarrhea gets very severe.[16]
- The doctor will perform a physical examination and take a stool sample. The stool sample will allow your doctor to determine if the diarrhea is the result of a parasite infection.
-
3Talk to your doctor about prescription medication for severe diarrhea. If your severe diarrhea does not seem to slow down within 24-48 hours, you should seek medical care. Your doctor may prescribe antibiotics or antiparasitic medication. She may also put you on an IV if you cannot drink enough fluids to stay hydrated.[17]
- You should also let your doctor know if you have been camping or hiking in the wild recently, as there are a number of parasites and other microorganisms that can cause severe diarrhea.
- Your doctor may suggest anti-diarrheal medications, such as over-the-counter medications like Loperamide (Imodium) or Bismuth subsalicylate (Kaopectate, Pepto-Bismol). Or, she may recommend prescription anti-diarrheal medications like Lomotil, Lonox, Loperamide, Crofelemer, Rifaximin, and Opium tincture/Peregoric.
-
4Consider getting tested for food allergies. Severe and/or chronic diarrhea can be caused by medical issues like Irritable Bowel Syndrome or Crohn's disease, as well as parasite infections. Some severe diarrhea can also be caused by food intolerances. Your doctor can run tests on you to determine if you have a food allergy or intolerance to the following products:[18]
- Gluten, found in bread and wheat products
- Lactose, found in dairy products
- Casein, found in hard cheeses
- High fructose corn syrup intolerance, found in sweetened drinks and sauces
References
- ↑ https://www.uofmhealth.org/health-library/sig18272
- ↑ https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/fda/fdaDrugXsl.cfm?setid=33baaf04-498d-44f2-9288-02b8f874f914&type=display
- ↑ https://iffgd.org/gi-disorders/diarrhea/managing-diarrhea/
- ↑ https://www.drugs.com/dosage/psyllium.html
- ↑ https://www.drugs.com/dosage/psyllium.html
- ↑ https://medlineplus.gov/diarrhea.html
- ↑ https://medlineplus.gov/ency/patientinstructions/000121.htm
- ↑ https://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/article/003281.htm
- ↑ https://aboutibs.org/treatment/ibs-diet/dietary-fiber/
- ↑ http://familydoctor.org/familydoctor/en/prevention-wellness/food-nutrition/weight-loss/brat-diet-recovering-from-an-upset-stomach.html
- ↑ http://www.uptodate.com/contents/acute-diarrhea-in-adults-beyond-the-basics
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK373095/
- ↑ http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15802416
- ↑ https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/4108-diarrhea
- ↑ http://www.mayoclinic.org/symptoms/diarrhea/basics/when-to-see-doctor/sym-20050926
- ↑ https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/digestive-diseases/diarrhea/symptoms-causes
- ↑ https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/digestive-diseases/diarrhea/treatment
- ↑ https://www.cdc.gov/healthywater/hygiene/disease/chronic_diarrhea.html














-Step-12.webp)

















-Step-12.webp)






























Medical Disclaimer
The content of this article is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, examination, diagnosis, or treatment. You should always contact your doctor or other qualified healthcare professional before starting, changing, or stopping any kind of health treatment.
Read More...