X
This article was co-authored by Jurdy Dugdale, RN. Jurdy Dugdale is a Registered Nurse in Florida. She received her Nursing License from the Florida Board of Nursing in 1989.
There are 7 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page.
This article has been viewed 47,071 times.
You've been taking gabapentin for a little while now, but you're ready to start weaning off. But how can you taper off carefully without having any harmful side effects? You've come to the right article. We'll walk you through the safest way to get off gabapentin with the help of a medical professional.
Steps
Method 1
Method 1 of 3:
Weaning Off
-
1Ask your doctor about a tapering off schedule. Often, your doctor will not want you to go off this medication cold turkey. Rather, they'll want you to slowly decrease your dose over time, which can lessen withdrawal symptoms.[1]
- If you stop this medication without tapering off, you may experience seizures.
-
2Reduce your dose gradually over at least a week. The doctor will likely have you reduce your dose little by little each day. Typically, this reduction process lasts at least a week, to get your body used to not taking the medication.
- How much you reduce each day is based on your health, how much you're taking, and how long your doctor wants you to continue tapering.
- For instance, if you're on 600 milligrams of gabapentin, your doctor might suggest taking 500 milligrams for 2 days, 400 milligrams for the next 2 days, 300 milligrams of the next 2 days, and so on until you've tapered off the medication and started a new one.
Advertisement -
3Treat withdrawal symptoms as they appear. You may notice insomnia, excess sweating, headaches, nausea and vomiting, and anxiety as you are tapering off this medication. Tapering will reduce the severity of these symptoms, but you may still experience them.[2]
- You can take medications to treat the withdrawal symptoms, such as a pain medication for headaches and an anti-nausea medication. Talk to your doctor about what's appropriate to take.
Advertisement
Method 2
Method 2 of 3:
Talking to Your Doctor
-
1Make an appointment to see your doctor. If the milder side effects are bothering you, schedule an appointment with your doctor. They may be able to help you find ways to deal with these side effects.
-
2Write down a list of symptoms ahead of time. When visiting your doctor, it's always a good idea to bring a list of symptoms with you. That way, you'll be able to remember everything when it comes time to talk to your doctor.
- Include the frequency and severity of the symptom. For instance, if you're getting headaches, write down how often you have them, how painful they are, and how long they last.
-
3Discuss getting off the medication with your doctor. If you feel the symptoms are too severe, ask your doctor if you can stop taking this medication. They may have a suggestion for another medication you can be on instead or discuss how to balance the side effects and keep you seizure-free.[3]
- Don't stop taking this medication without consulting with your doctor first.
- All seizure medications will have side effects.
Advertisement
Method 3
Method 3 of 3:
Side Effects of Gabapentin
-
1Visit the emergency room for a severe allergic reaction. While a severe allergic reaction is rare, it does happen. If you notice symptoms like trouble breathing, a skin rash, and tightness in your chest, go to the emergency room or call emergency services.
- Also look for swelling in your lips, tongue, throat, and mouth, as well as the rest of your face.
- If you experience seizures within the first few doses of gabapentin, visit the emergency room.
-
2Call your doctor immediately for a lesser allergic reaction after starting gabapentin. An allergic reaction is still serious, so talk to your doctor if you notice symptoms like a fever. You may also notice that your lymph nodes (in your neck, groin, or armpits) are swollen and tender.[4]
- Other indications of severe reactions include abnormal bruising or bleeding, as well as signs of jaundice, such as skin with a yellow tinge or yellow eyes. Have blood tests performed on your liver if you have any jaundice symptoms within 1-8 weeks.[5]
-
3Talk to your doctor immediately about changes in your mental health. In some people, this medication can cause drastic changes in your thinking. For instance, it can cause some people to have suicidal thoughts. Talk to your doctor right away if you suddenly start having suicidal thoughts, which can happen as quickly as a week after beginning the medication.[6]
- It can also cause anxiety, irritability, panic attacks, insomnia, mania, and depression. Talk to a skilled professional to determine if these side effects stem from taking gabapentin.
-
4Discuss other symptoms that are severe or not going away. Like any medication, gabapentin has a number of possible side effects. If you experience them, bring them up with your doctor, as they may be able to help.[7]
- Side effects can include balance issues, tiredness, headaches, dizziness, memory problems, stomach problems, joint pain, runny nose, red, itchy eyes, and ear pain. It can also cause increased appetite and weight gain.
- You may also notice blurred vision, vertigo, impotence, susceptibility to viral infections, and pneumonia.
- Some of the symptoms may also be signs of silent seizure activity.
- Many of these side effects will go away on their own.
Advertisement
Warnings
- Check with your doctor first if you want to stop taking gabapentin.⧼thumbs_response⧽
- Always seek emergency care if you are having trouble breathing or suffering other symptoms of a severe allergic reaction.⧼thumbs_response⧽
Advertisement
References
- ↑ https://www.somersetccg.nhs.uk/wp-content/uploads/2021/05/Tapering-gabapentinoid-1.pdf
- ↑ https://www.sps.nhs.uk/wp-content/uploads/2016/08/M-Protocol_for_Mgmt_of_pregab-gaba_Sussex.pdf
- ↑ https://www.aafp.org/afp/1998/0201/p513.html
- ↑ https://www.mayoclinic.org/drugs-supplements/gabapentin-oral-route/precautions/drg-20064011
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK548252/
- ↑ https://medlineplus.gov/druginfo/meds/a694007.html
- ↑ https://medlineplus.gov/druginfo/meds/a694007.html
About This Article
Advertisement
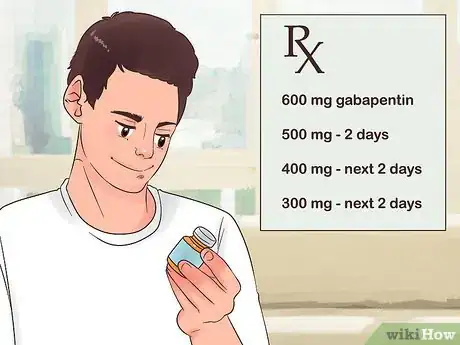






















































Medical Disclaimer
The content of this article is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, examination, diagnosis, or treatment. You should always contact your doctor or other qualified healthcare professional before starting, changing, or stopping any kind of health treatment.
Read More...